1 0 0 0 OA A5052-H14およびA2017-T4アルミニウム合金の疲労特性に及ぼす表面処理の影響
- 著者
- 城戸 竜太 桑野 亮一 日野 実 村山 敬祐 黒坂 成吾 小田 幸典 堀川 敬太郎 金谷 輝人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本金属学会
- 雑誌
- 日本金属学会誌 (ISSN:00214876)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.84, no.3, pp.74-79, 2020-03-01 (Released:2020-02-25)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
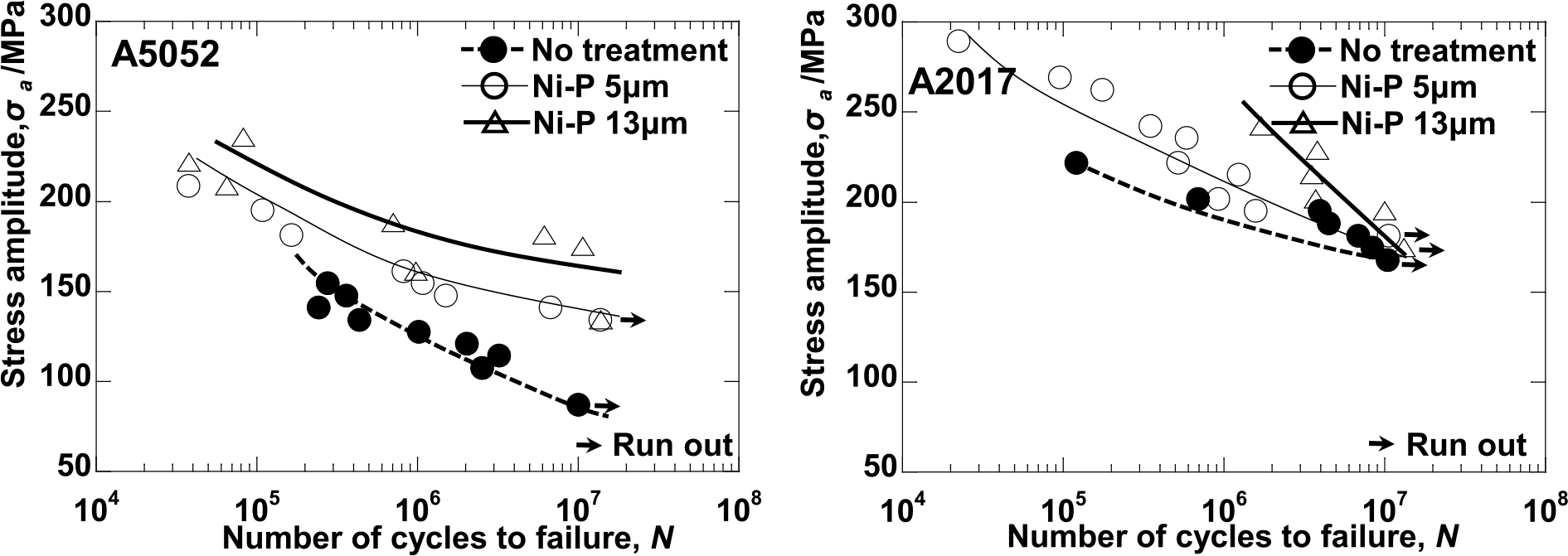
In this study, the effect of anodization and electroless Ni-P plating on the fatigue strength of commercial A5052-H14 and A2017-T4 aluminum alloys was investigated. The coated aluminum alloys were tested using a rotary bending fatigue testing machine. Anodization led to a slight increase in the fatigue strength of the A2017-T4 alloy of approximately 10% because of the suppression of the generation of fatigue crack, and anodization with a 5-µm thickness for A5052-H14 also led to a slight increase in the fatigue strength. However, anodization with a 20-µm thickness for A5052-H14 led to reduced fatigue strength because of the pits that formed in the film. In addition, electroless Ni-P plating drastically improved the fatigue strength of the A5052-H14 alloy by suppressing the generation of fatigue crack.It also improved the fatigue strength of the A2017-T4 alloy in the high-stress region. However, the fatigue strength in the low-stress region was the same as that of the non-coated specimens.This fatigue strength should have originated from the hydrogen embrittlement by the hydrogen introduced into the specimen during the plating.
1 0 0 0 OA 乗客の傷害度との相関に基づく鉄道車両の衝突安全性評価方法
- 著者
- 沖野 友洋 永田 恵輔 堀川 敬太郎 小林 秀敏
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本機械学会
- 雑誌
- 日本機械学会論文集 (ISSN:21879761)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.19-00249, (Released:2019-12-26)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 2
The crash safety structure of the railway vehicles is effective as one of the safety measures against the train crews and the passengers in the event of a collision accident. The standards for crashworthiness of railway vehicles are defined in Europe and the U.S., while there are no standards for crash safety in Japan. Therefore, it is important to establish the evaluation method for crashworthiness of railway vehicles considering the actual situation of collision accidents in Japan. The authors carried out finite element analyses of a level crossing accident under various conditions (collision speed, mass of the obstacle and relative position between the train and the obstacle) based on the statistical analysis of serious level-crossing accidents in the past in Japan, and calculated the deceleration time histories in the passenger area under each condition. We evaluated these deceleration waveforms according to European and the U.S. standards for crashworthiness, and we also performed finite element analyses of dummy’s behavior and injury values using these deceleration waveforms as input. We verified the correlation between the evaluation results in terms of the deceleration according to these standards and dummy’s injury values obtained by finite element analyses. As a result, the evaluation according to the velocity at which a passenger contacts the seat back ahead of him (the U.S. standards) was the most effective. Moreover, the integrated values of the deceleration of the passenger area during an integration time t360 had the highest correlation with the dummy’s injury values.
1 0 0 0 OA 踏切衝突事故時の各因子が列車乗員の被害度に及ぼす影響評価
- 著者
- 沖野 友洋 永田 恵輔 佐藤 裕之 堀川 敬太郎 小林 秀敏
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本機械学会
- 雑誌
- 日本機械学会論文集 (ISSN:21879761)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.85, no.869, pp.18-00270, 2019 (Released:2019-01-25)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 2 4
The crash safety structure of the railway vehicles is effective as one of the safety measures against the train crews and the passengers in the event of a collision accident. However there is no standard for crash safety in Japan. In order to discuss guidelines for the crash safety design of the vehicle structure, it is important to grasp the actual situation of collision accidents in Japan. Therefore, firstly the authors performed the statistical analysis of serious level-crossing accidents for the past 30 years. Secondly, we carried out finite element analyses of a level crossing accident with a dump-truck under various conditions (collision position, collision angle, collision speed and mass of the load on the dump-truck) based on the result of the statistical analysis. We also evaluated their results in terms of the contact force, the deformation energy of the rail vehicle, the deformation amount of the cabin, the mean deceleration of passenger’s area (conformable to European standard), the maximum deceleration of the passenger’s area and the secondary impact velocity of the passenger (American standard). The degree of correlation among these results was discussed. The analyses showed that the horizontal collision position of the dump-truck and the collision speed had a comparatively large effect on the safety of passengers, and further that the mass of the load on the dump-truck also affected it when the secondary impact velocity was used as an evaluation index.
- 著者
- 小林 秀敏 富永 直路 堀川 敬太郎 渡辺 圭子
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人日本機械学会
- 雑誌
- バイオエンジニアリング講演会講演論文集
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2012, no.24, pp."8G33-1"-"8G33-2", 2012-01-06