- 著者
- Hiroyuki Nojima Yasuomi Kiyota Genki Terashi Mayuko Takeda-Shitaka Hajime Matsubara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.10, pp.1061-1071, 2019-10-01 (Released:2019-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 41
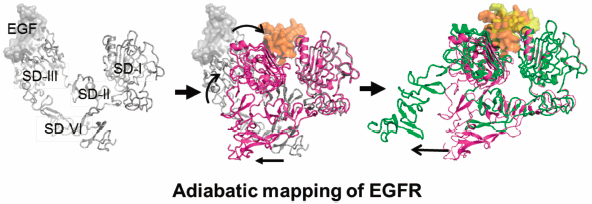
The activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) involves the geometrical conversion of the extracellular domain (ECD) from the tethered to the extended forms with the dynamic rearrangement of the relative positions of four subdomains (SDs); however, this conversion process has not yet been thoroughly understood. We compare the two different forms of the X-ray crystal structures of ECD and simulate the ECD conversion process using adiabatic mapping that combines normal mode analysis of the elastic network model (ENM-NMA) and energy optimization. A comparison of the crystal structures reveals the rigidity of the intradomain geometry of the SD-I and -III backbone regardless of the form. The forward mapping from the tethered to the extended forms retains the intradomain geometry of the SD-I and -III backbone and reveals the trends to rearrange the relative positions of SD-I and -III and to dissociate the C-terminal tail of SD-IV from the hairpin loop in SD-II. The reverse mapping from the extended to the tethered forms complements the promotion of ECD conversion in the presence of epidermal growth factor (EGF).
- 著者
- Genki Terashi Yuuki Nakamura Hiromitsu Shimoyama Mayuko Takeda-Shitaka
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.8, pp.744-753, 2014-08-01 (Released:2014-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 6
In the absence of experimentally determined three dimensional (3D) structures of proteins, the prediction of protein structures using computational methods is a standard alternative approach in bioinformatics. When using the predicted protein models to compute the native structure of an unknown target protein, estimating the actual quality of the protein models is important for selecting the best or near-best model. Moreover, estimates of the differences between the protein models and the native protein structure are obviously useful to end users who can then decide on the utility of the models for their specific problems. This article describes two new single-model quality assessment (QA) programs, pure single-model QA method (psQA) and a template based QA method (tbQA), that we developed. psQA is a pure single-model QA program that uses a neural network method to predict residue–residue distance matrices of the native protein structures. tbQA is a quasi-single-model QA program that mainly uses target-template sequence alignments and template structures. The performance of these two model QA programs was analyzed in a data set of 24022 models for 94 targets from the 10th critical assessment of protein structure prediction (CASP10) experiment.