3 0 0 0 OA Timing of hyponatremia development in patients with salt-wasting-type 21-hydroxylase deficiency
- 著者
- Rohi Shima Kentaro Sawano Nao Shibata Hiromi Nyuzuki Sunao Sasaki Hidetoshi Sato Yohei Ogawa Yuki Abe Keisuke Nagasaki Akihiko Saitoh
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Pediatric Endocrinology
- 雑誌
- Clinical Pediatric Endocrinology (ISSN:09185739)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.29, no.3, pp.105-110, 2020 (Released:2020-07-11)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Newborn screening (NBS) can detect 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21-OHD), allowing for early treatment initiation. However, many patients present with adrenal crises or hyponatremia at their first visit. Age (in days) of hyponatremia development in infants with salt-wasting (SW)-type 21-OHD remains unclear. Therefore, we determined the earliest age of hyponatremia diagnosis in this retrospective observational study using medical records of 40 patients with classic 21-OHD in Niigata Prefecture, Japan, from April 1989 to March 2019. We determined the earliest diagnosis of hyponatremia (serum sodium levels < 130 mEq/L) and created a sodium decrease rate model to estimate hyponatremia development age. Of 23 patients with SW-type 21-OHD, 10 (43.5%) were identified during NBS; the earliest case to present with hyponatremia was at day 7. Serum sodium levels were significantly and negatively correlated with age in days, and hyponatremia was estimated to develop at 6.6 d after birth. Genotype or serum 17-hydroxyprogesterone levels were not associated with sodium decrease rate. Thus, hyponatremia development age is earlier (within 7 d) than the previously described time-point (10–14 d) in infants with SW-type 21-OHD. Efforts to reduce the time lag from obtaining results to consultation may be required in patients with high 17-hydroxyprogesterone levels on NBS.
- 著者
- Takashi Nakada Kiyoshi Sugihara Takahiro Jikoh Yuki Abe Toshinori Agatsuma
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.3, pp.173-185, 2019-03-01 (Released:2019-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 82
- 被引用文献数
- 98 230
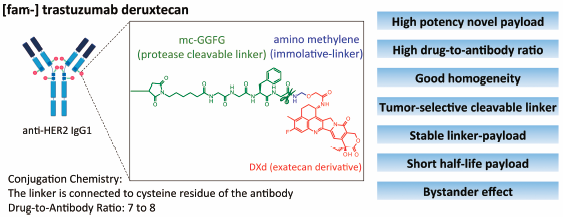
A major limitation of traditional chemotherapy for cancer is dose-limiting toxicity, caused by the exposure of non-tumor cells to cytotoxic agents. Use of molecular targeted drugs, such as specific kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies, is a possible solution to overcome this limitation and has achieved clinical success so far. Use of an antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) is a rational strategy for improving efficacy and reducing systemic adverse events. ADCs use antibodies selectively to deliver a potent cytotoxic agent to tumor cells, thus drastically improving the therapeutic index of chemotherapeutic agents. Lessons learned from clinical failure of early ADCs during the 1980s to 90s have recently led to improvements in ADC technology, and resulted in the approval of four novel ADCs. Nonetheless, further advances in ADC technology are still required to streamline their clinical efficacy and reduce toxicity. [fam-] Trastuzumab deruxtecan (DS-8201a) is a next-generation ADC that satisfies these requirements based on currently available evidence. DS-8201a has several innovative features; a highly potent novel payload with a high drug-to-antibody ratio, good homogeneity, a tumor-selective cleavable linker, stable linker-payload in circulation, and a short systemic half-life cytotoxic agent in vivo; the released cytotoxic payload could exert a bystander effect. With respect to its preclinical profiles, DS-8201a could provide a valuable therapy with a great potential against HER2-expressing cancers in clinical settings. In a phase I trial, DS-8201a showed acceptable safety profiles with potential therapeutic efficacy, with the wide therapeutic index.
1 0 0 0 OA Efficient and Repetitive Neutron Generation by Double-Laser-Pulse Driven Photonuclear Reaction
- 著者
- Yasunobu ARIKAWA Yusuke KATO Yuki ABE Shuto MATSUBARA Hidetaka KISHIMOTO Nozomi NAKAJIMA Alessio MORACE Akifumi YOGO Hiroaki NISHIMURA Mitsuo NAKAI Shinsuke FUJIOKA Hiroshi AZECHI Kunioki MIMA Shunsuke INOUE Yoshihide NAKAMIYA Kensuke TERAMOTO Masaki HASHIDA Shuji SAKABE
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Plasma Science and Nuclear Fusion Research
- 雑誌
- Plasma and Fusion Research (ISSN:18806821)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, pp.2404009, 2018-02-15 (Released:2018-03-27)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 3
A short and high-intensity neutron pulse can be produced efficiently by using photonuclear reactions caused by Bremsstrahlung hard X-rays in a lase-irradiated high-Z target. The efficient and repetitive neutron generation was demonstrated with the combination of 1 Hz, 0.5 J, 25 fs, 5 × 1019 W/cm2 laser pulses and a rotating tungsten disc targe. Here we applied double laser pulse irradiation scheme to increase the neutron generation efficiency. The first low-intensity laser pulse produces a long-scale under-critical-density plasma on the tungsten target surface prior to the second pulse irradiatio. High energy electrons above the ponderomotive scaling value are accelerated by the second hig-intensity pulse in the preformed plasm, this results in the increment of hard X-ray photons and photonuclear neutron. 3.5 × 104 neutron/pulse was obtained with optimized laser irradiation conditions.