- 著者
- Shiori Tomita Fumiko Sekiguchi Maho Tsubota Atsufumi Kawabata
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.9, pp.1343-1346, 2023-09-01 (Released:2023-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 1
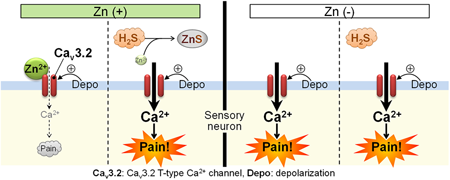
Cav3.2 channels belong to the T-type calcium channel (T-channel) family, i.e., low voltage-activated calcium channels, and are abundantly expressed in the nociceptors, playing a principal role in the development of pathological pain. The channel activity of Cav3.2 is suppressed by zinc under physiological conditions. We thus tested whether dietary zinc deficiency would cause Cav3.2-dependent nociceptive hypersensitivity in mice. In the mice fed with zinc deficient diet for 2 weeks, plasma zinc levels declined by more than half, and mechanical allodynia developed. The dietary zinc deficiency-induced allodynia was restored by T-channel inhibitors or by Cav3.2 gene silencing. These data demonstrate that zinc deficiency induces Cav3.2-dependent nociceptive hypersensitivity in mice, thereby suggesting that pain experienced by patients with diseases accompanied by zinc deficiency (e.g., chronic kidney disease) might involve the increased Cav3.2 activity.
- 著者
- Maho Tsubota Kazuki Matsui Saaya Fukushi Kyoko Okazaki Fumiko Sekiguchi Atsufumi Kawabata
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.3, pp.461-464, 2021-03-01 (Released:2021-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 6
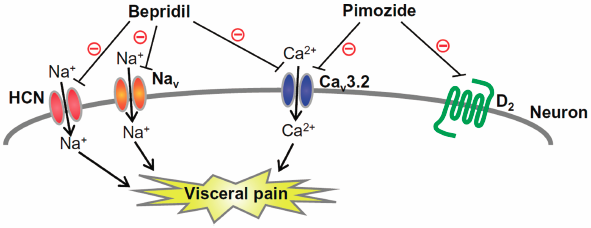
T-Type Ca2+ channels (T-channels), particularly Cav3.2, are now considered as therapeutic targets for treatment of intractable pain including visceral pain. Among existing medicines, bepridil, a multi-channel blocker, used for treatment of arrhythmia and angina, and pimozide, a dopamine D2 receptor antagonist, known as a typical antipsychotic, have potent T-channel blocking activity. We thus tested whether bepridil and pimozide could suppress visceral pain in mice. Colonic and bladder pain were induced by intracolonic administration of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) and systemic administration of cyclophosphamide (CPA), respectively. Referred hyperalgesia was assessed by von Frey test, and colonic hypersensitivity to distension by a volume load with intracolonic water injection and spontaneous bladder pain were evaluated by observing nociceptive behaviors in conscious mice. The mice exhibited referred hyperalgesia and colonic hypersensitivity to distension on day 6 after TNBS treatment. Systemic administration of bepridil at 10–20 mg/kg or pimozide at 0.1–0.5 mg/kg strongly reduced the referred hyperalgesia on the TNBS-induced referred hyperalgesia and colonic hypersensitivity to distension. CPA treatment caused bladder pain-like nociceptive behavior and referred hyperalgesia, which were reversed by bepridil at 10–20 mg/kg or pimozide at 0.5–1 mg/kg. Our data thus suggest that bepridil and pimozide, existing medicines capable of blocking T-channels, are useful for treatment of colonic and bladder pain, and serve as seeds for the development of new medicines for visceral pain treatment.
- 著者
- Yoshihito Kasanami Takashi Yamamoto Tomoyoshi Miyamoto Sumio Matzno Mikio Sakakibara Masahiro Iwaki Atsufumi Kawabata
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.12, pp.1699-1705, 2023-12-01 (Released:2023-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
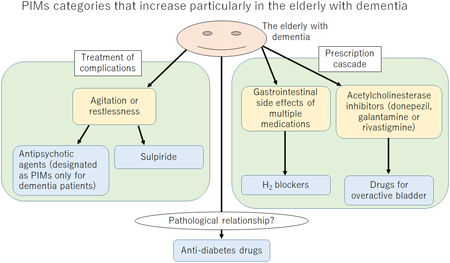
Community pharmacists may play a key role in promoting deprescribing of potential inappropriate medications (PIMs) that are highly prevalent among community-dwelling elderly with dementia. To characterize PIMs categories that need a special attention for dementia patients, in the present study, we analyzed the anonymized pharmacy claims data of patients aged 65 years and older (n = 333869) who visited nationwide 905 community-based pharmacies of Sugi Pharmacy Co., Ltd. during December 1–31, 2019. A dementia group was defined as patients who received typical dementia medications marketed in Japan, i.e., donepezil, galantamine, memantine or rivastigmine, and a non-dementia group was defined as patients who received no such medications. After propensity score matching on the basis of patients’ age, gender and home healthcare insurance usage, the data of 11486 patients in each group were subjected to logistic regression analyses, to identify PIMs categories particularly important for dementia patients. Univariate analysis indicated that the proportions of dementia patients who received 1 and 2≤ of PIMs were significantly (p < 0.001) greater than those of non-dementia patients (odds ratios were 1.35 and 1.47, respectively). Multivariate analyses identified 5 categories of PIMs that were significantly more frequently prescribed in dementia patients, i.e., ‘H2 blockers,’ ‘drugs for overactive bladder,’ ‘anti-diabetes drugs’ and ‘sulpiride’ listed as PIMs categories for non-specific cases (adjusted odds ratios (aORs): 1.29, 1.91, 1.17, and 1.38, respectively), in addition to ‘antipsychotics’ listed only for dementia patients (aOR: 4.29). These results provide useful information to establish strategies for pharmacist-led deprescribing of PIMs in dementia patients.
- 著者
- Fumiko Sekiguchi Atsufumi Kawabata
- 出版者
- (公社)日本薬理学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pharmacological Sciences (ISSN:13478613)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.13R05CP, (Released:2013-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 19 64
Low-voltage-activated T-type Ca2+ channels (T-channels), especially Cav3.2 among the three isoforms (Cav3.1, Cav3.2, and Cav3.3), are now considered to play pivotal roles in processing of pain signals. Cav3.2 T-channels are functionally modulated by extracellular substances such as hydrogen sulfide and ascorbic acid, by intracellular signaling molecules including protein kinases, and by glycosylation. Cav3.2 T-channels are abundantly expressed in both peripheral and central endings of the primary afferent neurons, regulating neuronal excitability and release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as substance P and glutamate, respectively. Functional upregulation of Cav3.2 T-channels is involved in the pathophysiology of inflammatory, neuropathic, and visceral pain. Thus, Cav3.2 T-channels are considered to serve as novel targets for development of drugs for treatment of intractable pain resistant to currently available analgesics.