- 著者
- Daisuke Furushima Hiroshi Yamada Michiko Kido Yuko Ohno
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.3, pp.409-418, 2018-03-01 (Released:2018-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 2
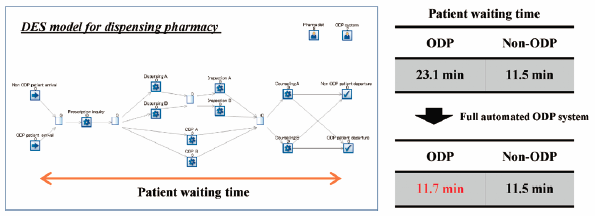
Improvement in patient waiting time in dispensing pharmacies is an important element for patient and pharmacists. The One-Dose Package (ODP) of medicines was implemented in Japan to support medicine adherence among elderly patients; however, it also contributed to increase in patient waiting times. Given the projected increase in ODP patients in the near future owing to rapid population aging, development of improved strategies is a key imperative. We conducted a cross-sectional survey at a single dispensing pharmacy to clarify the impact of ODP on patient waiting time. Further, we propose an improvement strategy developed with use of a discrete event simulation (DES) model. A total of 673 patients received pharmacy services during the study period. A two-fold difference in mean waiting time was observed between ODP and non-ODP patients (22.6 and 11.2 min, respectively). The DES model was constructed with input parameters estimated from observed data. Introduction of fully automated ODP (A-ODP) system was projected to reduce the waiting time for ODP patient by 0.5 times (from 23.1 to 11.5 min). Furthermore, assuming that 40% of non-ODP patients would transfer to ODP, the waiting time was predicted to increase to 56.8 min; however, introduction of the A-ODP system decreased the waiting time to 20.4 min. Our findings indicate that ODP is one of the elements that increases the waiting time and that it might become longer in the future. Introduction of the A-ODP system may be an effective strategy to improve waiting time.
- 著者
- Daisuke FURUSHIMA Ibuki SUGIYAMA Yuzuki NOMURA Keiko UNNO Hiroshi YAMADA
- 出版者
- Center for Academic Publications Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology (ISSN:03014800)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.6, pp.540-546, 2022-12-31 (Released:2022-12-31)
- 参考文献数
- 30
l-Theanine, the most abundant amino acid component in green tea, has anti-stress effects and refreshes the mental state. A recent study demonstrated that l-arginine, the second most abundant amino acid in green tea, might enhance the anti-stress effects of l-theanine. The aim of this study was to evaluated the effects of combined ingestion of l-theanine and l-arginine on psychological stress in humans. A randomized placebo-controlled trial was conducted including 120 healthy young adults (mean age 22.4 y, 63.3% female). Subjects were randomly assigned to theanine (200 mg l-theanine), combined theanine/arginine (200 mg l-theanine, 50 mg l-arginine), or placebo groups. After consuming a test beverage, we administered a stress-loading test (Uchida-Kraepelin performance test) and performed salivary alpha-amylase activity (sAA) measurements to assess the physiological stress response at 0 min (immediately after), 5 min, and 15 min. The changes in sAA at 15 min after the stress-loading test were −2.75 (11.2) kIU/L in the theanine/arginine group, −0.40 (11.5) kIU/L in the theanine group, and 6.95 (18.6) kIU/L in the placebo group. The values in the theanine/arginine (p=0.007) and theanine (p=0.02) groups differed significantly from those in the placebo group. However, the difference between theanine/arginine and theanine groups, was not statistically significant (p=0.74). From this study, no clear conclusion could be drawn regarding the potentiating effect of theanine and arginine combined ingestion on anti-stress effects in human.