- 著者
- Yağız Anıl Çiçek David C. Luther Jessica A. Kretzmann Vincent M. Rotello
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.3, pp.304-311, 2019-03-01 (Released:2019-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 83
- 被引用文献数
- 4
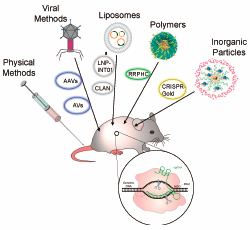
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9) technology has revolutionized therapeutic gene editing by providing researchers with a new method to study and cure diseases previously considered untreatable. While the full range and power of CRISPR technology for therapeutics is being elucidated through in vitro studies, translation to in vivo studies is slow. To date there is no totally effective delivery strategy to carry CRISPR components to the target site in vivo. The complexity of in vivo delivery is furthered by the number of potential delivery methods, the different forms in which CRISPR can be delivered as a therapeutic, and the disease target and tissue type in question. There are major challenges and limitations to delivery strategies, and it is imperative that future directions are guided by well-conducted studies that consider the full effect these variables have on the eventual outcome. In this review we will discuss the advances of the latest in vivo CRISPR/Cas9 delivery strategies and highlight the challenges yet to be overcome.
- 著者
- edited by James E. Martin and David C. Parris
- 出版者
- Geological Society of America
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 2007
- 著者
- David C. GAZE
- 出版者
- 日本薬物動態学会 会長/日本薬物動態学会 DMPK編集委員長
- 雑誌
- Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (ISSN:13474367)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.24, no.4, pp.333-341, 2009 (Released:2009-09-10)
- 参考文献数
- 70
- 被引用文献数
- 84
The diagnosis of cardiac ischemia remains a challenge in contemporary emergency medicine. A blood-borne biomarker is an attractive alternative to cardiac imaging or stress testing as it would be cheaper and logistically faster to obtain. A number of candidate biomarkers have been proposed for the detection of cardiac ischemia; however, only Ischemia Modified Albumin (IMA) has been released for clinical use. IMA is a good discriminator between ischemic and non-ischemic patients. Changes in IMA concentration have shown to occur during coronary angioplasty-induced ischemia. Clinical studies indicate that IMA appears to offer on admission an early test which can be combined with electrocardiographic findings and cardiac troponin measurements for the early exclusion of acute coronary syndrome. IMA is an independent predictor of short and long term adverse outcomes in patients with acute chest pain. However, this test is relatively new and uncertainties remain. Elevations of IMA occur in conditions other than chest pain, thus questioning its specificity. The mechanism of IMA formation and the precise entity being measured are not fully known. Nevertheless, IMA measurement remains the only current clinical biomarker which may be used for the diagnosis of patients suspected of cardiac ischemia.
- 著者
- Sheng Xu Luyuan Zhang Stewart P. H. T. Freeman Xiaolin Hou Katsuhiko Yamaguchi Alan J. Cresswell David C. W. Sanderson
- 出版者
- GEOCHEMICAL SOCIETY OF JAPAN
- 雑誌
- GEOCHEMICAL JOURNAL (ISSN:00167002)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, no.3, pp.287-291, 2016-05-18 (Released:2016-05-30)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 4
This paper reports iodine (127I and 129I) and cesium (137Cs) isotope concentrations in groundwater of confined and unconfined aquifers in the vicinity of the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant (FDNPP). 127I and 129I concentrations range from 2–13 μg/L and 5 × 107–8 × 1010 atom/L respectively, resulting in 129I/127I atomic ratios from 5 × 10–9 to 2 × 10–6. In all samples, 137Cs concentrations were below detection limit. The deep-sealed groundwater from the confined aquifer did not contain significant quantities of Fukushima-derived 129I compared to the groundwater in the unconfined aquifer. The minimal 129I/137Cs activity ratios in the groundwater are more than 2–500 times higher than the FDNPP source ratio. These data can be explained by rainwater infiltrating through the surface soils, with the more water-soluble 129I preferentially extracted into the aqueous phase and the 137Cs preferentially retained in the soil.
- 著者
- David C. Durst
- 出版者
- Lexington Books
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 2004