- 著者
- Michiaki Okuda Yuki Fujita Hachiro Sugimoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.10, pp.1694-1706, 2019-10-01 (Released:2019-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 135
- 被引用文献数
- 2 12
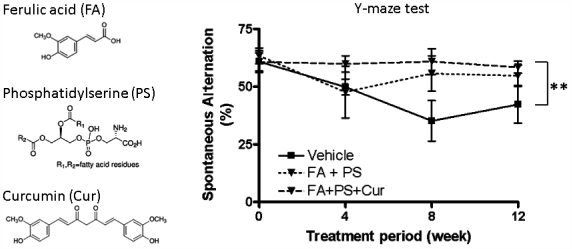
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia and its prevention and treatment is a worldwide issue. Many natural components considered to be effective against AD have been identified. However, almost all clinical trials of these components for AD reported inconclusive results. We thought that multiple factors such as amyloid β (Aβ) and tau progressed the pathology of AD and that a therapeutic effect would be obtained by using multiple active ingredients with different effects. Thus, in this study, we treated ferulic acid (FA), phosphatidylserine (PS) and curcumin (Cur) in combination or alone to APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mice and evaluated cognitive function by Y-maze test. Consequently, only the three-ingredient group exhibited a significant improvement in cognitive function compared to the control group. In addition, we determined the amounts of Aβ, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), interleukin (IL)-1β, acetylcholine and phosphorylated tau in the mouse brains after the treatment. In the two-ingredient (FA and PS) group, a significant decrease in IL-1β and an increasing trend in acetylcholine were observed. In the Cur group, significant decreases in Aβ and phosphorylated tau and an increasing trend in BDNF were observed. In the three-ingredient group, all of them were observed. These results indicate that the intake of multiple active ingredients with different mechanisms of action for the prevention and treatment of AD.
- 著者
- Yuki Takada-Takatori Toshiaki Kume Yasuhiko Izumi Tetsuhiro Niidome Takeshi Fujii Hachiro Sugimoto Akinori Akaike
- 出版者
- The Japanese Pharmacological Society
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pharmacological Sciences (ISSN:13478613)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.112, no.3, pp.265-272, 2010 (Released:2010-03-19)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 4
We have previously shown that chronic donepezil treatment induces nicotinic acetylcholine receptor up-regulation and enhances the sensitivity of the neurons to the neuroprotective effect of donepezil. Further analyses revealed that the nicotinic receptor is involved in this enhancement. In this study, we examined whether nicotinic receptor stimulation is sufficient to make neurons more sensitive to donepezil. We treated primary cultures of rat cortical neurons with nicotine and confirmed that chronic nicotine treatment induced nicotinic receptor up-regulation and made the neurons more sensitive to the neuroprotective effects of donepezil. Analyses with receptor antagonists and kinase inhibitors revealed that the effects of chronic nicotine treatment are mediated by nicotinic receptors and their downstream effectors including phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. In contrast to chronic donepezil treatment that enhanced the level of nicotine-induced Ca2+ influx, chronic nicotine treatment did not significantly alter the level of Ca2+ influx.
1 0 0 0 OA Serofendic Acid Promotes Stellation Induced by cAMP and cGMP Analogs in Cultured Cortical Astrocytes
- 著者
- Toshiaki Kume Ryo Ito Ryota Taguchi Yasuhiko Izumi Hiroshi Katsuki Tetsuhiro Niidome Yuki Takada-Takatori Hachiro Sugimoto Akinori Akaike
- 出版者
- The Japanese Pharmacological Society
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pharmacological Sciences (ISSN:13478613)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.109, no.1, pp.110-118, 2009 (Released:2009-01-17)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 10 12
We investigated the effect of serofendic acid, a neuroprotective substance derived from fetal calf serum, on the morphological changes in cultured cortical astrocytes. Cultured astrocytes developed a stellate morphology with several processes following exposure to dibutylyl cAMP (dbcAMP), a membrane-permeable cAMP analog; 8-Br-cGMP, a membrane-permeable cGMP analog; or phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), a protein kinase C activator. Serofendic acid significantly accelerated the stellation induced by dbcAMP- and 8-Br-cGMP. In contrast, the PMA-induced stellation was not affected by serofendic acid. Next, we attempted to elucidate the mechanism underlying the dbcAMP-induced stellation and explore the site of action of serofendic acid. Both the stellation induced by dbcAMP and the promotional effect of serofendic acid were partially inhibited by KT5720, a specific protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor. Furthermore, serofendic acid failed to facilitate the stellation induced by Y-27632, an inhibitor of Rho-associated kinase (ROCK). These results indicate that serofendic acid promotes dbcAMP- and 8-Br-cGMP-induced stellation and the promotional effect on dbcAMP-induced stellation is mediated at least partly by the regulation of PKA activity and not by controlling ROCK activity.