- 著者
- Hirofumi Watanabe Masaki Okawara Yoshiharu Matahira Takashi Mano Tatsuya Wada Naoko Suzuki Tsuyoshi Takara
- 出版者
- Japan Oil Chemists' Society
- 雑誌
- Journal of Oleo Science (ISSN:13458957)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.69, no.12, pp.1597-1607, 2020 (Released:2020-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 9
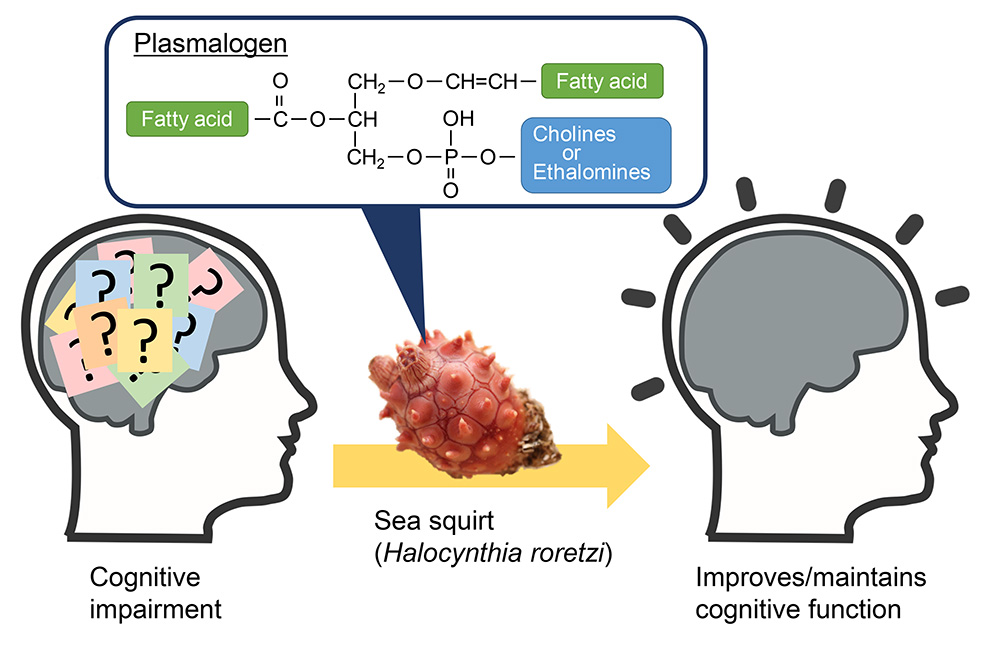
Objectives: Plasmalogen, phospholipids with previously shown associations with dementia, has attracted attention as a substance found in some studies to improve cognitive function. The effects of ascidian-derived plasmalogens on cognitive performance improvement were assessed in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study including Japanese adult volunteers with mild forgetfulness.Methods: Participants consumed either the active food containing ascidian-derived plasmalogen (1 mg as plasmalogen) or the placebo food for 12 weeks, and their cognitive performance was assessed by Cognitrax. Participants were randomly allocated into the intervention (ascidian-derived plasmalogen; 8 males, and 17 females; 45.6 ± 11.1 years) or the placebo (9 males, and 15 females; mean age, 46.4 ± 10.8 years) group. Results: Compared to the placebo group, the intervention group showed a significant increase score in composite memory (eight weeks: 3.0 ± 16.3 points, 12 weeks: 6.7 ± 17.5 points), which was defined as the sum of verbal and visual memory scores.Conclusions: These results indicate the consumption of ascidian-derived plasmalogen maintains and enhances memory function. This study was registered at the University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trial Registry (UMIN-CTR, registry no. UMIN000026297). This study did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
- 著者
- Chiduru Watanabe Hirofumi Watanabe Yoshio Okiyama Daisuke Takaya Kaori Fukuzawa Shigenori Tanaka Teruki Honma
- 出版者
- Chem-Bio Informatics Society
- 雑誌
- Chem-Bio Informatics Journal (ISSN:13476297)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, pp.5-18, 2019-03-22 (Released:2019-03-23)
- 参考文献数
- 47
- 被引用文献数
- 26
We developed an automated FMO calculation protocol (Auto-FMO protocol) to calculate huge numbers of protein and ligand complexes, such as drug discovery targets, by an ab initio FMO method. The protocol performs not only FMO calculations but also pre-processing of input structures by homology modeling of missing atoms and subsequent MM-based optimization, as well as post-processing of calculation results. In addition, QM/MM optimization of complex structures, conformational searches of ligand structures in solvent, and MM-PBSA/GBSA calculations can be optionally carried out. In this paper, FMO calculations for 149 X-ray complex structures of estrogen receptor α and p38 MAP kinase were performed at the K computer and in-house PC cluster server by using the Auto-FMO protocol. To demonstrate the usefulness of the Auto-FMO protocol, we compared the ligand binding interaction energies by the Auto-FMO protocol with those of manually prepared data. In most cases, the data calculated by the Auto-FMO protocol showed reasonable agreement with the manually prepared data. Further improvement of the protocol is necessary for the treatment of ionization and tautomerization at the structure preparation stage, because some outlier data were observed due to these issues. The Auto-FMO protocol provides a powerful tool to deal with huge numbers of complexes for drug design, as well as for the construction of the FMO database (http://drugdesign.riken.jp/FMODB/) released in 2019.