- 著者
- Takashi Omoto Junichi Asaka Takamasa Sakai Fumihiko Sato Nobuyuki Goto Kenzo Kudo
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.5, pp.627-634, 2021-05-01 (Released:2021-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 5
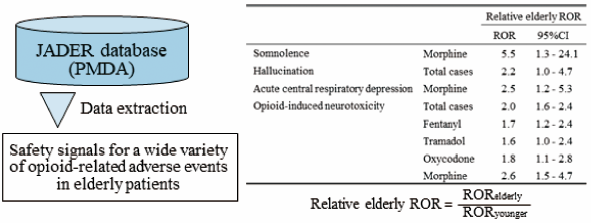
Opioids are widely used for the treatment of moderate/severe pain in cancer and noncancer patients. In this study, we searched for safety signals for a wide variety of opioid-related adverse events (AEs) in elderly patients by disproportionality analysis using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) database. Data from the JADER database from April 2004 to May 2018 were obtained from the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency website. Safety signal detection of opioid-related AEs in elderly patients was defined using the relative elderly reporting odds ratio (ROR). Among the analyzed AEs, opioid-induced neurotoxicity (OIN) was assessed based on the time to onset using the Weibull shape parameter. The following safety signals were detected in elderly patients: respiratory depression, somnolence, hallucinations, akathisia and OIN. Fentanyl, tramadol, oxycodone and morphine exhibited a large relative elderly ROR for OIN. The median time to onset of OIN of transdermal fentanyl, oral tramadol, oral oxycodone and oral morphine was 13.5, 6, 9, and 6 d, respectively. These opioids were classified as early failure types using the Weibull distribution. Our results showed that elderly patients who are administered opioids should be closely monitored for AEs, such as respiratory depression, OIN and akathisia.
- 著者
- Shumpei Unno Masamichi Shinoda Kumi Soma Asako Kubo Barry J Sessle Tomoyuki Matsui Masatoshi Ando Junichi Asaka Katsuhiko Otsuki Hisashi Yonemoto Hiroki Onose Kousuke Sakanashi Koichi Iwata
- 出版者
- Nihon University School of Dentistry
- 雑誌
- Journal of Oral Science (ISSN:13434934)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.19-0512, (Released:2020-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 31
To investigate neuronal activity involved in responses to noxious stimuli in conscious monkeys, the animals were subjected to a task that required them to detect a small change in facial skin temperature or light (second temperature: T2, second light: V2) relative to an initial condition (T1 or V1), and to detect changes in V2 along with a heat task. Recordings were obtained from 57 neurons in the ventral premotor cortex (PMv) during the heat or light detection task. T1 neurons and T2 neurons showed increased activity only during T1 or T2, and T1/T2 neurons were activated by both T1 and T2 stimuli. T1/T2 neurons showed an increase in firing at higher T1 temperatures, whereas T1 neurons did not. About half of the non-light/heat-sensitive T1/T2 neurons showed increased firing at higher T2 temperatures, whereas T2 neurons showed no such increase. The heat responses of heat-sensitive PMv neurons were significantly suppressed when monkeys shifted their attention from heat to light. The present findings suggest that heat-sensitive PMv neurons may be involved in motor responses to noxious heat, whereas light/heat-PMv neurons may be involved in emotional and motivational aspects of pain and inappropriate motor responses to allow escape from noxious stimuli.
- 著者
- Shinji Okada Hiroto Saito Yutaka Matsuura Lou Mikuzuki Shiori Sugawara Hiroki Onose Junichi Asaka Kinuyo Ohara Jun Lee Toshimitsu Iinuma Ayano Katagiri Koichi Iwata
- 出版者
- Nihon University School of Dentistry
- 雑誌
- Journal of Oral Science (ISSN:13434934)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.146-155, 2019 (Released:2019-03-28)
- 参考文献数
- 77
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Bright light stimulation of the eye activates trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (Vc) neurons in rats. Sensory information is conveyed to the Vc via the trigeminal ganglion (TG). Thus, it is likely that TG neurons respond to photic stimulation and are involved in photic hypersensitivity. However, the mechanisms underlying this process are unclear. Therefore, the hypothesis in this study is bright light stimulation enhances the excitability of TG neurons involved in photic hypersensitivity. Expressions of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) were significantly higher in TG neurons from 5 min to 12 h after photic stimulation of the eye. Phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 (pERK1/2) was enhanced in TG neurons within 5 min after photic stimulation, while pERK1/2 immunoreactivity in satellite glial cells (SGCs) persisted for more than 12 h after the stimulus. Activation of SGCs was observed from 5 min to 2 h. Expression of CGRP, nNOS, and pERK1/2 was observed in small and medium TG neurons, and activation of SGCs and pERK1/2-immunoreactive SGCs encircling large TG neurons was accelerated after stimulation. These results suggest that upregulation of CGRP, nNOS, and pERK1/2 within the TG is involved in photic hypersensitivity.