- 著者
- Shota YAMASHITA Ryuta SAITO Shin-ichiro OSAWA Kuniyasu NIIZUMA Kazushi UKISHIRO Masayuki KANAMORI Kazuo KAKINUMA Kyoko SUZUKI Teiji TOMINAGA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.11, pp.661-666, 2021 (Released:2021-11-15)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 3
In cases of malignant gliomas located at language eloquent area, it is often difficult to preoperatively detect those area with functional MRI. Awake surgery is often used to spare the language eloquent area during surgery for such tumors; it is not available for a patient whose intracranial pressure is elevated due to the malignant tumor. The Wada test involves infusing anesthetic agents into the internal carotid artery to determine language dominancy before surgery for epilepsy or brain tumor. The super-selective Wada test is a technique to detect more detailed functional localization by infusing anesthetics into far distal middle cerebral artery branches. We present a 37-year-old man suffering from a left frontal lobe glioblastoma, in whom detection of an artery supplying Broca’s area was attempted by a super-selective Wada test. The super-selective Wada test successfully detected the branch of middle cerebral artery supplying Broca’s area. Total resection of the contrast-enhancing area was achieved without damaging the artery supplying Broca’s area without any neurological sequelae. This is the first report describing the usefulness of the super-selective Wada test in glioblastoma treatment. Our findings suggest that the super-selective Wada test is a powerful and useful means to distinguish the artery that supplies the language area from the tumor feeding artery in cases of tumors in the language eloquent area.
- 著者
- Kazuo KAKINUMA Keisuke MORIHARA Yoshiteru SHIMODA Nobuko KAWAKAMI Shigenori KANNO Mayuko OTOMO Teiji TOMINAGA Kyoko SUZUKI
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- NMC Case Report Journal (ISSN:21884226)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.10, pp.9-14, 2023-12-31 (Released:2023-02-09)
- 参考文献数
- 43
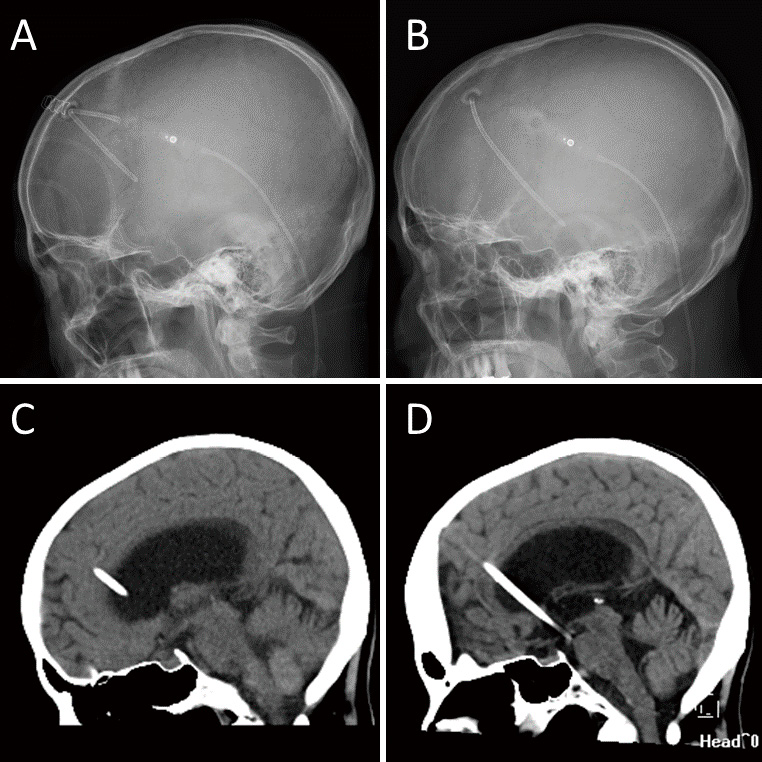
Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) is a neurological disorder that typically presents with gait disturbance, cognitive impairment, and urinary incontinence. Although most patients respond to cerebrospinal-fluid shunting, some do not react well because of shunt failure. A 77-year-old female with iNPH underwent ventriculoperitoneal shunt implantation, and her gait impairment, cognitive dysfunction, and urge urinary incontinence improved. However, 3 years after shunting (at the age of 80), her symptoms gradually recurred for 3 months and she did not respond to shunt valve adjustment. Imaging studies revealed that the ventricular catheter detached from the shunt valve and migrated into the cranium. With immediate revision of the ventriculoperitoneal shunt, her gait disturbance, cognitive dysfunction, and urinary incontinence improved. When a patient whose symptoms have been relieved by cerebrospinal-fluid shunting experiences an exacerbation, it is important to suspect shunt failure, even if many years have passed since the surgery. Identifying the position of the catheter is crucial to determine the cause of shunt failure. Prompt shunt surgery for iNPH can be beneficial, even in elderly patients.