- 著者
- Kentaro Nakanishi Keiichi Hiramoto Kazuya Ooi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.6, pp.884-887, 2021-06-01 (Released:2021-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Several studies have been conducted to investigate the anti-cancer effects of vitamin C (VC). However, the effect of high-dose VC administration on tumor angiogenesis remains unclear. Focusing on our high-dose VC, our study investigated the effect of high-dose VC (4 g/kg) on vascular endothelial growth in mice with xenografts of a rectal cancer cell line referred to as Colon 26. Male mice harboring Colon 26 tumors were established, and high-dose VC solution was orally administered once daily for 14 d. On the final day of the study, the lower limb tumor tissues and serum samples were collected and analyzed for the expression of tumor angiogenesis related proteins as well as the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Oral VC administration decreased tumor volumes and increased p53 and endostatin levels. In addition, plasma and in tumor part ROS levels and tissue hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) were reduced by VC administration. In addition, the levels of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGFD) were decreased by VC administration. These results suggest that VC exerts its anti-cancer effects by suppressing angiogenesis.
- 著者
- Atsuo Fujito Keiichi Hiramoto Masashi Imai Shota Tanaka Kazuya Ooi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b23-00108, (Released:2023-05-17)
- 参考文献数
- 30
Anticancer drugs exhibit many side effects, including skin pigmentation, which often lowers patient quality of life. However, the mechanism of pigmentation caused by anticancer drugs remains unknown. The purpose of this study was to elucidate the mechanism of anticancer drug-induced skin pigmentation using 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a widely used anticancer drug. Specific pathogen-free, 9-week-old Hos:HRM-2 male mice were intraperitoneally administered 5-FU daily for 8 weeks. Skin pigmentation was observed at the end of the study. Mice treated with 5-FU were also administered inhibitors of cAMP, α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) for analysis. Administration of oxidative stress, nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), cAMP, and ACTH inhibitors reduced pigmentation in 5-FU-treated mice. These results indicate that the oxidative stress/NF-κB/ACTH/cAMP/tyrosinase pathway plays an important role in pigmentation in 5-FU-treated mice.
- 著者
- Kentaro Nakanishi Keiichi Hiramoto Eisuke F Sato Kazuya Ooi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.1, pp.75-81, 2021-01-01 (Released:2021-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 4 7
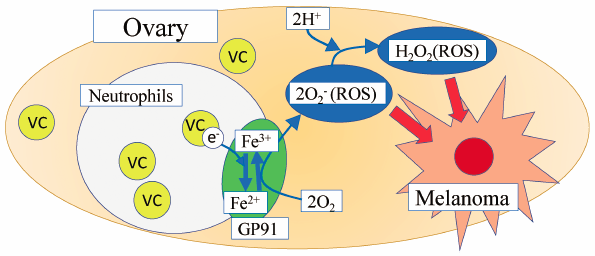
Several studies have been conducted to explore the anticancer effects of vitamin C (VC). However, the effect of high-dose VC administration on melanoma is still unknown. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the effects of high-dose VC (4 g/kg) on the invasion and proliferation of melanoma cells in various organs of mice. B16 melanoma cells (1 × 106 cells/100 µL) were intravenously injected into the tails of female mice, and VC solution (4 g/kg) was orally administered once a day for 14 d. On the 15th day, samples from the liver, lungs, jejunum, and ovaries were collected and analyzed for invasion and proliferation of melanoma cells. Oral VC administration decreased the number of dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA)-positive cells and gp100-positive melanoma cells in the ovaries and suppressed the invasion and proliferation of melanoma. Compared to melanoma-administered mice, macrophage inflammatory protein-2 levels and number of neutrophils were increased in the VC + melanoma-administered mice. Furthermore, the concentrations of VC, iron, and hydrogen peroxide, and the number of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick end labeling (TUNEL)-positive cells were significantly increased in the ovaries of VC + melanoma-administered mice compared to those of melanoma-administered mice. These results suggest that VC can reduce the invasion and proliferation of melanoma cells in the ovaries, and neutrophils in the ovaries play an important role in achieving this melanoma-suppressive effect.
- 著者
- Kazuya Ooi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.8, pp.1037-1043, 2021-08-01 (Released:2021-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Dry skin is a common symptom of various conditions, and elderly individuals commonly exhibit this physiological symptom. Dry skin develops owing to sebum deficiency; however, the use of moisturizers can typically overcome this issue, particularly in patients in whom there are no other skin problems. If dry skin is left untreated, itching and eczema can occur, resulting in skin damage. Additionally, hemodialysis patients exhibit reduced barrier function and can experience pain associated with repeated needle insertion; the repeated use of lidocaine tape to manage the pain can cause further skin damage. To reduce the occurrence of dry skin, the skin is hydrated using moisturizers. Dry skin is also prominent in patients with varicose veins in the lower extremities, and many biochemical studies have shown that skin immunity is altered in patients with dry skin. Moreover, the incidences of dry skin and pruritus differ in male and female patients. Furthermore, in elderly patients, zinc deficiency is likely to cause dry skin, and zinc supplementation may maintain skin hydration. To date, few reports have described dry skin from a clinical point of view. In this review, research on dry skin is presented, and the findings of basic research studies are integrated.