- 著者
- Shigeyoshi Soga Taro Koyama Ayako Mikoshi Tatsuhiko Arafune Makoto Kawashima Kazuhiro Kobayashi Hiroshi Shinmoto
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- 雑誌
- Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences (ISSN:13473182)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.2, pp.160-165, 2021 (Released:2021-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Purpose: Although androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is a common cause of hair loss, little is known regarding the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the AGA or scalp. This study aimed to analyze whether MRI for hair and scalp (MRH) can evaluate anatomical changes in the scalp caused by AGA.Methods: Twenty-seven volunteers were graded for the severity of AGA using the Hamilton–Norwood Scale (HNS), commonly used classification system. All subjects underwent MRH; two radiologists independently analyzed the images. As a quantitative measurement, the number of hair follicles was analyzed and compared with the HNS. As a qualitative analysis, each MRH scan was visually graded in terms of the severity of alopecia, using a 4-point MR severity score. The scores were compared with the HNS.Results: The volunteers were divided into two groups of 12 and 15 males without and with AGA at their vertex, respectively. Inter-observer agreements for the hair count and the MR severity score were excellent. The mean hair count on MRI in the normal group was significantly higher than that in the AGA group (P < 10−4). The MR severity score in the AGA group was significantly more severe than that in the control group (P < 10−4). In terms of the presence or absence of thinning hair, the MR severity score was consistent with the HNS determined by a plastic surgeon in 96% of cases. MR severity scores of clinically moderate AGA cases were significantly lower than those of severe cases (P = 0.022).Conclusion: MRH could depict scalp anatomy showing a clear difference between AGA and normal scalps, in both hair count and subjective visual assessment. The MR severity score was in good agreement with the clinical stages by HNS. The results support the potential of MRH as a promising imaging technique for analyzing healthy and pathological scalps.
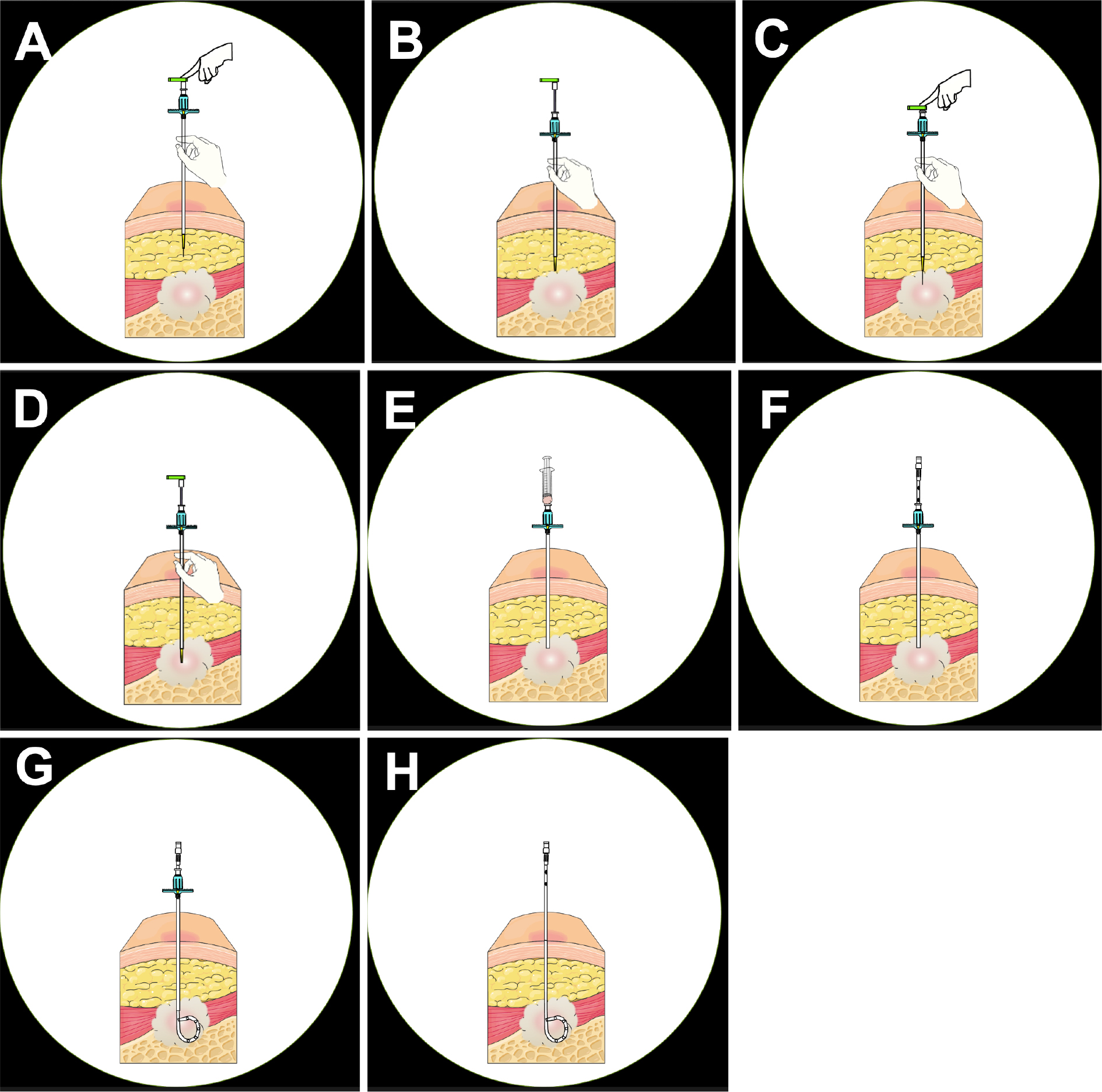
2 0 0 0 OA Computed Tomography-guided Drainage with Modified Trocar Technique Using a Drainaway Drainage Kit
- 著者
- Koji Togawa Seishi Nakatsuka Jitsuro Tsukada Nobutake Ito Yosuke Yamamoto Togo Kogo Hiroki Yoshikawa Manabu Misu Masashi Tamura Shigeyoshi Soga Masanori Inoue Hideki Yashiro Tadayoshi Kurata Masahiro Okada Masahiro Jinzaki
- 出版者
- Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology
- 雑誌
- Interventional Radiology (ISSN:24320935)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.8, no.3, pp.130-135, 2023-11-01 (Released:2023-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 10
Purpose: Image-guided percutaneous drainage for abscesses is known as a safe and effective treatment. The computed tomography-guided percutaneous drainage kit Drainaway (SB Kawasumi Co., Ltd.), developed on the basis of a modified trocar method, has made it possible to complete the procedure only under computed tomography guidance without radiographic fluoroscopy. This study investigated the feasibility and safety of Drainaway for abscess drainage.Material and Methods: In this retrospective observational study, 28 procedures in 27 patients (18 men and 9 women; age 67.0 ± 12.3 years) who underwent computed tomography-guided drainage using Drainaway between March and December 2021 at seven affiliated hospitals were analyzed. Patients with symptomatic, puncturable on computed tomography and refractory abscesses were included. Technical success (successful drainage with computed tomography alone), primary clinical success (successful drainage with Drainaway alone), secondary clinical success (avoidance of surgery), and complications were evaluated.Results: The sites of the abscesses were the intraperitoneal, retroperitoneal, and thoracic cavities in 19, 5, and 2 patients, respectively, and subcutaneous tissue in 1 patient. The mean size of the abscesses was 7.1 ± 3.4 cm. The technical success rate was 96.4%; the ligament of the puncture route could not be penetrated in one case. The primary clinical success rate was 77.8%, whereas the secondary clinical success rate of catheter upsizing or replacement was 96.3%. Complications included one case of biliary pleurisy that required drainage.Conclusions: Drainaway is a useful device that allows abscess drainage using only computed tomography guidance without radiographic fluoroscopy.
- 著者
- Shigeyoshi Soga Taro Koyama Ayako Mikoshi Tatsuhiko Arafune Makoto Kawashima Kazuhiro Kobayashi Hiroshi Shinmoto
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- 雑誌
- Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences (ISSN:13473182)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.mp.2020-0026, (Released:2020-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 1 2
Purpose: Although androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is a common cause of hair loss, little is known regarding the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the AGA or scalp. This study aimed to analyze whether MRI for hair and scalp (MRH) can evaluate anatomical changes in the scalp caused by AGA.Methods: Twenty-seven volunteers were graded for the severity of AGA using the Hamilton–Norwood Scale (HNS), commonly used classification system. All subjects underwent MRH; two radiologists independently analyzed the images. As a quantitative measurement, the number of hair follicles was analyzed and compared with the HNS. As a qualitative analysis, each MRH scan was visually graded in terms of the severity of alopecia, using a 4-point MR severity score. The scores were compared with the HNS.Results: The volunteers were divided into two groups of 12 and 15 males without and with AGA at their vertex, respectively. Inter-observer agreements for the hair count and the MR severity score were excellent. The mean hair count on MRI in the normal group was significantly higher than that in the AGA group (P < 10−4). The MR severity score in the AGA group was significantly more severe than that in the control group (P < 10−4). In terms of the presence or absence of thinning hair, the MR severity score was consistent with the HNS determined by a plastic surgeon in 96% of cases. MR severity scores of clinically moderate AGA cases were significantly lower than those of severe cases (P = 0.022).Conclusion: MRH could depict scalp anatomy showing a clear difference between AGA and normal scalps, in both hair count and subjective visual assessment. The MR severity score was in good agreement with the clinical stages by HNS. The results support the potential of MRH as a promising imaging technique for analyzing healthy and pathological scalps.
1 0 0 0 OA A Versatile MR Elastography Research Tool with a Modified Motion Signal-to-noise Ratio Approach
- 著者
- Daiki Ito Tetsushi Habe Tomokazu Numano Shigeo Okuda Shigeyoshi Soga Masahiro Jinzaki
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- 雑誌
- Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences (ISSN:13473182)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.mp.2022-0149, (Released:2023-04-12)
- 参考文献数
- 41
Purpose: This study aimed to facilitate research progress in MR elastography (MRE) by providing a versatile and convenient application for MRE reconstruction, namely the MRE research tool (MRE-rTool). It can be used for a series of MRE image analyses, including phase unwrapping, arbitrary bandpass and directional filtering, noise assessment of the wave propagation image (motion SNR), and reconstruction of the elastogram in both 2D and 3D MRE acquisitions. To reinforce the versatility of MRE-rTool, the conventional method of motion SNR was modified into a new method that reflects the effects of image filtering.Methods: MRE tests of the phantom and liver were performed using different estimation algorithms for stiffness value (algebraic inversion of the differential equation [AIDE], local frequency estimation [LFE] in MRE-rTool, and multimodel direct inversion [MMDI] in clinical reconstruction) and acquiring dimensions (2D and 3D acquisitions). This study also tested the accuracy of masking low SNR regions using modified and conventional motion SNR under various mechanical vibration powers.Results: The stiffness values estimated using AIDE/LFE in MRE-rTool were comparable to that of MMDI (phantom, 3.71 ± 0.74, 3.60 ± 0.32, and 3.60 ± 0.54 kPa in AIDE, LFE, and MMDI; liver, 2.26 ± 0.31, 2.74 ± 0.16, and 2.21 ± 0.26 kPa in AIDE, LFE, and MMDI). The stiffness value in 3D acquisition was independent of the direction of the motion-encoding gradient and was more accurate than that of 2D acquisition. The masking of low SNR regions using the modified motion SNR worked better than that in the conventional motion SNR for each vibration power, especially when using a directional filter.Conclusion: The performance of MRE-rTool on test data reached the level required in clinical MRE studies. MRE-rTool has the potential to facilitate MRE research, contribute to the future development of MRE, and has been freely released online.