- 著者
- Kotaro Koiwai Kana Morohashi Kazue Inaba Kana Ebihara Hirotatsu Kojima Takayoshi Okabe Ryunosuke Yoshino Takatsugu Hirokawa Taiki Nampo Yuuta Fujikawa Hideshi Inoue Fumiaki Yumoto Toshiya Senda Ryusuke Niwa
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.75-87, 2021-02-20 (Released:2021-02-26)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 6
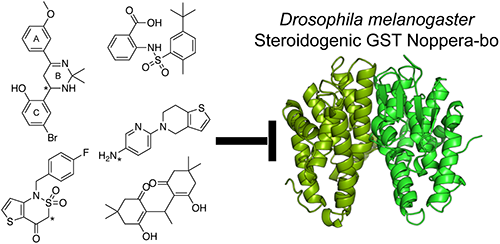
Insect growth regulators (IGRs) can be developed by elucidating the molecular mechanisms of insect-specific biological events. Because insect molting, and metamorphosis are controlled by ecdysteroids, their biosynthetic pathways can serve as targets for IGR development. The glutathione S-transferase Noppera-bo (Nobo), which is conserved in dipteran and lepidopteran species, plays an essential role in ecdysteroid biosynthesis. Our previous study using 17β-estradiol as a molecular probe revealed that Asp113 of Drosophila melanogaster Nobo (DmNobo) is essential for its biological function. However, to develop IGRs with a greater Nobo inhibitory activity than 17β-estradiol, further structural information is warranted. Here, we report five novel non-steroidal DmNobo inhibitors. Analysis of crystal structures of complexes revealed that DmNobo binds these inhibitors in an Asp113-independent manner. Among amino acid residues at the substrate-recognition site, conformation of conserved Phe39 was dynamically altered upon inhibitor binding. Therefore, these inhibitors can serve as seed compounds for IGR development.
- 著者
- Kotaro Koiwai Kana Morohashi Kazue Inaba Kana Ebihara Hirotatsu Kojima Takayoshi Okabe Ryunosuke Yoshino Takatsugu Hirokawa Taiki Nampo Yuuta Fujikawa Hideshi Inoue Fumiaki Yumoto Toshiya Senda Ryusuke Niwa
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.D20-072, (Released:2021-02-04)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Insect growth regulators (IGRs) can be developed by elucidating the molecular mechanisms of insect-specific biological events. Because insect molting, and metamorphosis are controlled by ecdysteroids, their biosynthetic pathways can serve as targets for IGR development. The glutathione S-transferase Noppera-bo (Nobo), which is conserved in dipteran and lepidopteran species, plays an essential role in ecdysteroid biosynthesis. Our previous study using 17β-estradiol as a molecular probe revealed that Asp113 of Drosophila melanogaster Nobo (DmNobo) is essential for its biological function. However, to develop IGRs with a greater Nobo inhibitory activity than 17β-estradiol, further structural information is warranted. Here, we report five novel non-steroidal DmNobo inhibitors. Analysis of crystal structures of complexes revealed that DmNobo binds these inhibitors in an Asp113-independent manner. Among amino acid residues at the substrate-recognition site, conformation of conserved Phe39 was dynamically altered upon inhibitor binding. Therefore, these inhibitors can serve as seed compounds for IGR development.