1 0 0 0 OA Environmental Risk Assessment of Active Human Pharmaceutical Ingredients in Urban Rivers in Japan
- 著者
- Toshinari Suzuki Yuki Kosugi Kimiyo Watanabe Haruka Iida Tetsuji Nishimura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.69, no.9, pp.840-853, 2021-09-01 (Released:2021-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 70
- 被引用文献数
- 5
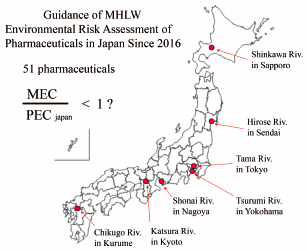
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) have become a public concern owing to their possible adverse effects on aquatic organisms. Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare in Japan (MHLW) issued “Guidance on the Environmental Risk Assessment (ERA) in new pharmaceutical development” in 2016. To evaluate the validity of phase 1 in the MHLW’s ERA guidance, we monitored the measured environmental concentrations (MECs) of approved APIs in urban rivers and sewage treatment plants (STPs) in Japan and compared these MECs with the predicted environmental concentration (PEC). We collected water samples from urban seven rivers and three STPs during each season. Fifty-one APIs for human and veterinary use and the artificial sweetener sucralose were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Forty-four APIs were observed in the rivers and 42 were found in the influent and effluent of STPs, with levels ranging from nanograms to micrograms per liter. The action limit in phase I of the MHLW’s guidance was set to 10 ng/L, and there was no API except for ketoprofen, for which PEC of the MHLW’s guidance (PECjapan) was lower than 10 ng/L and the maximum MEC (MECmax) was 10 ng/L or greater. Almost all APIs also had median MECs that were lower than those of the respective PECjapan. These results indicate that the PECjapan values in phase I of the MHLW’s guidance were appropriate. However, some APIs had MECmax values that were greater than those of the respective PECjapan due to overestimation of the dilution factor of river water and/or underestimation of API production.
1 0 0 0 OA Inflow and outflow loads of 484 daily-use chemicals in wastewater treatment plants across Japan
- 著者
- Kiwao KADOKAMI Takashi MIYAWAKI Katsumi IWABUCHI Sokichi TAKAGI Fumie ADACHI Haruka IIDA Kimiyo WATANABE Yuki KOSUGI Toshinari SUZUKI Shinichiro NAGAHORA Ruriko TAHARA Tomoaki ORIHARA Akifumi EGUCHI
- 出版者
- Japan Society for Environmental Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Environmental Monitoring and Contaminants Research (ISSN:24357685)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, pp.1-16, 2021 (Released:2021-03-05)
- 参考文献数
- 58
- 被引用文献数
- 6
With the increasing number and volume of chemicals used in modern life, their adverse effects on human health and aquatic organisms have increased concerns as well. To formulate appropriate management plans, the amounts/volumes used and emitted of these chemicals must be regulated. However, no data are available on the use of most chemicals, particularly daily-use chemicals such as pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs). Herein, we tested eight activated sludge wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) across Japan, each servicing populations of over 200,000, to investigate the emissions of 484 chemicals including 162 PPCPs. Twenty-four-hour composite samples were collected before and after the activated sludge component of treatment in each season of 2017. Targeted substances were solid-phase extracted and subsequently measured by LC-QTOF-MS-Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment-Ion Spectra Acquisition. The mean number of the detected substances and their mean total concentrations in inflows (n=32) and outflows (n=32) were 87 and 92 and 108,517 and 31,537 ng L−1, respectively. Pharmaceuticals comprised 50% of the screened chemicals in the inflow. The median removal efficiency was 31.3%: 29.2% for pharmaceuticals and 20.2% for pesticides, which were similar to those in the literature. Cluster analysis showed that spatial differences among the WWTPs are larger than seasonal differences in the same WWTP. Regardless, we detected seasonal differences in the amounts of substances in the inflows: the amounts of sucralose, UV-filters, and insecticides were larger in summer than in winter, whereas those of ibuprofen and chlorpheniramine were larger in winter than in summer. The total inflow and outflow population equivalent loads estimated using wastewater volume, detected concentrations, and populations were 44.7 and 13.0 g 1,000 capita−1 d−1, respectively. The extrapolated total annual Japan-wide inflow and outflow loads were 2,079 and 671 tons y−1, respectively. Using the data obtained in this study, we identified 13 candidates of marker substances for estimating real-time population in a sewage treatment area and 22 candidates of marker substances for sewage contamination.