- 著者
- Yusuke Yamamoto Eiichiro Iwata Hideki Shigematsu Hiroshi Nakajima Masato Tanaka Akinori Okuda Yasuhiko Morimoto Keisuke Masuda Munehisa Koizumi Yasuhito Tanaka
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2017-0052, (Released:2018-02-28)
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Introduction To identify the temporal comparison of biochemical markers for early detection of surgical site infection (SSI) following instrumented spinal fusion that are not affected by operative factors.Materials and methods We reviewed data on C-reactive protein level and total white blood cell count and differential count before instrumented spinal fusion and at 1, 4, and 7 days postoperatively. The 141 patients in our sample were divided into an SSI group (patients who developed deep SSI) and a non-SSI group. We investigated the peak or nadir value day and identified those not affected by operative circumstances (operating time, intraoperative blood loss, and number of fusion segments) in the non-SSI group. If there was a significant difference between the peak or nadir value day and the next survey day, we considered the temporal comparison between these unaffected markers as an indicator of SSI and examined the usefulness of these indicators by calculating sensitivity and specificity. Furthermore, we investigated the usefulness of the combination of these markers (if even each one marker was recognized, we considered it positive).Results Four biochemical markers of SSI were selected: neutrophil percentage at postoperative day 4 more than day 1 (sensitivity 36%, specificity 95%), neutrophil count at postoperative day 4 more than day 1 (sensitivity 46%, specificity 93%), lymphocyte percentage at postoperative day 4 less than day 1 (sensitivity 36%, specificity 90%), and lymphocyte count at postoperative day 4 less than day 1 (sensitivity 36%, specificity 90%). The combination of these markers showed sensitivity 100%, specificity 80%, respectively.Conclusions Four markers are reliable indicators for early detection of SSI following spinal instrumented fusion because they are not affected by operative factor. The combination of each indicator had both high sensitivity and specificity. Therefore, it is reliable and much useful for early detection of SSI.
- 著者
- Ikuya Yamada Yuta Kato Hiroshi Nakajima Hidekazu Ikeno Shigeo Mori Shogo Kawaguchi
- 出版者
- The Japan Institute of Metals and Materials
- 雑誌
- MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS (ISSN:13459678)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.MT-MG2022005, (Released:2023-01-10)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 1
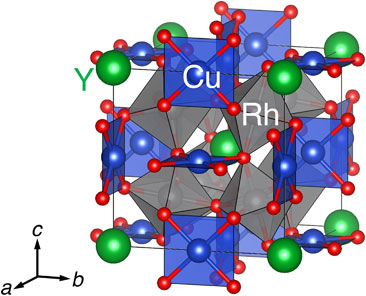
A novel oxide YCu3Rh4O12 has been obtained using high-pressure and high-temperature conditions of 12 GPa and 1573 K. Electron diffraction and synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction data demonstrates that YCu3Rh4O12 crystallizes in a cubic AA′3B4O12-type quadruple perovskite structure. The valence state is estimated to be Y3+Cu3+3Rh3+4O12 by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The electric resistivity and magnetization data prove that YCu3Rh4O12 is a diamagnetic insulator, which is expected from the electron configurations of Cu3+ (3d8, low spin, S = 0) and Rh3+ (4d6, low spin, S = 0) ions. The first-principle calculation displays the insulating band structure for YCu3Rh4O12. The valence state transition from Ca2+Cu2.8+3Rh3.4+4O12 to Y3+Cu3+3Rh3+4O12 indicates that the doped electrons by the substitution of Y3+ for Ca2+ are not simply injected to Cu and/or Rh ions, realizing unusual charge redistributions consisting of the simultaneous Cu oxidation (Cu2.8+ → Cu3+) and Rh reduction (Rh3.4+ → Rh3+).