1 0 0 0 OA Temporal Kinetics of Microgliosis in the Spinal Dorsal Horn after Peripheral Nerve Injury in Rodents
- 著者
- Keita Kohno Junko Kitano Yuta Kohro Hidetoshi Tozaki-Saitoh Kazuhide Inoue Makoto Tsuda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.7, pp.1096-1102, 2018-07-01 (Released:2018-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 33
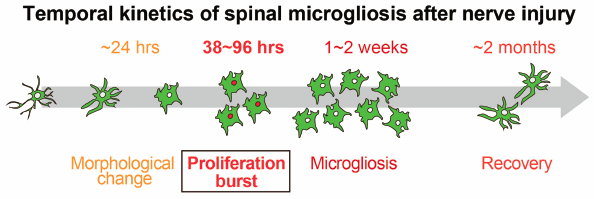
Neuropathic pain, a highly debilitating chronic pain following nerve damage, is a reflection of the aberrant functioning of a pathologically altered nervous system. Previous studies have implicated activated microglia in the spinal dorsal horn (SDH) as key cellular intermediaries in neuropathic pain. Microgliosis is among the dramatic cellular alterations that occur in the SDH in models of neuropathic pain established by peripheral nerve injury (PNI), but detailed characterization of SDH microgliosis has yet to be realized. In the present study, we performed a short-pulse labeling of proliferating cells with ethynyldeoxyuridine (EdU), a marker of the cell cycle S-phase, and found that EdU+ microglia in the SDH were rarely observed 32 h after PNI, but rapidly increased to the peak level at 40 h post-PNI. Numerous EdU+ microglia persisted for the next 20 h (60 h post-PNI) and decreased to the baseline on day 7. These results demonstrate a narrow time window for rapidly inducing a proliferation burst of SDH microglia after PNI, and these temporally restricted kinetics of microglial proliferation may help identify the molecule that causes microglial activation in the SDH, which is crucial for understanding and managing neuropathic pain.
- 著者
- Kazuhide INOUE
- 出版者
- 日本学士院
- 雑誌
- Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Series B (ISSN:03862208)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.93, no.4, pp.174-182, 2017-04-11 (Released:2017-04-11)
- 参考文献数
- 53
- 被引用文献数
- 35
Nerve injury often causes debilitating chronic pain, referred to as neuropathic pain, which is refractory to currently available analgesics including morphine. Many reports indicate that activated spinal microglia evoke neuropathic pain. The P2X4 receptor (P2X4R), a subtype of ionotropic ATP receptors, is upregulated in spinal microglia after nerve injury by several factors, including CC chemokine receptor CCR2, the extracellular matrix protein fibronectin in the spinal cord, interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) and IRF5. Inhibition of P2X4R function suppresses neuropathic pain, indicating that microglial P2X4R play a key role in evoking neuropathic pain.