1 0 0 0 OA Psychiatric Patients with Antipsychotic Drug-Induced Hyperprolactinemia and Menstruation Disorders
- 著者
- Kenshi Takechi Yurika Yoshioka Hitoshi Kawazoe Mamoru Tanaka Shingo Takatori Miwako Kobayashi Ichiro Matsuoka Hiroaki Yanagawa Yoshito Zamami Masaki Imanishi Keisuke Ishizawa Akihiro Tanaka Hiroaki Araki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.10, pp.1775-1778, 2017-10-01 (Released:2017-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 7 8
Treatment with antipsychotic drugs has been associated with hyperprolactinemia. The same antipsychotic drugs have also been associated with side effects such as menstruation disorders. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prevalence of hyperprolactinemia and menstruation disorders in women undergoing antipsychotic treatment. We performed a retrospective chart review study of psychiatric patients who underwent laboratory testing for serum prolactin (PRL) level between March 2011 and March 2015 in Ehime University Hospital. Patients presenting with and without menstruation disorders were evaluated to determine if they presented concomitant hyperprolactinemia. Patients with menstrual disorders had a significant increase in serum PRL level with a mean of approximately 90 ng/mL. Those with menstrual disorders presented increased PRL levels by 2-fold that of patients without menstrual disorder. However, there was no significant difference in the equivalent dose of chlorpromazine between these two groups. Additionally, about 70% of patients with menstrual disorders received risperidone treatment. The receiver operating characteristic curve showed that the optimal cutoff point of serum PRL level associated with the development of menstrual disorders was 60 ng/mL. Based on these results, we concluded that patients with menstrual disorders presented increased serum PRL, and that most of them underwent treatment with risperidone.
- 著者
- Yasutaka Sato Satoshi Sakaguchi Kenshi Takechi Masayuki Chuma Kenta Yagi Chikako Kane Mitsuhiro Goda Hirofumi Hamano Yuki Aoe Hiroshi Nokihara Yoshiaki Kubo Ichiro Hashimoto Hiroaki Yanagawa
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.3, pp.374-377, 2022-03-01 (Released:2022-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 15
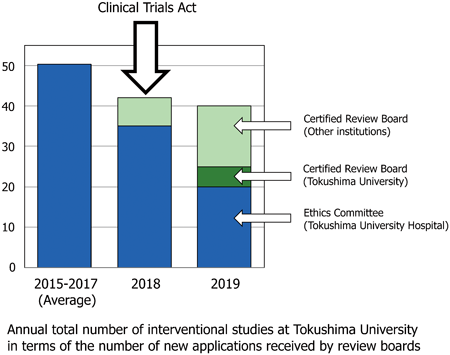
In April 2018, the Clinical Trials Act pertaining to investigator-initiated clinical trials was passed in Japan. The purpose of this study was to investigate activity in investigator-initiated clinical studies before and after enforcement of the new Clinical Trials Act. This was done by analysing the records of the Ethics Committee of Tokushima University Hospital, which reviews studies based on the Japanese government’s Ethical Guidelines for Medical and Health Research Involving Human Subjects prior to the Clinical Trials Act, and records of the Certified Review Board established at Tokushima University under the Clinical Trials Act in 2018. The number of new applications to these two review boards during fiscal years 2015–2017 (pre-Act) and fiscal years 2018 and 2019 (post-Act) were used as an indicator of activity in investigator-initiated clinical studies. The number of new applications to the Ethics Committee was 303, 261, 316, 303, and 249 in 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019, respectively. The data show that the total number of new interventional studies decreased from 50.3 in average in 2015–2017 (pre-Act) to 42 in 2018 and 40 in 2019 (post-Act), respectively. These results suggest that fewer interventional studies were started following enforcement of the new Clinical Trials Act. To confirm this trend and identify contributing factors, further studies are required. In addition, possible way, such as broader contribution of clinical research coordinators, to promote clinical studies in the new Clinical Trials Act era should be examined.