- 著者
- Kentaro Ayada Masahiro Tsuchiya Hiroyuki Yoneda Kouji Yamaguchi Hiroyuki Kumamoto Keiichi Sasaki Takeshi Tadano Makoto Watanabe Yasuo Endo
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.8, pp.1326-1330, 2017-08-01 (Released:2017-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Recent studies suggest that histamine—a regulator of the microcirculation—may play important roles in exercise. We have shown that the histamine-forming enzyme histidine decarboxylase (HDC) is induced in skeletal muscles by prolonged muscular work (PMW). However, histological analysis of such HDC induction is lacking due to appropriate anti-HDC antibodies being unavailable. We also showed that the inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α can induce HDC, and that PMW increases both IL-1α and IL-1β in skeletal muscles. Here, we examined the effects (a) of PMW on the histological evidence of HDC induction and (b) of IL-1β and TNF-α on HDC activity in skeletal muscles. By immunostaining using a recently introduced commercial polyclonal anti-HDC antibody, we found that cells in the endomysium and around blood vessels, and also some muscle fibers themselves, became HDC-positive after PMW. After PMW, TNF-α, but not IL-1α or IL-1β, was detected in the blood serum. The minimum intravenous dose of IL-1β that would induce HDC activity was about 1/10 that of TNF-α, while in combination they synergistically augmented HDC activity. These results suggest that PMW induces HDC in skeletal muscles, including cells in the endomysium and around blood vessels, and also some muscle fibers themselves, and that IL-1β and TNF-α may cooperatively mediate this induction.
- 著者
- Shiho Miyazaki Masahiro Kusano Dmitry S. Bulgarevich Satoshi Kishimoto Atsushi Yumoto Makoto Watanabe
- 出版者
- The Japan Institute of Metals and Materials
- 雑誌
- MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS (ISSN:13459678)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.4, pp.561-568, 2019-04-01 (Released:2019-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 17
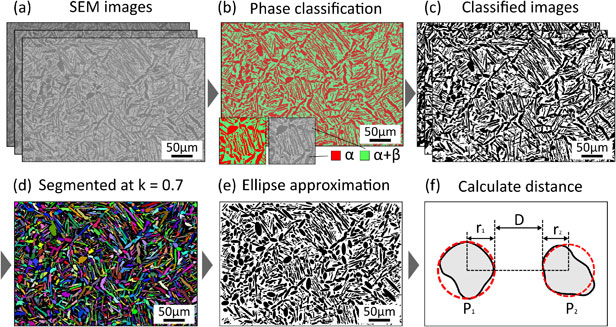
The selective laser melting could be employed in fabrication of near-net shape products for airplane and biomedical applications from Ti–6Al–4V alloy, which is difficult-to-process material. In this method, the localized laser irradiation forms the unique Ti–6Al–4V microstructures which correspond to the laser scanning patterns and local thermal history as it could be observed from sample cross-sections with OM or SEM. In this study, the effects of heat treatments on mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V samples produced by selective laser melting are discussed based on quantitative analysis of microstructures with image processing and machine learning tools. It was found that microstructures of heat-treated samples retained their original morphologies and secondary α phase precipitated regularly at β grain boundaries with increased treatment time. These microstructures were appropriately segmented and classified. Each α particle geometrical characteristics were successfully extracted and evaluated by image analysis. Importantly, the hardness of the heat-treated samples was lower compared to that of as-built ones and it tended to increase with the area fraction of α phase, the α particle width, and the nearest neighbor distance between α particles.