- 著者
- Nobuhiko Taguchi Minoru Yuriguchi Takuya Ando Ryosuke Kitai Hitomi Aoki Takahiro Kunisada
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.9, pp.1446-1449, 2019-09-01 (Released:2019-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 4 13
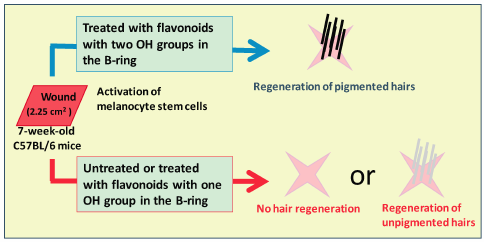
During the process of skin regeneration following a skin injury, de novo hair follicle regeneration is initiated after wounding; however, these regenerated hairs are mostly unpigmented. The activation of epidermal melanocyte stem cells and their differentiation into regenerating hair follicles have been shown to be necessary for the pigmented hair regeneration after wounding. To determine the role of flavonoids in the regeneration of pigmented hairs, we applied the candidate flavonoids to the regenerating hair follicles after wounding and identified the flavonoid species that maximally induced pigmented hair regeneration. Flavonoids with two OH groups in the B-ring, such as sterubin, luteolin, and hydroxygenkwanin, showed promising effects in regenerating black pigmented hairs, while those with one OH group in the B-ring showed no significant change. Thus, flavonoids with two OH groups in their B-ring could be studied further as potential wound healing agents with the ability to regenerate pigmented hair.
- 著者
- Nobuhiko Taguchi Takumi Homma Hitomi Aoki Takahiro Kunisada
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.10, pp.1451-1454, 2020-10-01 (Released:2020-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Hair follicular keratinocyte stem cells (HFKSC) which provide a functional niche for melanocyte stem cells (MSC) are the primary target of hair graying. However, little research has been done on anti-hair graying medicines targeting HFKSC. We focused on Eriodictyon angustifolium (Ea), which reduces human hair graying when applied topically. To investigate the protective effect of dietary Ea tea (EaT) on hair pigmentation, we used an acute mouse model of hair graying that mimics X-ray-induced DNA damage associated with age-related hair graying. Our results suggest that dietary EaT maintained the niche HFKSC function against X-ray-induced DNA damage and hair graying. These results indicate that dietary EaT may prevent age-related hair graying and serve as an anti-hair graying herbal medicine.