- 著者
- Yusuke Imayoshi Shuji Ohsaki Hideya Nakamura Satoru Watano
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.c23-00168, (Released:2023-04-22)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 1
A rotary tableting machine is used for the continuous tableting process. Tableting conditions often result in capping, leading to serious problems during production. Several studies have been conducted to predict the tablet capping tendency. However, as most previous studies were conducted using a compaction simulator, there is a lack of technology that can be readily applied during actual production. Therefore, the present study aimed to develop a novel method for predicting tablet capping in a rotary tableting machine. We hypothesized that capping occurs when residual stress of the tablet inside a die exceeds the critical stress immediately before ejection. Residual stress was evaluated by measuring the in-line die-wall pressure in a rotary tableting machine. Additionally, critical stress was estimated from the tablet strength inside the die using the Rumpf’s equation. The critical and residual stresses were compared to determine the capping tendency to some extent. The findings of this study will substantially contribute to the rapid detection of tablet capping during tablet production.
2 0 0 0 OA Optimum Water Content Estimation for Wet Granulation of Iron Ore Powders with Quicklime Binder
- 著者
- Shota Yokokawa Hideya Nakamura Tomotaka Otsu Shuji Ohsaki Satoru Watano Shohei Fujiwara Takahide Higuchi
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.ISIJINT-2022-498, (Released:2023-01-19)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Wet granulation plays an important role in the processing of fine ore powder. Water content is a critical process parameter that determines the granule properties during wet granulation. However, in the ironmaking industry, various types of iron ore powder imported from different regions are blended, quicklime powder is added as a binder, and used as raw materials. Therefore, the physicochemical properties of the raw powders are not always consistent, which makes it difficult to determine the optimum water content. In this study, we present a method to determine the optimum water content using the agitation torque of wet ore powder blended with quicklime. First, we investigated the agitation torque for blending of various types and ratios of ore powders and quicklime. Two types of torque profiles were observed: a unimodal torque profile (Type I) and a torque profile with a plateau region (Type II). From the agitation torque profile, the characteristic water content (
- 著者
- Kazuki Ohshima Shuji Ohsaki Hideya Nakamura Satoru Watano
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.70, no.5, pp.383-390, 2022-05-01 (Released:2022-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Numerous efforts have been devoted to improving the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. Recently, it was reported that the use of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), which are a new class of porous materials consisting of metal ions and organic ligands, is effective in improving the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. Our previous study demonstrated an improvement in the solubility of indomethacin (IDM) triggered by the zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8). The present study aimed to elucidate the solubilization mechanism using the ZIF series, namely, ZIF-8, ZIF-67, and ZIF-L. It was confirmed that the solubility of ZIF-trapped IDM and ibuprofen (IBU) was enhanced compared to the raw drugs, regardless of the ZIF type. This study focused on 2-methylimidazole (2-MIM), which is commonly used as a ZIF organic ligand. Both IDM and IBU were easily dissolved by the addition of 2-MIM, suggesting that the presence of 2-MIM enhanced the solubility of the drugs. Inductively coupled plasma measurements also confirmed the presence of metal ions of ZIFs in the supernatant solution after the drug release tests, indicating the decomposition of ZIFs during drug release. The findings of this study demonstrated the solubilization mechanism of poorly water-soluble drugs using ZIF particles. We observed that the drugs loaded on the ZIFs were released simultaneously with the decomposition of some of the ZIFs. The 2-MIM molecules were also released concurrently. The presence of 2-MIM improved the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs.
2 0 0 0 OA Determining Optimum Water Content for Iron Ore Granulation using Agitation Torque of Wet Ore Powder
- 著者
- Tomotaka Otsu Hideya Nakamura Shuji Ohsaki Satoru Watano Shohei Fujiwara Takahide Higuchi
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.ISIJINT-2022-009, (Released:2022-03-12)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Wet granulation of iron ore powders is a key process in ironmaking. In wet granulation, it is important to determine the optimum content of water added to the original ore powders. To determine the optimum water content, it is important to understand the saturation state in wet ore powder, which can be done by measuring the agitation torque of the wet powder. This study proposes a methodology for determining the optimum water content of various iron ore powders using the agitation torque of wet ore powders. First, measurement of the agitation torque and wet granulation of various iron ore powders were conducted. By comparing the results, it was found that the optimum water content, which was defined as the minimum water content required to diminish fine particles in the original powder, corresponded to the water content exhibiting the maximum agitation torque, regardless of the original powder. Using the agitation torque at different water contents, the saturation degree S, which is the volume ratio of water to the interparticle voids, was calculated, resulting in a range of 0.999 ≤ S ≤ 1.173 at the optimum water content. This suggests that the state between the funicular and capillary states is a suitable saturation state for the wet granulation of ore powders. Consequently, it was demonstrated that it is possible to determine the optimum water content for wet granulation of various iron ore powders based on the water content exhibiting the maximum agitation torque of wet ore powders.
- 著者
- Ryosuke Mitani Shuji Ohsaki Hideya Nakamura Satoru Watano
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.8, pp.726-736, 2020-08-01 (Released:2020-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 10
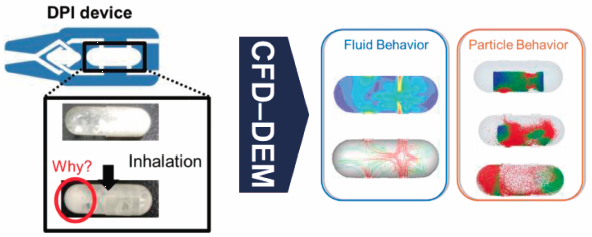
This study investigated the particle adhesion mechanism in a capsule of dry powder inhaler (DPI) based on a combined computational fluid dynamics and discrete element method (CFD–DEM) approach. In this study, the Johnson–Kendall–Roberts (JKR) theory was selected as the adhesion force model. The simulation results corroborated the experimental results—numerous particles remained on the outlet side of the capsule, while a few particles remained on the inlet side. In the computer simulation, the modeled particles were placed in a capsule. They were quickly dispersed to both sides of the capsule, by air fed from one side of the capsule, and delivered from the air inlet side to the outlet side of the capsule. It was confirmed that vortex flows were seen at the outlet side of the capsule, which, however, were not seen at the inlet side. Numerous collisions were observed at the outlet side, while very few collisions were observed at the inlet side. These results suggested that the vortex flows were crucial to reduce the amount of residual particles in the capsule. The original capsule was then modified to enhance the vortex flow in the area, where many particles were found remaining. The modified capsule reduced the number of residual particles compared to the original capsule. This investigation suggests that the CFD–DEM approach can be a great tool for understanding the particle adhesion mechanism and improving the delivery efficiency of DPIs.