- 著者
- Kazunori Miwa Yan Guo Masayuki Hata Yoshinori Hirano Norio Yamamoto Tyuji Hoshino
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.12, pp.897-905, 2023-12-01 (Released:2023-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 40
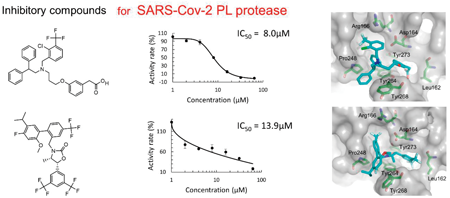
Virtual screening with high-performance computers is a powerful and cost-effective technique in drug discovery. A chemical database is searched to find candidate compounds firmly bound to a target protein, judging from the binding poses and/or binding scores. The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-Cov-2) infectious disease has spread worldwide for the last three years, causing severe slumps in economic and social activities. SARS-Cov-2 has two viral proteases: 3-chymotrypsin-like (3CL) and papain-like (PL) protease. While approved drugs have already been released for the 3CL protease, no approved agent is available for PL protease. In this work, we carried out in silico screening for the PL protease inhibitors, combining docking simulation and molecular mechanics calculation. Docking simulations were applied to 8,820 molecules in a chemical database of approved and investigational compounds. Based on the binding poses generated by the docking simulations, molecular mechanics calculations were performed to optimize the binding structures and to obtain the binding scores. Based on the binding scores, 57 compounds were selected for in vitro assay of the inhibitory activity. Five inhibitory compounds were identified from the in vitro measurement. The predicted binding structures of the identified five compounds were examined, and the significant interaction between the individual compound and the protease catalytic site was clarified. This work demonstrates that computational virtual screening by combining docking simulation with molecular mechanics calculation is effective for searching candidate compounds in drug discovery.
- 著者
- Kazunori Miwa Yan Guo Masayuki Hata Norio Yamamoto Tyuji Hoshino
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.5, pp.360-367, 2023-05-01 (Released:2023-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 39
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Computational screening is one of the fundamental techniques in drug discovery. Each compound in a chemical database is bound to the target protein in virtual, and candidate compounds are selected from the binding scores. In this work, we carried out combinational computation of docking simulation to generate binding poses and molecular mechanics calculation to estimate binding scores. The coronavirus infectious disease has spread worldwide, and effective chemotherapy is strongly required. The viral 3-chymotrypsin-like (3CL) protease is a good target of low molecular-weight inhibitors. Hence, computational screening was performed to search for inhibitory compounds acting on the 3CL protease. As a preliminary assessment of the performance of this approach, we used 51 compounds for which inhibitory activity had already been confirmed. Docking simulations and molecular mechanics calculations were performed to evaluate binding scores. The preliminary evaluation suggested that our approach successfully selected the inhibitory compounds identified by the experiments. The same approach was applied to 8820 compounds in a database consisting of approved and investigational chemicals. Hence, docking simulations, molecular mechanics calculations, and re-evaluation of binding scores including solvation effects were performed, and the top 200 poses were selected as candidates for experimental assays. Consequently, 25 compounds were chosen for in vitro measurement of the enzymatic inhibitory activity. From the enzymatic assay, 5 compounds were identified to have inhibitory activities against the 3CL protease. The present work demonstrated the feasibility of a combination of docking simulation and molecular mechanics calculation for practical use in computational virtual screening.
- 著者
- WANG Mei YAN Guo-Hui YUE Wen-Sheng SIU Chung-Wah YIU Kai-Hang LEE Stephen W. L. LAU Chu Pak TSE Hung-Fat
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本循環器学会
- 雑誌
- Circulation journal : official journal of the Japanese Circulation Society (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.76, no.3, pp.682-688, 2012-02-25
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 1 9
<b><i>Background:</i></b> Left ventricular (LV) mechanical dyssynchrony can lead to impairment of LV function and is associated with adverse clinical outcomes in coronary artery disease (CAD) patients. The impact of LV dyssynchrony on exercise capacity (EC) in patients with CAD was investigated. <b><i>Methods and Results:</i></b> An echocardiographic examination with tissue Doppler imaging and exercise treadmill testing in 151 CAD patients with normal LV ejection fraction was performed. LV intra- and inter-ventricular dyssynchrony were defined by the standard deviation of time interval between LV 6 basal segments (Ts-SD), and the time interval from the right ventricular (RV) free wall to LV lateral wall (Ts-RV) respectively, and EC was measured as metabolic equivalents (METs) on the treadmill. Patients with impaired EC (defined by a METs ≤8, which is the mean MET of the study population) were older (71±7 vs. 62±2 years, P<0.01), however, there were no differences in gender and clinical status such as prevalence of prior myocardial infarction (MI), regional wall motion abnormality (RWMA), and coronary revascularization between patients with (n=90) or without (n=61) impaired EC. Univariate analysis showed that age, body mass index, LV systolic and diastolic volume, mitral inflow A velocity, and Ts-SD were all significantly associated with METs (all P<0.05). However, multivariate regression analysis revealed that old age (odd ratio [OR]: 1.136, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.080-1.196, P<0.001), and Ts-SD (OR: 1.026, 95%CI: 1.003-1.049, P=0.027) only were independent predictors for impaired EC. <b><i>Conclusions:</i></b> In patients with CAD, LV systolic dyssynchrony predicts impaired EC independently of history of previous MI or RWMA. (<i>Circ J</i> 2012; <b>76:</b> 682-688)<br>