1 0 0 0 OA Morphological Analysis of the Sylvian Fissure Stem to Guide a Safe Trans-sylvian Fissure Approach
- 著者
- Yasutaka IMADA Chie MIHARA Hitoshi KAWAMOTO Kaoru KURISU
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.11, pp.502-512, 2022-11-15 (Released:2022-11-15)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 1
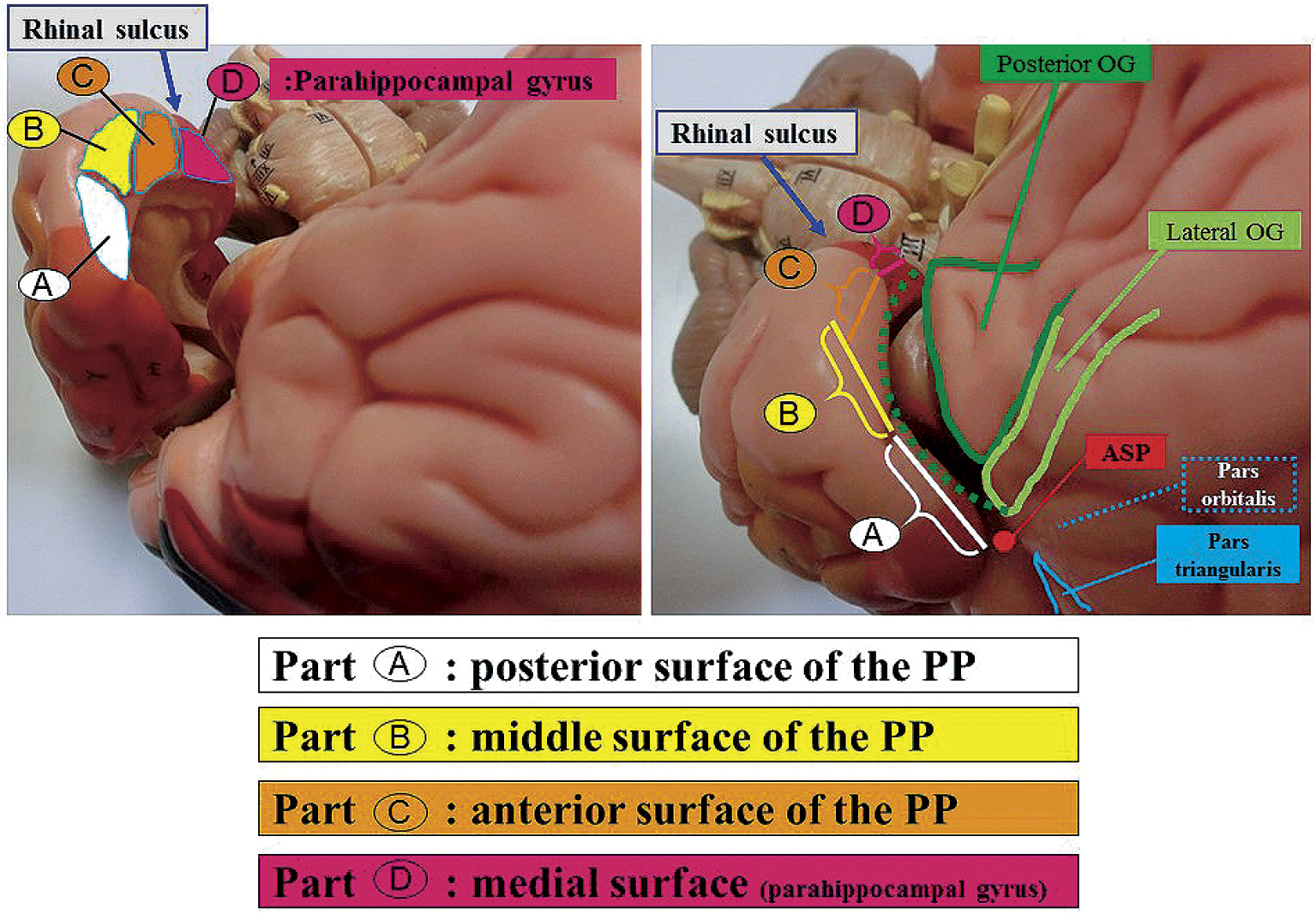
The sylvian fissure stem and its deep cisternal part (SDCP) consist mainly of the orbital gyrus (OG) and anterior medial portion of the temporal lobe. SDCP's adhesion has been found to make a trans-sylvian approach difficult due to the various patterns of adhesion. Thus, in this study, we aim to clarify the morphological features of the SDCP, and to guide a safe trans-sylvian approach. We retrospectively classified the morphology of the SDCP in 81 patients into 3 types (tight, moderate, loose type) according to the degree of adhesion of the arachnoid membrane and analyzed the morphological features of the OG and the temporal lobe using intraoperative video images. In addition, we have retrospectively measured each width of the SDCP's subarachnoid space at the three points (Point A, lateral superior portion; Point B, downward portion; Point C, medial inferior portion of SDCP) and analyzed their relationship to the degree of adhesion using the preoperative coronal three-dimensional computed tomography angiography (3D-CTA) images of 44 patients. As per the results, SDCP's adhesions were determined to be significantly tighter in cases with large OG and young cases. The temporal lobe had four surfaces (posterior, middle, anterior, and medial) that adhered to the OG in various patterns. The tighter the adhesion between the OG and each of the three distal surfaces of the temporal lobe, the narrower the width of the subarachnoid space at each point (A, B, C). Understanding of the morphological features of the SDCP, and estimating its adhesion preoperatively are useful in developing a surgical strategy and obtaining correct intraoperative orientation in the trans-sylvian approach.
- 著者
- Yasutaka IMADA Kaoru KURISU Toru TAKUMI Hirohiko AOYAMA Takashi SADATOMO Keisuke MIGITA Kiyoshi YUKI
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.7, pp.264-270, 2019 (Released:2019-07-15)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 1 9
In this study, we used 45 adult cadaveric cerebral hemispheres to investigate the anatomical classification of the superficial middle cerebral vein (SMCV) based on the number of stems, course, and anastomosis at the distal portion. We classified the SMCVs into five types based on embryological concept. Type A (18 cases, 40.0%) is that the frontosylvian veins (FSVs) merge with the vein of Trolard (VT) and the vein of Labbé (VL) at the distal portion of the sylvian fissure. Type B (5 cases, 11.1%) is that the temporosylvian veins (TSVs) merge with the VT and the VL at the distal portion. Type C (13 cases, 28.9%) is that no vein merge with the VT and the VL at the distal portion. The VT merges with the SMCV from the FSV and the VL merges with the SMCV from the TSV. They course along the sylvian fissure and merge at the proximal portion. In Type D (eight cases: 17.8%), the VT and the VL merge at the distal portion, and the SMCV from the FSV and the SMCV from the TSV join their confluence without merging. Type E (one case, 2.2%) show an undeveloped SMCV. Formation rate of intravenous anastomoses or bridging veins(BVs) at the distal portion between the frontosylvian trunk (FST) and the temporosylvian trunk (TST), between the FST and the temporal lobe, and between the TST and the frontal lobe was very low, because these formation may be difficult to occur during the embryological process in which the SMCV is formed from the telencephalic vein.
- 著者
- Yasutaka IMADA Kaoru KURISU Toru TAKUMI Hirohiko AOYAMA Takashi SADATOMO Keisuke MIGITA Kiyoshi YUKI
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.oa.2018-0284, (Released:2019-05-11)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 9
In this study, we used 45 adult cadaveric cerebral hemispheres to investigate the anatomical classification of the superficial middle cerebral vein (SMCV) based on the number of stems, course, and anastomosis at the distal portion. We classified the SMCVs into five types based on embryological concept. Type A (18 cases, 40.0%) is that the frontosylvian veins (FSVs) merge with the vein of Trolard (VT) and the vein of Labbé (VL) at the distal portion of the sylvian fissure. Type B (5 cases, 11.1%) is that the temporosylvian veins (TSVs) merge with the VT and the VL at the distal portion. Type C (13 cases, 28.9%) is that no vein merge with the VT and the VL at the distal portion. The VT merges with the SMCV from the FSV and the VL merges with the SMCV from the TSV. They course along the sylvian fissure and merge at the proximal portion. In Type D (eight cases: 17.8%), the VT and the VL merge at the distal portion, and the SMCV from the FSV and the SMCV from the TSV join their confluence without merging. Type E (one case, 2.2%) show an undeveloped SMCV. Formation rate of intravenous anastomoses or bridging veins(BVs) at the distal portion between the frontosylvian trunk (FST) and the temporosylvian trunk (TST), between the FST and the temporal lobe, and between the TST and the frontal lobe was very low, because these formation may be difficult to occur during the embryological process in which the SMCV is formed from the telencephalic vein.