15 0 0 0 OA Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Digoxin Toxicity in Heart Failure: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
- 著者
- Yuki Asai Takumi Tashiro Yoshihiro Kondo Makoto Hayashi Hiroki Arihara Saki Omote Ena Tanio Saena Yamashita Takashi Higuchi Ei Hashimoto Momoko Yamada Hinako Tsuji Yuji Hayakawa Ryohei Suzuki Hiroya Muro Yoshiaki Yamamoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.4, pp.614-620, 2023-04-01 (Released:2023-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 1
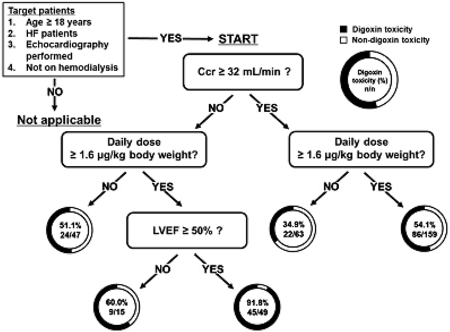
Digoxin toxicity (plasma digoxin concentration ≥0.9 ng/mL) is associated with worsening heart failure (HF). Decision tree (DT) analysis, a machine learning method, has a flowchart-like model where users can easily predict the risk of adverse drug reactions. The present study aimed to construct a flowchart using DT analysis that can be used by medical staff to predict digoxin toxicity. We conducted a multicenter retrospective study involving 333 adult patients with HF who received oral digoxin treatment. In this study, we employed a chi-squared automatic interaction detection algorithm to construct DT models. The dependent variable was set as the plasma digoxin concentration (≥ 0.9 ng/mL) in the trough during the steady state, and factors with p < 0.2 in the univariate analysis were set as the explanatory variables. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to validate the DT model. The accuracy and misclassification rates of the model were evaluated. In the DT analysis, patients with creatinine clearance <32 mL/min, daily digoxin dose ≥1.6 µg/kg, and left ventricular ejection fraction ≥50% showed a high incidence of digoxin toxicity (91.8%; 45/49). Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that creatinine clearance <32 mL/min and daily digoxin dose ≥1.6 µg/kg were independent risk factors. The accuracy and misclassification rates of the DT model were 88.2 and 46.2 ± 2.7%, respectively. Although the flowchart created in this study needs further validation, it is straightforward and potentially useful for medical staff in determining the initial dose of digoxin in patients with HF.
- 著者
- Hayahide Ooi Yuki Asai Yoshiki Koriyama Masaaki Takahashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.12, pp.1731-1736, 2023-12-01 (Released:2023-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 20
The albumin–bilirubin (ALBI) score is an index of hepatic functional reserve and is calculated from serum albumin and total bilirubin levels. However, the relationship between ceftriaxone (CTRX)-induced liver injury and ALBI score remains unknown. Therefore, we aimed to elucidate the risk of CTRX-induced liver injury based on the ALBI scores and CTRX dosage. This was a single-center, retrospective, case-control study of 490 patients and the primary outcome was CTRX-induced liver injury. We performed a COX regression analysis using age ≥75 years, male sex, alanine aminotransferase levels, ALBI score, and CTRX dosage regimen (4 ≥2 or 1 g/d) as explanatory factors. We also performed 1 : 1 propensity score matching between non-liver injury and liver injury groups. The incidence of liver injury was 10.0% (49/490). In COX regression analysis, CTRX 4 g/d was an independent risk factor for liver injury (95% coefficient interval: 1.05–6.96, p = 0.04). Meanwhile, ALBI score ≥−1.61 was an independent factor for liver injury (95% coefficient interval: 1.03–3.22, p = 0.04) with the explanatory factor of ≥2 and 1 g/d. The Kaplan–Meier curve indicated that the cumulative risk for CTRX-induced liver injury was significantly higher in the ALBI score ≥−1.61 group than in the ALBI score <−1.61 group before propensity score matching (p = 0.032); however, no significant differences were observed after propensity score matching (p = 0.791). These findings suggest that in patients treated with CTRX with ALBI score ≥−1.61, frequent liver function monitoring should be considered.