- 著者
- Ryota Sakamoto Yusuke T. Maeda
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.3, pp.e200032, 2023 (Released:2023-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 52
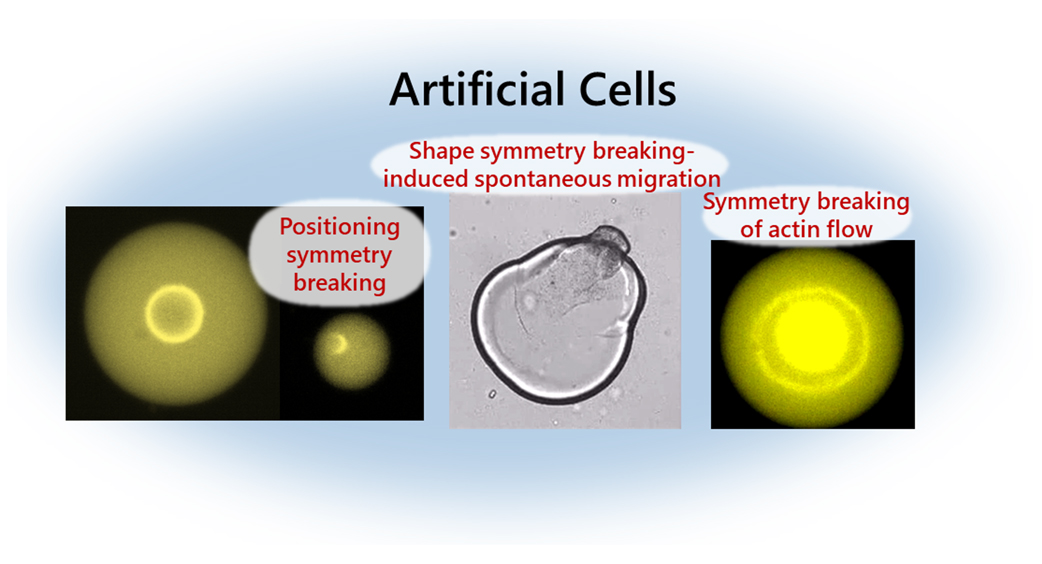
Single-cell behaviors cover many biological functions, such as cell division during morphogenesis and tissue metastasis, and cell migration during cancer cell invasion and immune cell responses. Symmetry breaking of the positioning of organelles and the cell shape are often associated with these biological functions. One of the main players in symmetry breaking at the cellular scale is the actin cytoskeleton, comprising actin filaments and myosin motors that generate contractile forces. However, because the self-organization of the actomyosin network is regulated by the biochemical signaling in cells, how the mechanical contraction of the actin cytoskeleton induces diverse self-organized behaviors and drives the cell-scale symmetry breaking remains unclear. In recent times, to understand the physical underpinnings of the symmetry breaking exhibited in the actin cytoskeleton, artificial cell models encapsulating the cytoplasmic actomyosin networks covered with lipid monolayers have been developed. By decoupling the actomyosin mechanics from the complex biochemical signaling within living cells, this system allows one to study the self-organization of actomyosin networks confined in cell-sized spaces. We review the recent developments in the physics of confined actomyosin networks and provide future perspectives on the artificial cell-based approach. This review article is an extended version of the Japanese article, The Physical Principle of Cell Migration Under Confinement: Artificial Cell-based Bottom-up Approach, published in SEIBUTSU BUTSURI Vol. 63, p. 163–164 (2023).
- 著者
- Kazusa Beppu Yusuke T. Maeda
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, pp.e190020, 2022 (Released:2022-06-03)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Ordered collective motion emerges in a group of autonomously motile elements (known as active matter) as their density increases. Microswimmers, such as swimming bacteria, have been extensively studied in physics and biology. A dense suspension of bacteria forms seemingly chaotic turbulence in viscous fluids. Interestingly, this active turbulence driven by bacteria can form a hidden ensemble of many vortices. Understanding the active turbulence in a bacterial suspension can provide physical principles for pattern formation and insight into the instability underlying biological phenomena. This review presents recent findings regarding ordered structures causing active turbulence and discusses a physical approach for controlling active turbulence via geometric confinement. When the active matter is confined in a compartment with a size comparable to the correlation length of the collective motion, vortex-like rotation appears, and the vortex pairing order is indicated by the patterns of interacting vortices. Additionally, we outline the design principle for controlling collective motions via the geometric rule of the vortex pairing, which may advance engineering microdevices driven by a group of active matter. This article is an extended version of the Japanese article, Ordered Structure and Geometric Control of Active Matter in Dense Bacterial Suspensions, published in SEIBUTSU BUTSURI Vol. 60, p. 13–18 (2020).