- 著者
- Toyokazu Yokoyama C.C. Huang
- 出版者
- 公益財団法人ホソカワ粉体工学振興財団
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.23, pp.7-17, 2005 (Released:2014-03-29)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 11 24
The nanoparticle technology, relating to the preparation, characterization, processing, and applications of nano-sized particles, plays an increasingly important role in the emerging nano-technology. Although the nanoparticles have many unique functional properties superior to the coarser particles, they also suffer from dispersion and stability problems because of their strong cohesiveness and high specific surface areas. To make the best use of nanoparticles and solve their application problems, the development of nanomaterial processing techniques is essential.New chemical synthesis methods for producing nano-sized oxides particles in the gas phase and producing biocompatible polymeric nano-composite particles in the solution phase were elucidated in the paper. In addition, mechanical breakdown method (e.g. nano-grinding) was briefly discussed. Furthermore, newly developed dry particle processing systems for making high performance nanocomposites as well as their applications in Fuel Cells, Drug Delivery Systems, and Cosmetics were introduced.
- 著者
- Sara E. Maloney Jeffrey B. Mecham Anthony J. Hickey
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2023013, (Released:2022-09-03)
- 参考文献数
- 65
- 被引用文献数
- 2
It is well established that the critical performance metrics for aerosol products are aerodynamic particle size distribution (APSD) and delivered dose uniformity (DDU). In broad terms, these performance characteristics dictate the efficiency and reproducibility with which an aerosol is administered clinically. However, these properties alone do not support in-vitro, in-vivo correlations. There have been numerous publications attempting to more directly link product performance testing to physiological relevance or further to draw direct correlations of relevance to bioequivalence testing for the development of generic products. While these novel methods have been employed in product development activity, their suitability for compendial testing has yet to be established. This paper explores the potential to establish biologically relevant compendial standards for dry powder inhaler products while maintaining accuracy and reproducibility of data collected to support the quality and performance of the product.
- 著者
- Erik J.G. Sewalt Fuweng Zhang Volkert van Steijn J. Ruud van Ommen Gabrie M.H. Meesters
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021017, (Released:2020-09-19)
- 参考文献数
- 79
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Sticking of particles has a tremendous impact on powder-processing industries, especially for hygroscopic amorphous powders. A wide variety of experimental methods has been developed to measure at what combinations of temperature and moisture content material becomes sticky. This review describes, for each method, how so-called stickiness curves are determined. As particle velocity also plays a key role, we classify the methods into static and dynamic stickiness tests. Static stickiness tests have limited particle motion during the conditioning step prior to the measurement. Thus, the obtained information is particularly useful in predicting the long-term behavior of powder during storage or in packaging. Dynamic stickiness tests involve significant particle motion during conditioning and measurement. Stickiness curves strongly depend on particle velocity, and the obtained information is highly relevant to the design and operation of powder production and processing equipment. Virtually all methods determine the onset of stickiness using powder as a starting point. Given the many industrial processes like spray drying that start from a liquid that may become sticky upon drying, future effort should focus on developing test methods that determine the onset of stickiness using a liquid droplet as a starting point.
- 著者
- Myungjoon Kim Saho Osone Taesung Kim Hidenori Higashi Takafumi Seto
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, pp.80-90, 2017 (Released:2017-02-28)
- 参考文献数
- 48
- 被引用文献数
- 146 230
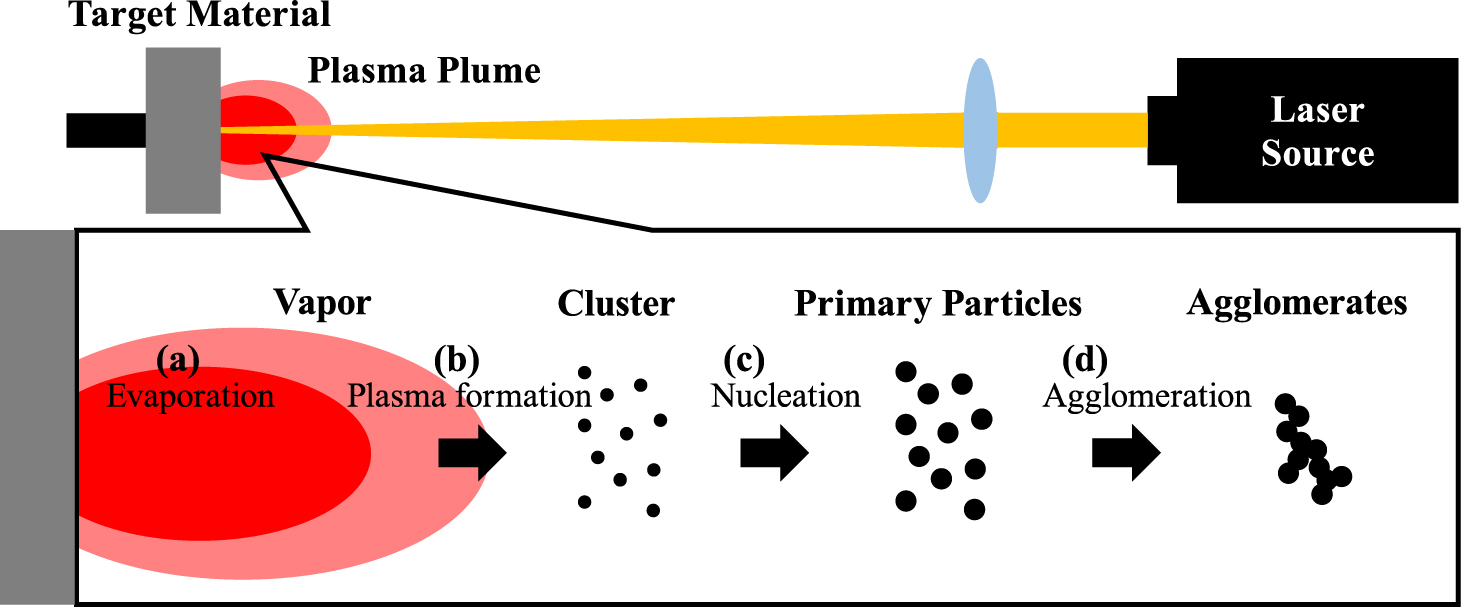
Laser ablation is a method for fabricating various kinds of nanoparticles including semiconductor quantum dots, carbon nanotubes, nanowires, and core shell nanoparticles. In this method, nanoparticles are generated by nucleation and growth of laser-vaporized species in a background gas. The extremely rapid quenching of vapor is advantageous in producing high purity nanoparticles in the quantum size range (< 10 nm). In this review, the formation mechanism of nanoparticles by laser ablation is summarized. Recent progress on the control of nanoparticle size and the challenges for functional nanoparticle synthesis by advanced laser ablation technology are then discussed.
2 0 0 0 OA From Quasi-static to Intermediate Regimes in Shear Cell Devices: Theory and Characterisation
- 著者
- Victor Francia Lyes Ait Ali Yahia Raffaella Ocone Ali Ozel
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021018, (Released:2020-09-26)
- 参考文献数
- 148
- 被引用文献数
- 8
The design of new technology for processing and manufacturing particulate products requires understanding granular rheology over a broad range of conditions. Powders display a complex behaviour due to their ability to rearrange under stress, and as a result, granular flow is generally classified into three flow regimes, namely a quasi-static regime dominated by frictional contacts, an inertial regime dominated by collisional and kinematic stresses and an intermediate regime where the three sources of stress are important to establish a stress-strain rate relationship. Characterisation of the flowability is generally restricted to the flow initiation in quasi-static regime, even if, transition into inertial conditions is very common in practical applications involving the control of dense flows, such as powder handling, particle formation processes or additive manufacturing. This work presents a critical review of available techniques to characterise the departure from the quasi-static regime into an intermediate flow. We revise the application of shear cells and present different strategies to modify classic devices with external actuation, such as aeration, to operate at higher inertial numbers. We pay particular attention to innovative designs using aerated Couette flow configurations, highlight the complexity in the standardisation and the challenges in advancing towards a universal model.
2 0 0 0 OA Rheology and Sedimentation of Aqueous Suspension of Na-montmorillonite in the Very Dilute Domain
- 著者
- Yasuhisa Adachi Yoko Tsujimoto Kawashima Muhamad Ezral Bin Ghazali
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2020019, (Released:2019-10-31)
- 参考文献数
- 102
- 被引用文献数
- 7
The scheme of DLVO theory and the concept of fractal structure of flocs applied to the suspension of montmorillonite have revealed out the unique nature of this clay dispersion. In this context, two major regimes are recognized. The first is the electrostatically dispersed regime. And the second is the coagulated regime. In the former, the formation of a diffusive electric double layer (EDL) characterized by reciprocal Debye length measured from the surface of the particle is distinctively important. Intrinsic viscosity with electroviscous effects and yield stress are interpreted by the steric presence of EDL. In the latter, the unit of transportation is a coagulated floc with finite cohesive strength. Sedimentation process reflecting these factors is carefully observed to recognize the turbulence generation by the formation of large flocs at the moment of gel collapse. Waiting time prior to gel collapse was found to be determined reflecting the pH-dependent charging behavior. By taking into account the effect pH-dependent charge, the DLVO based two regimes are further categorized into five. The developed tools can be extensively used for the system involved with different ionic species, pH, volume fraction and organic substances.
2 0 0 0 OA Challenges Associated with the Pulmonary Delivery of Therapeutic Dry Powders for Preclinical Testing
- 著者
- Dominique N. Price Nitesh K. Kunda Pavan Muttil
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2019008, (Released:2018-03-31)
- 参考文献数
- 95
- 被引用文献数
- 27
Significant progress has been made over the last half-century in delivering therapeutics by the pulmonary route. Inhaled therapeutics are administered to humans using metered-dose inhalers, nebulizers, or dry powder inhalers, and each device requires a different formulation strategy for the therapeutic to be successfully delivered into the lung. In recent years, there has been a shift to the use of dry powder inhalers due to advantages in the consistency of the dose delivered, ease of administration, and formulation stability. Numerous preclinical studies, involving small and large animals, have evaluated dry powder drugs, vaccines, and immunotherapeutics delivered by the pulmonary route. These studies used different dry powder delivery devices including nose-only, whole-body, and intratracheal administration systems, each of which works with different aerosolization mechanisms. Unfortunately, these delivery platforms usually lead to variable powder deposition in the respiratory tract of animals. In this review, we will discuss obstacles and variables that affect successful pulmonary delivery and uniform powder deposition in the respiratory tract, such as the type of delivery device, dry powder formulation, and the animal model used. We will conclude by outlining factors that enhance the reproducible deposition of dry powders in the respiratory tract of preclinical animal models and identifying knowledge and technology gaps within the field. We will also outline the important factors necessary for successful translation of studies performed in preclinical models to humans.
- 著者
- Brian J. Schoeman Johan Sterte
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, pp.150-158, 1997 (Released:2014-05-30)
- 被引用文献数
- 16 18
A method for the preparation of stable colloidal suspensions containing discrete molecular sieve crystals is presented. The hydrothermal synthesis of the all-silica tetrapropylammonium silicalite-1 molecular sieve illustrates the preparation. The discrete colloidal crystals ( < 150 nm) are aggregates of plate-like primary particles and they are stabilized in aqueous solution via steric forces that arise as a result of the strong adsorption of the tetrapropylammonium cation on the siliceous surface. The silicalite-1 surface charge is a function of pH as shown by electrophoretic measurements. These properties may be utilized for fabricating advanced materials. An example of the application of the colloidal materials is illustrated by the preparation of a thin silicalite-1 film on a non-charged gold substrate. Knowledge of the surface chemistry of the participating interfaces and the properties of the colloidal crystals allows for the preparation of microporous films with a thickness less than 300 nm.
- 著者
- Karsten Wegner Björn Schimmöller Bénédicte Thiebaut Claudio Fernandez Tata N. Rao
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.29, pp.251-265, 2011 (Released:2014-03-29)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 55 73
With the rapid advancement of nanotechnology and with nanoparticles beginning to enter into products, the demand for production-level quantities of advanced nanopowders such as multi-component or coated oxides is rising. Such advanced nanoparticles can be effectively made by flame spray pyrolysis (FSP), and research with laboratory reactors yielded a spectrum of new nanomaterials for catalysis, pigments, ceramics, optics, energy and biomaterials, among others. Here, the transfer of FSP nanopowder synthesis from gram-level lab-scale to pilot reactors with up to 10 metric tons annual production rate is investigated by the example of FSP pilot plants that were realized in industrial-oriented settings. Design considerations for such pilot-scale systems are addressed and guides to production cost estimates are given. Special attention is brought to safe and contained nanoparticle manufacture in order to address the growing awareness of the potential health and environmental effects of nanoparticles.
- 著者
- Rens Kamphorst P. Christian van der Sande Kaiqiao Wu Evert C. Wagner M. Kristen David Gabrie M.H. Meesters J. Ruud van Ommen
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2024007, (Released:2023-06-17)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Vibro-assisted fluidization of cohesive micro-silica has been studied by means of X-ray imaging, pressure drop measurements, and off-line determination of the agglomerate size. Pressure drop and bed height development could be explained by observable phenomena taking place in the bed; slugging, channeling, fluidization or densification. It was observed that channeling is the main cause of poor fluidization of the micro-silica, resulting in poor gas-solid contact and little internal mixing. Improvement in fluidization upon starting the mechanical vibration was achieved by disrupting the channels. Agglomerate sizes were found to not significantly change during experiments.
1 0 0 0 OA NMR as a Tool to Characterize the Aggregation Structure of Silica Nanoparticles in a Liquid
- 著者
- Chika Takai-Yamashita Emiko Sato Masayoshi Fuji
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, pp.233-243, 2020-01-10 (Released:2020-02-29)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 7 15
The NMR-based solvent relaxation technique, a non-invasive tool to characterize the surface of particles, which are dispersed in a liquid, was applied to characterize the nanoparticles’ aggregation structure. The liquid molecules in a dispersion undergo a rapid exchange between the bound states at the interface and highly mobile free states in a bulk liquid. The relaxation time of the liquid molecules bound on the particle surface is shorter than that of the free states liquid. By detecting how much liquid is bound on the particle surface, the wetted specific surface area (SNMR) can be determined. In this study, it was clarified that the water adsorbed at more than a 1.138 layer from the silica surface can be detected by the NMR and the maximum limitation ranged from 2.160 and 3.336 layers. The model aggregates with an artificial solid neck among the particles were mixed with the silica nanoparticle dispersion. Although the determined SNMR was underestimated compared to SBET from gas adsorption, even a low ratio (5 mass%) of the model aggregates in the dispersion can be detected.
- 著者
- George Biskos Vincent Vons Caner U. Yurteri Andreas Schmidt-Ott
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.26, pp.13-35, 2008 (Released:2014-03-29)
- 参考文献数
- 200
- 被引用文献数
- 60 79
Traditionally, the generation of nanoparticles for technological applications has been mostly performed by classical wet chemistry or lithographic methods, and their size has been commonly determined in situ by electron microscopy techniques. Advances in aerosol technology over the past 30 years have provided methods that enable the generation and measurement of nanosize building blocks, and have opened up new opportunities in the assembly of nanostructured materials and nanodevices. This article provides a brief review on state-of-the-art techniques for generating nanoparticles of well-defined size and chemical composition in view of applications in nanotechnology. Covering atomization techniques from the liquid phase and nanoparticle synthesis from the gas phase, we discuss the advantages and limitations of each method. Considering the advantages of on-line methods that aerosols instruments offer, we describe the most efficient techniques for measuring the size distributions of airborne nanosize particles. Finally, we provide a brief discussion on existing and emerging applications of aerosol-based nanotechnology.
- 著者
- Alowasheeir Azhar Jacob Earnshaw Mohamed Barakat Zakaria Ping Cheng Yusuf Valentino Kaneti Md. Shahriar A. Hossain Saad M. Alshehri Tansir Ahamad Yusuke Yamauchi Jongbeom Na
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021015, (Released:2020-08-29)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 2
This work demonstrates the fabrication of a nanoporous iron carbide-iron oxide/reduced graphene oxide (IC-IO/rGO) hybrid via a controlled one-step thermal treatment of Prussian blue (PB)/GO hybrid at 450 °C under N2 flow. The PB/GO hybrid is initially prepared through the in-situ deposition of PB nanoparticles on the GO sheets through electrostatic interactions. The morphological analysis of the hybrid reveals the uniform coverage of the rGO sheets by IC-IO nanoparticles and the even distribution of carbon (C), oxygen (O), and iron (Fe) on the rGO nanosheets. As a result of the hybrid composition and controlled morphology, the surface area of the obtained IC-IO/rGO hybrid (~40 m2/g) is significantly enhanced compared to those of the calcined GO sheets and PB nanoparticles (without GO).
1 0 0 0 OA Polymer-Particle Enhanced Visible Light Range Photocatalytic Activity on Textile Applications
- 著者
- Asena Cerhan Haink G. Bahar Basim
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021011, (Released:2020-07-17)
- 参考文献数
- 31
Extension of photocatalytic activity within the visible light range has an immense importance on the ability of manufacturing self-cleaning textiles that are active indoors. This study focuses on assisting problems, which have delayed the commercialization of the photo-catalytically active textiles by following innovative technological developments in nanotechnology. Polymeric additives are utilized to prepare composite photocatalytic particles with the ability of extending light absorption in the visible light range. Techniques are introduced to avoid the deterioration of the composite particles during their application on textiles in addition to uniform coating strategies to enable an optimized concentration for improved photocatalytic efficiency. It is demonstrated that the titania (TiO2) particles in anatase form extended absorption in the visible light range in the presence of branched titania particles. Correspondingly, an optimized dip coating process is evaluated for textile manufacturing, providing a systematic methodology to enable the production of self-cleaning textiles to be able to manufacture them with commercialization potential.
- 著者
- Joanne Peart
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, pp.34-45, 2001 (Released:2014-05-30)
- 被引用文献数
- 22 46
Powder electrostatics remains an integral and challenging aspect of powder processing. During powder handling operations, such as particle size reduction, mixing and powder transfer processes, particles invariably develop electrostatic charge due to particle-particle and particle-surface interactions. Triboelectrification of powders is a complex phenomenon as most powders are organic crystals and behave as insulators under ambient conditions. However, it is generally accepted that charging occurs as a result of electron transfer between materials of different electrical properties. Factors influencing charging properties include particle size and shape, nature and work function of the contacting surface and the particulate material, area and frequency of contact, surface purity, and atmospheric conditions. Consequences of charge generation upon particle dynamics and powder behavior are often unpredictable. The standard method for measurement of electrostatic charge is the Faraday pail or well, with various application-specific modifications. Electrostatics, regarded by many as a nuisance and hazard, plays an important and ever emerging role in many industrial applications, including powder coating, xerography, and pharmaceutical processing.
- 著者
- Konrat Kerdnawee Chompoopitch Termvidchakorn Pacharaporn Yaisanga Jirapat Pakchamsai Cheewapon Chookiat Apiluck Eiad-ua Winadda Wongwiriyapan Weerawut Chaiwat Sakhon Ratchahat Kajornsak Faungnawakij Komkrit Suttiponparnit Tawatchai Charinpanitkul
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, pp.24-43, 2017 (Released:2017-02-28)
- 参考文献数
- 100
- 被引用文献数
- 4 16
An increase in global consumption has led to an exponential increase in industrial production activities which inevitably results in overwhelming remain of industrial waste. Consequently it has driven increasing attentions of research and development teams in various countries to propose and investigate novel methodologies to utilize such industrial waste. Instead of using as alternative energy sources, usage of industrial waste for production of carbonaceous nanomaterials has been examined via various routes, such as catalytic pyrolysis, hydrothermal treatment and so on. Meanwhile, for sustainable and secure continuity of the carbonaceous nanomaterial production, broad spectra of promising applications have also been examined. Among those emerging applications, utilization of carbonaceous nanomaterials in pollution control and prevention has been focused worldwide. Therefore, in this review, relevant research works focusing on catalytic pyrolysis of carbonaceous industrial waste for carbonaceous nanomaterial production were comprehensively analyzed and summarized. In addition, promising applications involving with antibiotic removal, spilled oil handling and pollutant gas detection were also reviewed.
- 著者
- Ferry Iskandar Erlandy Dwinanto Mikrajuddin Abdullah Khairurrijal Oki Muraza
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.33, pp.3-16, 2016 (Released:2016-02-28)
- 参考文献数
- 82
- 被引用文献数
- 5 34
Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) in the last several years has become an important factor in oil production due to the shortfall in high quality crude oil. Heavy oil as one of the unconventional hydrocarbons is still vastly abundant in nature and is hence frequently explored with EOR. The viscous characteristic of heavy oil necessitates further in-situ upgrading processes to be executed before extraction. An interesting upgrading method is through aquathermolysis under the addition of catalyst. This review focuses on presenting nanoparticle catalysts, such as nickel-, iron- and cobalt-based nanocatalyst. The explanation covers topics from synthesis methods and characterization up to the effect of reducing the viscosity of heavy oil. Lastly, concluding remarks and future perspectives are highlighted regarding the visibility and available approaches of developing nanofluids for EOR.
- 著者
- Agam R. Sheth David J.W. Grant
- 出版者
- Hosokawa Powder Technology Foundation
- 雑誌
- KONA Powder and Particle Journal (ISSN:02884534)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.23, pp.36-48, 2005 (Released:2014-03-29)
- 参考文献数
- 165
- 被引用文献数
- 18 37
The majority of drug products are solid dosage forms, most of which contain the drug substance in the crystalline state. This review considers the forces responsible for crystal packing, the various types of pharmaceutical crystals, and the methods used to determine the structure of pharmaceutical crystals. These topics provide background for the main thrust, which focuses on the importance of studying the structure of pharmaceutical crystals with particular stress on phase changes of crystal forms of drugs during pharmaceutical processing and implications of different solid forms of drugs on its mechanical properties. The present review does not consider pharmaceutical co-crystals, which could be the subject of another review.