- 著者
- Natsumi MARUYAMA Isuzu FUKUNAGA Tomoaki KOGO Tsutomu ENDO Wataru FUJII Masami KANAI-AZUMA Kunihiko NAITO Koji SUGIURA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2023-021, (Released:2023-11-06)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Senescent cells play a detrimental role in age-associated pathogenesis by producing factors involved in senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). The present study was conducted to examine the possibility that senescent cells are present in aged ovaries and, if so, to determine the tissue region where senescent cells accumulate using a mouse model. Female mice at 2–4 and 8–10 months were used as reproductively young and aged models, respectively; the latter included mice with and without reproductive experience. Cells positive for senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-Gal) staining, one of the markers of cellular senescence, were detected in the stromal region of aged, but not young, ovaries regardless of reproductive experience. Likewise, the localization of cells expressing CDKN2A (cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A), another senescence marker, in the stromal region of aged ovaries was detected with immunohistochemistry. CDKN2A expression detected by western blotting was significantly higher in the ovaries of aged mice with reproductive experience than in those without the experience. Moreover, cells positive for both γH2AX (a senescence marker) and fluorescent SA-β-Gal staining were present in those isolated from aged ovaries. In addition, the transcript levels of several SASP factors were significantly increased in aged ovaries. These results suggest that senescent cells accumulate in the ovarian stroma and may affect ovarian function in aged mice. Additionally, reproductive experience may promote accumulation.
- 著者
- Koki YAMADA Mayuko NAGAE Tetsuya MANO Hitomi TSUCHIDA Safiullah HAZIM Teppei GOTO Makoto SANBO Masumi HIRABAYASHI Naoko INOUE Yoshihisa UENOYAMA Hiroko TSUKAMURA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2023-019, (Released:2023-07-28)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Hypothalamic kisspeptin neurons are master regulators of mammalian reproduction via direct stimulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone and consequent gonadotropin release. Here, we generated novel Kiss1 (kisspeptin gene)-Cre rats and investigated the developmental changes and sex differences in visualized Kiss1 neurons of Kiss1-Cre-activated tdTomato reporter rats. First, we validated Kiss1-Cre rats by generating Kiss1-expressing cell-specific Kiss1 knockout (Kiss1-KpKO) rats, which were obtained by crossing the current Kiss1-Cre rats with Kiss1-floxed rats. The resulting male Kiss1-KpKO rats lacked Kiss1 expression in the brain and exhibited hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, similar to the hypogonadal phenotype of global Kiss1 KO rats. Histological analysis of Kiss1 neurons in Kiss1-Cre-activated tdTomato reporter rats revealed that tdTomato signals in the anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV) and arcuate nucleus (ARC) were not affected by estrogen, and that tdTomato signals in the ARC, AVPV, and medial amygdala (MeA) were sexually dimorphic. Notably, neonatal AVPV tdTomato signals were detected only in males, but a larger number of tdTomato-expressing cells were detected in the AVPV and ARC, and a smaller number of cells in the MeA was detected in females than in males at postpuberty. These findings suggest that Kiss1-visualized rats can be used to examine the effect of estrogen feedback mechanisms on Kiss1 expression in the AVPV and ARC. Moreover, the Kiss1-Cre and Kiss1-visualized rats could be valuable tools for further detailed analyses of sexual differentiation in the brain and the physiological role of kisspeptin neurons across the brain in rats.
- 著者
- Shuichi CHIBA Masatoshi SUZUKI Keitaro YAMANOUCHI Masugi NISHIHARA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.2, pp.297-307, 2007 (Released:2007-05-12)
- 参考文献数
- 54
- 被引用文献数
- 43 54
Recent studies have demonstrated the presence of neurogenesis in the adult mammalian hippocampus, and it has been suggested that estrogen and various growth factors influence the processes of adult neurogenesis. The present study assessed cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus and the mRNA expression levels of granulin, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus 4 h after treatment with estradiol benzoate (EB) in 3- and 12-month old ovariectomized rats. At 3 months of age, mRNA expression of granulin precursor and cell proliferation were increased by EB treatment, although the mRNA expressions of IGF-I and BDNF remained unchanged. At 12 months of age, however, neither mRNA expression of the three genes nor cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus were affected by EB treatment. In addition, 17β-estradiol enhanced the proliferation of neural progenitor cells derived from hippocampal tissue of 3-month-old female rats in vitro; this was inhibited by neutralization of granulin with specific antibody. These results suggest that estrogen induces granulin gene expression in the hippocampus and that the product of this gene is involved in the mitogenic effects of estrogen in the dentate gyrus, although the responses to estrogen decline with age.
- 著者
- Pramod DHAKAL Akiko HIRAMA Yasuo NAMBO Takehiro HARADA Fumio SATO Kentaro NAGAOKA Gen WATANABE Kazuyoshi TAYA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.58, no.5, pp.522-530, 2012 (Released:2012-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 21 17
The present study was conducted to elucidate the profile of circulating gonadotropins and gonadal hormones from birth to puberty and relationship between gonadal seasonality and hormonal secretion in both sexes of Thoroughbred horses. Spring-born colts (n=6) and fillies (n=9) were blood sampled weekly from jugular vein from birth to 60 weeks of age. Circulating FSH, LH, prolactin, testosterone, progesterone, estradiol-17β, and immunoreactive (ir)-inhibin were measured by radioimmunoassay. In both sexes, the steroid hormones levels were remarkably high at birth, rapidly dropped within a week and remained at the lower levels until the start of second spring after birth. Ir-inhibin was also high during the birth, remaining lowest during winter and again increasing towards the second summer. There was an increase in FSH concentration in foals during the first summer months after birth and in the next summer, the FSH concentration along with that of LH increased significantly. The seasonal increase in circulating prolactin was remarkable even in the first year, and no differences were noted between the two summers. These results clearly demonstrated that the hypothalamo-pituitary axis is already responsive to changes in photoperiod and secrete prolactin similar to adult horses, but pituitary gonadotrophs for FSH and LH secretion is less sensitive. When the values of these hormones in the second breeding season after birth were compared with adult values of the respective sex in the breeding season, no significant differences were observed, indicating that spring-born fillies and colts have already attained the stage of puberty at the second breeding season after birth.
- 著者
- Kumiko TAKEDA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.65, no.6, pp.485-489, 2019 (Released:2019-12-18)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 7 12
Animal cloning technology has been developed to produce progenies genetically identical to a given donor cell. However, in nuclear transfer protocols, the recipient oocytes contribute a heritable mitochondrial genomic (mtDNA) background to the progeny. Additionally, a small amount of donor cell-derived mitochondria accompanies the transferred nucleus in the process; hence, the mtDNAs of two origins are mixed in the cytoplasm (heteroplasmy) of the reconstituted oocyte. Herein, I would like to introduce some of our previous results concerning five key considerations associated with animal cloning, including: mtDNA heteroplasmy in somatic cell nuclear transferred (SCNT) animals, the variation in the transmission of mtDNA heteroplasmy to subsequent generations SCNT cows and pigs, the influence of mtDNA sequence differences on mitochondrial proteins in SCNT cows and pigs, the effects of the introduction of mitochondria derived from somatic cells into recipient oocytes on embryonic development, and alterations of mtDNA heteroplasmy in inter/intraspecies nuclear transfer embryos.
- 著者
- Yui WAKE Christopher A. VAKULSKAS Steve E. GLENN Takehito KANEKO
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-067, (Released:2022-07-14)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Genetically engineered animals can be produced quickly using genome editing technology. A new electroporation technique, technique for animal knockout system by electroporation (TAKE), aids in the production of genome-edited animals by introducing nucleases into intact embryos using electroporation instead of microinjection. It is difficult to confirm nuclease delivery into embryos after electroporation using the conventional TAKE method. We previously reported the successful visualization of fluorescently-labeled tracrRNA in embryos after electroporation Cas9 paired with the crRNA:tracrRNA-ATTO550 duplex. However, the amount of fluorescence signal from labeled tracrRNA in embryos did not correlate with the genome editing rate of the offspring. This study examined the visualization of Cas9 protein in embryos after electroporation and its correlation with the genome editing rate of the offspring using a fluorescent Cas9 fusion protein. The fluorescent Cas9 protein was observed in all embryos that survived following electroporation. We found that the efficiency of Cas9 protein delivery into embryos via electroporation depended on the pulse length. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the amount of fluorescent Cas9 protein detected in the embryos correlated with the genome editing efficiency of the embryos. These data indicate that the TAKE method using fluorescently-labeled nucleases can be used to optimize the delivery conditions and verify nuclease delivery into individual embryos prior to embryo transfer for the efficient production of genome-edited animals.
- 著者
- Arisa SUGIMOTO Hitomi TSUCHIDA Mayuko NAGAE Naoko INOUE Yoshihisa UENOYAMA Hiroko TSUKAMURA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.3, pp.190-197, 2022 (Released:2022-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Reproductive function is suppressed during lactation owing to the suckling-induced suppression of the kisspeptin gene (Kiss1) expression in the arcuate nucleus (ARC) and subsequent suppression of luteinizing hormone (LH) release. Our previous study revealed that somatostatin (SST) neurons mediate suckling-induced suppression of LH release via SST receptor 2 (SSTR2) in ovariectomized lactating rats during early lactation. This study examined whether central SST-SSTR2 signaling mediates the inhibition of ARC Kiss1 expression and LH release in lactating rats during late lactation and whether the inhibition of glutamatergic neurons, stimulators of LH release, is involved in the suppression of LH release mediated by central SST-SSTR2 signaling in lactating rats. A central injection of the SSTR2 antagonist CYN154806 (CYN) significantly increased ARC Kiss1 expression in lactating rats on day 16 of lactation. Dual in situ hybridization revealed that few ARC Kiss1-positive cells co-expressed Sstr2, and some of the ARC Slc17a6 (a glutamatergic neuronal marker)-positive cells co-expressed Sstr2. Furthermore, almost all ARC Kiss1-positive cells co-expressed Grin1, a subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. The numbers of Slc17a6/Sstr2 double-labeled and Slc17a6 single-labeled cells were significantly lower in lactating dams than in non-lactating rats whose pups had been removed after parturition. A central injection of an NMDA antagonist reversed the CYN-induced increase in LH release in lactating rats. Overall, these results suggest that central SST-SSTR2 signaling, at least partly, mediates the suppression of ARC Kiss1 expression and LH release by inhibiting ARC glutamatergic interneurons in lactating rats.
- 著者
- Kazuo YAMAGATA Rinako SUETSUGU Teruhiko WAKAYAMA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.3, pp.343-350, 2009 (Released:2009-07-02)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 58 75
Mammalian preimplantation embryonic development is achieved by tightly coordinated regulation of a great variety of temporal and spatial changes. Therefore, it would be valuable to analyze these events three-dimensionally and dynamically. We have previously developed a live-cell imaging method based on the expression of fluorescent proteins, using mRNA injection and time-lapse florescence microscopy. However, with conventional fluorescent microscopy, three-dimensional images could not be obtained due to the thickness of the embryos and the optical problem in which `out-of focus blur' cannot be eliminated. Moreover, as the repeated exposure of intense excitation light to the cell yields phototoxicity, long-term observation was detrimental to embryonic development. Here, we improved our imaging system to enable six-dimensional live-cell imaging of mouse preimplantation embryos (x, y and z axes, time-lapse, multicolor and multisample). Importantly, by improving the imaging devices and optimizing the conditions for imaging, such as intensity of excitation and time intervals for image acquisition, the procedure itself was not detrimental to full-term development, although it is a prolonged imaging process. For example, live pups were obtained from embryos to which two different wavelengths of excitation (488 and 561 nm) were applied at 7.5-min intervals for about 70 h, and 51 images were acquired in the z axis at each time point; thus, a total of 56,814 fluorescent images were taken. All the pups were healthy, reproductively normal and not transgenic. Thus, this live-cell imaging technology is safe for full-term mouse development. This offers a novel approach for developmental and reproductive research in that it enables both retrospective and prospective analyses of development. It might also be applicable to assessment of embryo quality in fields such as human reproductive technology and production animal research.
- 著者
- Fernando LÓPEZ-GATIUS
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.2, pp.135-139, 2021 (Released:2021-04-21)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Since the 1970s, luteolytic doses used for synchronizing estrus in dairy cattle have remained unchanged. This study aimed to evaluate the dose-response effect of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α), which is used for synchronizing estrus, and subsequent fertility in cows with two or more corpora lutea (CL). The study population consisted of 1,683 cows with a single CL (1CL), 501 cows with multiple CL receiving a single dose of PGF2α (2CL1), and 252 cows with multiple CL receiving a 1.5 × PGF2α dose (2CL1.5). Cows with a single CL (n = 1,245) showed estrus significantly (P < 0.01) earlier (3.01 ± 1.23 days; mean ± SD) than cows with multiple CL (n = 287; 3.33 ± 1.69 days). Using 1CL cows as reference, the odds ratio (OR) for the estrus response in 2CL1 cows was 0.13 (P < 0.0001), whereas the ORs for estrus response and pregnancy of 2CL1.5 cows were 1.8 (P = 0.0001) and 1.7 (P = 0.001), respectively. Based on the results for only the 2CL1 cows, the OR for the estrus response was 0.7 (P = 0.01) for cows producing ≥ 45 kg of milk at treatment, compared to the remaining cows producing < 45 kg of milk. Our results showed that the presence of multiple CL reduced the estrus response to that induced by a single PGF2α dose and milk production was inversely associated with this response, whereas an increased PGF2α dose improved the estrus response. Therefore, an increase in the standard PGF2α dose is recommended.
1 0 0 0 OA Possible causes and treatment strategies for the estrus and ovulation disorders in dairy cows
- 著者
- Natsumi ENDO
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-125, (Released:2022-02-12)
- 被引用文献数
- 5
The reproductive performance of dairy cows has declined, along with an increase in their milk yield. First-service conception rates in lactating dairy cows are often lower than 50%. The precise detection of estrus is an important factor in the reproductive management of dairy cows for successful fertilization and pregnancy. However, estrus expression has been decreasing in modern dairy cows, affecting the detection rate of estrus. In addition to estrus, a high incidence of ovulation disorders affects the fertility of dairy cows. To address these problems, it is necessary to understand the changes in the endocrine functions that underlie estrus and ovulation disorders, and to develop effective treatment strategies. Recent studies have revealed that neurokinin B and neurokinin 3 receptor signaling play important roles in the regulation of the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing and luteinizing hormones, suggesting a potential clinical avenue for the stimulation of gonadal function. In this review, I have discussed the problems in estrus and ovulation disorders in modern dairy cows as well as the possible applications of neurokinin 3 receptor agonists in the treatment of these disorders.
- 著者
- Yoshiki HIRATA Yusuke KATSUKURA Yuka HENMI Ren OZAWA Sayaka SHIMAZAKI Akira KUROSAWA Yasushi TORII Hironori TAKAHASHI Hisataka IWATA Takehito KUWAYAMA Koumei SHIRASUNA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.4, pp.257-264, 2021 (Released:2021-08-27)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 9
Advanced maternal age is a risk factor for female infertility, and placental dysfunction is considered one of the causes of pregnancy complications. We investigated the effects of advanced maternal aging on pregnancy outcomes and placental senescence. Female pregnant mice were separated into three groups: young (3 months old), middle (8–9 months old), and aged (11–13 months old). Although the body weights of young and middle dams gradually increased during pregnancy, the body weight of aged dams only increased slightly. The placental weight and resorption rate were significantly higher, and live fetal weights were reduced in a maternal age-dependent manner. Although mRNA expression of senescence regulatory factors (p16 and p21) increased in the spleen of aged dams, mRNA expression of p16 did not change and that of p21 was reduced in the placenta of aged dams. Using a cytokine array of proteins extracted from placental tissues, the expression of various types of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) factors was decreased in aged dams compared with young and middle dams. The aged maternal placenta showed reduced immune cell accumulation compared with the young placenta. Our present results suggest that models using pregnant mice older than 8 months are more suitable for verifying older human pregnancies. These findings suggest that general cellular senescence programs may not be included in the placenta and that placental functions, including SASP production and immune cell accumulation, gradually decrease in a maternal age-dependent manner, resulting in a higher rate of pregnancy complications.
- 著者
- Takumi YOSHIDA Md Emtiaj ALAM Keisuke HANAFUSA Yasunori TSUJIMOTO Masaya TSUKAMOTO Ryoji KANEGI Toshio INABA Kikuya SUGIURA Shingo HATOYA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-084, (Released:2022-01-07)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
We examined the effectiveness of saline, Euro-Collins solution (EC), and ET-Kyoto solution (ET-K) as preservation media for the cold storage of feline ovaries. Ovaries were maintained in these media at 4°C for 24, 48, or 72 h until oocyte retrieval. The ET-K group exhibited a higher oocyte maturation rate than the saline group after 72 h of storage. Moreover, ET-K could sustain the competence of the feline oocytes to cleave after 48 h, and the morula formation rate of the ET-K group was higher than that of the other groups after 24 and 48 h. Furthermore, the ET-K group exhibited a higher blastocyst formation rate than the other groups after storage for 24 h, and only ET-K retained the developmental competence in blastocysts after 48 h of storage. In addition, regarding the cell numbers of the blastocysts, there was no significant difference among the tested groups. In conclusion, our results indicate that ET-K is a suitable preservation medium for feline ovaries.
- 著者
- Fernando LÓPEZ-GATIUS
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-119, (Released:2021-12-30)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) and its analogs are used to induce luteolysis in estrus synchronization programs to terminate unwanted pregnancies or to promote ovulation in certain cow subpopulations. In the past few decades, the luteolytic dose of PGF2α has remained unchanged. This review explores the clinical implications of increasing the standard dose for these applications in high-producing dairy cows. Ultrasonography may assist in selecting the most appropriate PGF2α dose and improve the results. A reference has been used for PGF2α for promoting ovulation in herds showing poor reproductive performance.
1 0 0 0 OA Metabolic pathways regulating the development and non-genomic heritable traits of germ cells
- 著者
- Yasuhisa MATSUI Yohei HAYASHI
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-137, (Released:2021-12-25)
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Metabolism is an important cellular process necessary not only for producing energy and building blocks for cells, but also for regulating various cell functions, including intracellular signaling, epigenomic effects, and transcription. The regulatory roles of metabolism have been extensively studied in somatic cells, including stem cells and cancer cells, but data regarding germ cells are limited. Because germ cells produce individuals of subsequent generations, understanding the role of metabolism and its regulatory functions in germ cells is important. Although limited information concerning the specific role of metabolism in germ cells is available, recent advances in related research have revealed specific metabolic states of undifferentiated germ cells in embryos as well as in germ cells undergoing oogenesis and spermatogenesis. Studies have also elucidated the functions of some metabolic pathways associated with germ cell development and the non-genomic heritable machinery of germ cells. In this review, we summarized all the available knowledge on the characteristic metabolic pathways in germ cells, focusing on their regulatory functions, while discussing the issues that need to be addressed to enhance the understanding of germ cell metabolism.
1 0 0 0 OA Assisted reproductive techniques for canines: preservation of genetic material in domestic dogs
- 著者
- Hiroshi SUZUKI Hiroyuki WATANABE Yasuyuki ABE
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-111, (Released:2021-11-29)
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Assisted reproductive techniques (ARTs), such as artificial insemination, in vitro fertilization, and cryopreservation of gametes/zygotes, have been developed to improve breeding and reproduction of livestock and for the treatment of human infertility. Their widespread use has contributed to improvements in human health and welfare. However, in dogs, only artificial insemination using frozen semen is readily available as an ART to improve breeding and control genetic diversity. A recent priority in sperm cryopreservation is the development of alternatives to egg yolk, which is widely used as a component of the sperm extender. Egg yolk can vary in composition among batches and is prone to contamination by animal pathogens. The latter can be a problem for international exchange of cryopreserved semen. Low-density lipoprotein and skim milk are promising candidates for use as extenders, to ensure fertility after artificial insemination. Although not tested for its effects on fertility following artificial insemination, polyvinyl alcohol may also be a useful alternative to egg yolk as an extender. The development of cryopreservation techniques for canine embryos lags behind that for other mammals, including humans. However, given the success of non-surgical embryo transfer in 2011, studies have sought to refine this approach for practical use. Research on sperm cryopreservation has yielded satisfactory results. However, investigation of other approaches, such as cryopreservation of oocytes and gonadal tissues, remains insufficient. Techniques for the efficient induction of estrus may aid in the development of successful canine ARTs.
- 著者
- Ryosuke SAKUMOTO Ken-Go HAYASHI Kosuke IGA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-107, (Released:2021-11-20)
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effects of continuous administration of linoleic acid or linolenic acid into the intra-uterine horn, ipsilateral to the corpus luteum, on the duration of the estrous cycle and plasma progesterone (P4) concentration. The effects of linoleic and linolenic acids on bovine uterine and luteal functions were also studied using a tissue culture system. Intra-uterine administration of linoleic or linolenic acid (5 mg/10 ml of each per day) in cows, between days 12 and 21, resulted in a prolonged estrous cycle compared to the average duration of the last one to three estrous cycles before administration in each group (P < 0.05). Moreover, plasma P4 concentration in cows treated with linoleic or linolenic acid was high between days 19 and 21 (linoleic acid), or on day 20 (linolenic acid), compared to that of the control cows (saline administration; P < 0.05 or lower). Both linoleic (500 µg/ml) and linolenic (5 and 500 µg/ml) acids stimulated prostaglandin (PG) E2 but inhibited PGF2α production by cultured endometrial tissue (P < 0.01), while P4 production by cultured luteal tissue was not affected. These findings suggest that both linoleic and linolenic acids support luteal P4 production by regulating endometrial PG production and, subsequently, prolonging the duration of the estrous cycle in cows.
- 著者
- Tomoko ITAHASHI Toshinori OIKAWA Takashi NUMABE
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-070, (Released:2021-11-05)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
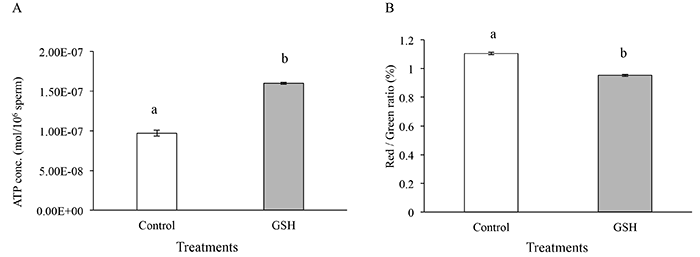
This study was conducted to examine the effects of adding glutathione (1 mM) to media used for sperm washing and in vitro fertilization (IVF) on the improvement of early development of embryos produced using cryopreserved spermatozoa of the less IVF-competent bull (the one considered unqualified as spermatozoa supplier for the production of bovine blastocysts using IVF). The cryopreserved spermatozoa of this bull were characterized by normal motility and lower ATP content and blastocyst productivity than those of IVF-competent bulls. The addition of glutathione to the sperm washing medium was more effective in improving the productivity of blastocysts and ATP content than the addition of glutathione to the IVF medium or no glutathione addition at all (control). These results suggest that this simple method may be used to improve the potential of cryopreserved spermatozoa of less IVF-competent bulls to fertilize oocytes in vitro and to induce normal embryonic development after fertilization.
- 著者
- Ryo INABA Ryouka KAWAHARA-MIKI Akihisa SHINOZAWA Taichi YASUHARA Takashi FUJII Keisuke KOYAMA Michiko MURATA-OKUBO Kousaku SOUMA Hiroki HIRAYAMA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-094, (Released:2021-10-31)
Although hormonal induction of parturition in cattle results in the successful delivery of healthy calves, the risk of retained fetal membrane is significantly increased. In a previous study, a combination of the long-acting glucocorticoid, triamcinolone acetonide, with a high dose of betamethasone partially normalized the placentomal gene expression during parturition; however, the incidence of retained fetal membrane remained high. This study further explored placentomal dysfunction and aimed to elucidate the mechanism of retained fetal membrane in parturition-induced cows. In this study, transcriptome analysis revealed that enhanced glucocorticoid exposure normalized the expression of a substantial fraction of genes in the cotyledons. In contrast, a significant reduction in the multiple signaling pathway activities, including interferon signaling, was found in the caruncles during induced parturition. Real-time PCR showed that the expression of interferon-tau in the caruncles, but not interferon-alpha or interferon-gamma, was significantly lower in induced parturition than spontaneous parturition. Interferon-stimulated gene expression was also significantly decreased in the caruncles during induced parturition. These results indicate that interferon signaling could be important for immunological control in placentomes during parturition. Additionally, this suggests that interferon-tau might be a pivotal ligand for interferon receptors in the caruncles. This study revealed that peripheral blood leukocytes in prepartum cows transcribed interferon-tau. Macrophage infiltration in the placentome is known to participate in the detachment of the fetal membrane from the caruncle. Thus, this study raised the possibility that immune cells migrating into the caruncles at parturition may act as a source of ligands that activate interferon signaling.
- 著者
- Yue SU Qianru LI Qiaochu ZHANG Zhiming LI Xinxin YAO Yong GUO Longfei XIAO Xiangguo WANG Hemin NI
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-077, (Released:2021-10-22)
- 被引用文献数
- 11
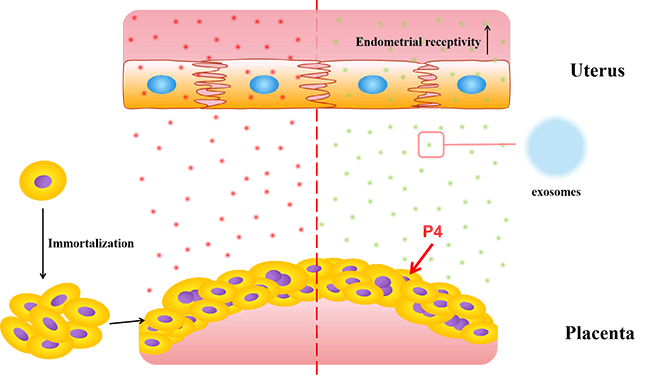
Inadequate fetomaternal interactions could directly lead to pregnancy failure in dairy cows. Exosomes are widely involved in endometrial matrix remodeling, immune function changes, placental development, and other processes of embryo implantation and pregnancy in dairy cows. However, the role of exosomes derived from placental trophoblast cells in regulating the receptivity of endometrial cells and facilitating fetomaternal interaction remains unclear. In this study, bovine trophoblast cells (BTCs) were obtained from bovine placenta and immortalized by transfection with telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT). Immortalized BTCs still possess the basic and key properties of primary BTCs without exhibiting any neoplastic transformation signs. Subsequently, the effect of trophoblast-derived exosomes (TDEs) on endometrial receptivity in endometrial epithelial cells (EECs) was determined, and the mechanism whereby TDEs and their proteins participate in the fetomaternal interaction during bovine pregnancy were explored. EECs were co-cultured with the exosomes derived from BTCs treated with progesterone (P4). Such treatment enhanced the expression of the endometrial receptivity factors, integrin αv, β3, Wnt7a, and MUC1 by changing the extracellular environment, metabolism, and redox balance in EECs via proteome alignment, compared with no treatment according to the DIA quantitation analysis. Our study demonstrated that trophoblast-derived exosome proteins are one of the most critical elements in fetomaternal interaction, and their changes may act as a key signal in altering endometrial receptivity and provide a potential target for improving fertility.
- 著者
- David MARTÍN-HIDALGO Beatriz MACÍAS-GARCÍA Lauro GONZÁLEZ-FERNÁNDEZ
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-075, (Released:2021-10-24)
- 被引用文献数
- 6
We aimed to analyze the influence of different cellular concentrations of boar sperm suspensions on the induction of capacitation and acrosome reaction. When spermatozoa were incubated at 100 or 200 mill/ml, significant increases in protein tyrosine phosphorylation in the p32 protein were observed, compared to those at 50 mill/ml. In addition, sperm concentration-dependent increases were observed in plasma membrane lipid disorganization (50 mill/ml vs. 200 mill/ml), induction of the acrosome reaction (50 mill/ml vs. 100 mill/ml and 200 mill/ml), and sperm viability (50 mill/ml vs. 100 mill/ml and 200 mill/ml). Our data indicate that an increase in sperm concentration stimulates the induction of capacitation and acrosome reaction in boars.