1 0 0 0 OA A5052-H14およびA2017-T4アルミニウム合金の疲労特性に及ぼす表面処理の影響
- 著者
- 城戸 竜太 桑野 亮一 日野 実 村山 敬祐 黒坂 成吾 小田 幸典 堀川 敬太郎 金谷 輝人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本金属学会
- 雑誌
- 日本金属学会誌 (ISSN:00214876)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.84, no.3, pp.74-79, 2020-03-01 (Released:2020-02-25)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
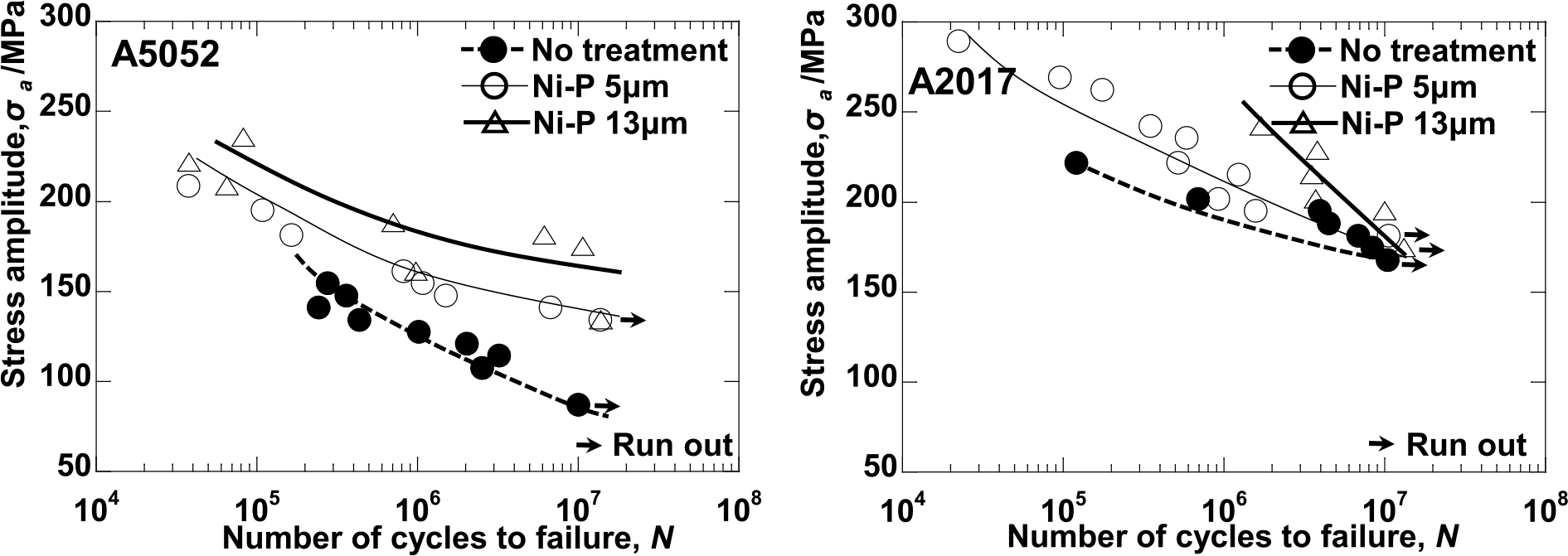
In this study, the effect of anodization and electroless Ni-P plating on the fatigue strength of commercial A5052-H14 and A2017-T4 aluminum alloys was investigated. The coated aluminum alloys were tested using a rotary bending fatigue testing machine. Anodization led to a slight increase in the fatigue strength of the A2017-T4 alloy of approximately 10% because of the suppression of the generation of fatigue crack, and anodization with a 5-µm thickness for A5052-H14 also led to a slight increase in the fatigue strength. However, anodization with a 20-µm thickness for A5052-H14 led to reduced fatigue strength because of the pits that formed in the film. In addition, electroless Ni-P plating drastically improved the fatigue strength of the A5052-H14 alloy by suppressing the generation of fatigue crack.It also improved the fatigue strength of the A2017-T4 alloy in the high-stress region. However, the fatigue strength in the low-stress region was the same as that of the non-coated specimens.This fatigue strength should have originated from the hydrogen embrittlement by the hydrogen introduced into the specimen during the plating.