6 0 0 0 OA Dosing Optimization of Ampicillin-Sulbactam Based on Cystatin C in Elderly Patients with Pneumonia
- 著者
- Kayoko Matsubara Kazuaki Matsumoto Yuta Yokoyama Erika Watanabe Yuki Enoki Akari Shigemi Kazuro Ikawa Hideyuki Terazono Norifumi Morikawa Tamao Ohshige Yasuo Takeda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.5, pp.732-736, 2021-05-01 (Released:2021-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 3
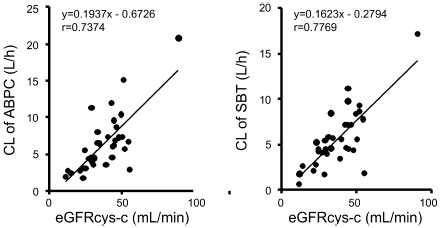
Ampicillin-sulbactam is a first-line therapy for pneumonia and is mainly excreted by the kidney. It is important to optimize the dose and dosing interval of ampicillin-sulbactam because in patients with decreased renal function and low skeletal muscle mass, such as the elderly, excess drug may burden renal function. In this study, we evaluated indices of renal function and optimized the dose and dosing interval of ampicillin-sulbactam based on pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics theory in elderly patients. The serum concentrations of ampicillin and sulbactam were measured by HPLC, and PK parameters were calculated. Correlations between the clearance of ampicillin or sulbactam and renal function were evaluated, and dosing optimization was calculated based on PK parameters. The PK parameters of ampicillin were CL = 6.5 ± 4.0 L/h, Vd = 19.3 ± 0.2 L, Ke = 0.4 ± 0.2, and t1/2 = 2.7 ± 1.6 h. The most correlated renal function index was estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFRcys-c) calculated by serum cystatin-c (r = 0.7374, correlation formula; CL of ampicillin = 0.1937 × eGFRcys-c−0.6726). Based on this formula, we calculated the clearance of ampicillin and developed dosing regimens for the elderly. Serum cystatin-c concentration is an ideal index to optimize ampicillin-sulbactam antimicrobial therapy in elderly patients with pneumonia.
- 著者
- Kazuaki Matsumoto Akari Shigemi Kazuro Ikawa Naoko Kanazawa Yuko Fujisaki Norifumi Morikawa Yasuo Takeda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.2, pp.235-238, 2015-02-01 (Released:2015-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 5 22
Ganciclovir is a nucleoside guanosine analogue that exhibits therapeutic activity against human cytomegalovirus infection, and is primarily excreted via glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion. The adverse effects induced by ganciclovir therapy are generally of a hematological nature and include thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. Low marrow cellularity and elevated serum creatinine have been identified as risk factors for ganciclovir-induced neutropenia. However, the risk factors for thrombocytopenia have yet to be determined. Therefore, this study investigated patients administered ganciclovir to determine the risk factors for thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. Thrombocytopenia occurred in 41 of these patients (30.6%). Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified three independent risk factors for thrombocytopenia: cancer chemotherapy (odds ratio (OR)=3.1), creatinine clearance (<20 mL/min) (OR=12.8), and the ganciclovir dose (≥12 mg/kg/d) (OR=15.1). Leukopenia occurred in 36 patients (28.6%), and white blood cell count (<6000 cells/mm3) (OR=3.7) and the ganciclovir dose (≥12 mg/kg/d) (OR=7.8) were identified as risk factors. These results demonstrated that several factors influenced the occurrence of ganciclovir-induced thrombocytopenia and leukopenia, and suggest that special attention should be paid to patients receiving cancer chemotherapy with a low creatinine clearance (<20 mL/min) and high dose (≥12 mg/kg/d) in order to avoid ganciclovir-induced thrombocytopenia.