1 0 0 0 OA iMusta4SLC: Database for the structural property and variations of solute carrier transporters
- 著者
- Akiko Higuchi Naoki Nonaka Kei Yura
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, pp.94-103, 2018 (Released:2018-04-27)
- 参考文献数
- 50
- 被引用文献数
- 7
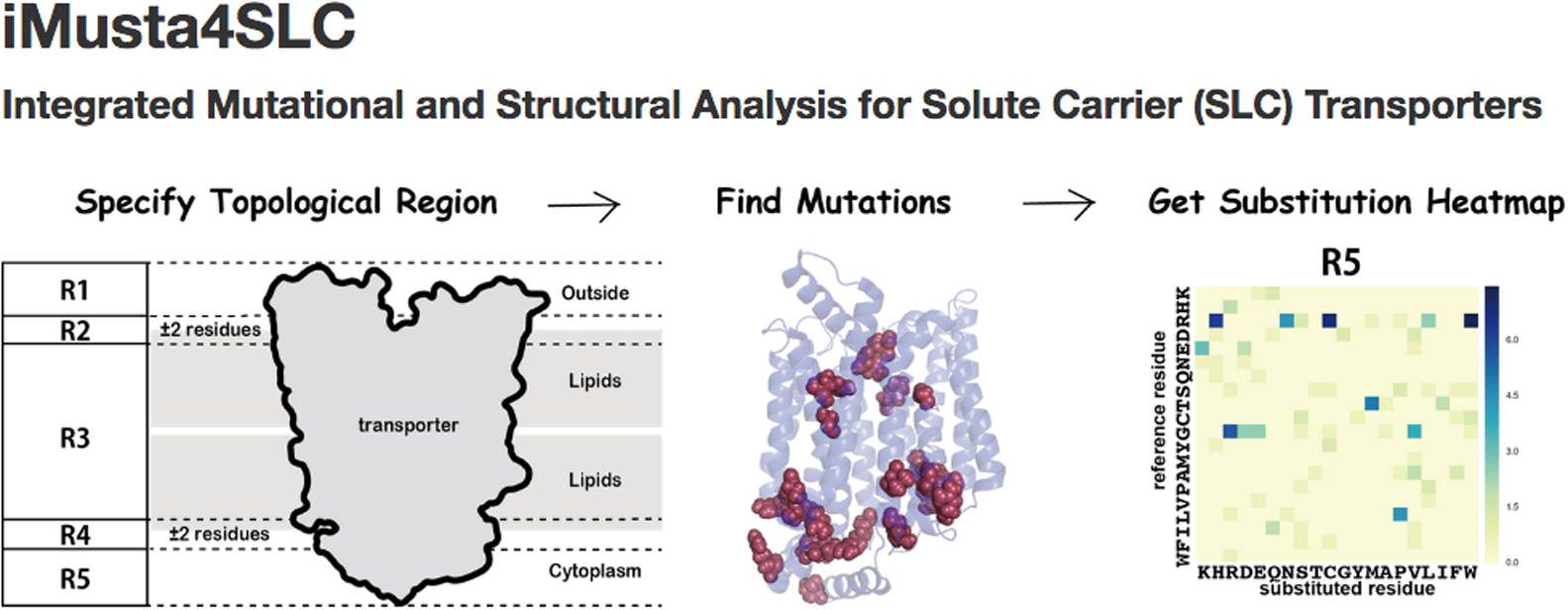
Membrane transporter proteins play important roles in transport of nutrients into the cell, in transport of waste out of the cell, in maintenance of homeostasis, and in signal transduction. Solute carrier (SLC) transporter is the superfamily, which has the largest number of genes (>400 in humans) in membrane transporter and consists of 52 families. SLC transporters carry a wide variety of substrates such as amino acids, peptides, saccharides, ions, neurotransmitters, lipids, hormones and related materials. Despite the apparent importance for the substrate transport, the information of sequence variation and three-dimensional structures have not been integrated to the level of providing new knowledge on the relationship to, for instance, diseases. We, therefore, built a new database named iMusta4SLC, which is available at http://cib.cf.ocha.ac.jp/slc/, that connected the data of structural properties and of pathogenic mutations on human SLC transporters. iMusta4SLC helps to investigate the structural features of pathogenic mutations on SLC transporters. With this database, we found that the mutations at the conserved arginine were frequently involved in diseases, and were located at a border between the membrane and the cytoplasm. Especially in SLC families 2 and 22, the conserved residues formed a large cluster at the border. In SLC2A1, one third of the reported pathogenic missense mutations were found in this conserved cluster.