- 著者
- Ayumi HASEGAWA Keiji MOCHIDA Narumi OGONUKI Michiko HIROSE Toshiko TOMISHIMA Kimiko INOUE Atsuo OGURA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.6, pp.539-545, 2017 (Released:2017-12-15)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 7 14
In embryo transfer experiments in mice, pseudopregnant females as recipients are prepared by sterile mating with vasectomized males. Because only females at the proestrus stage accept males, such females are selected from a stock of animals based on the appearance of their external genital tract. Therefore, the efficiency of preparing pseudopregnant females largely depends on the size of female colonies and the skill of the operators who select females for sterile mating. In this study, we examined whether the efficiency of preparing pseudopregnant females could be improved by applying an estrous cycle synchronization method by progesterone (P4) pretreatment, which significantly enhances the superovulation outcome in mice. We confirmed that after two daily injections of P4 (designated Days 1 and 2) in randomly selected females, the estrous cycles of most females (about 85%) were synchronized at metestrus on Day 3. When P4-treated females were paired with vasectomized males for 4 days (Days 4–8), a vaginal plug was found in 63% (20/32) of the females on Day 7. After the transfer of vitrified-warmed embryos into their oviducts, 52% (73/140) of the embryos successfully developed into offspring, the rate being comparable to that of the conventional embryo transfer procedure. Similarly, 77% (24/31) of females became pregnant by fertile mating with intact males for 3 days, which allowed the scheduled preparation of foster mothers. Thus, our estrous cycle synchronization method may omit the conventional experience-based process of visually observing the vagina to choose females for embryo transfer. Furthermore, it is expected that the size of female stocks for recipients can be reduced to less than 20%, which could be a great advantage for facilities/laboratories undertaking mouse-assisted reproductive technology.
- 著者
- Kento MIURA Shogo MATOBA Narumi OGONUKI Takafumi NAMIKI Junya ITO Naomi KASHIWAZAKI Atsuo OGURA
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2018-053, (Released:2018-05-05)
- 被引用文献数
- 9
In mammals, spermatozoa activate oocytes by triggering a series of intracellular Ca2+ oscillations with phospholipase C zeta (PLCζ), a sperm-borne oocyte-activating factor. Because the introduction of PLCζ alone can induce oocyte activation, it might be a promising reagent for assisted reproductive technologies. To test this possibility, we injected human PLCζ (hPLCζ) mRNA into mouse oocytes at different concentrations. We observed the oocyte activation and subsequent embryonic development. Efficient oocyte activation and embryonic development to the blastocyst stage was achieved only with a limited range of mRNA concentrations (0.1 ng/μl). Higher concentrations of mRNA caused developmental arrest of most embryos, suggesting that excessive PLCζ protein might be harmful at this stage. In a second series of experiments, we aimed to regulate the PLCζ protein concentration in oocytes by applying auxin-inducible degron (AID) technology that allows rapid degradation of the target protein tagged with AID induced by auxin. Injection of the hPLCζ protein tagged with AID and enhanced green fluorescent protein (hPLCζ–AID–EGFP) demonstrated that high EGFP expression levels at the late 1-cell stage were efficiently reduced by auxin treatment, suggesting efficient hPLCζ degradation by this system. Furthermore, the defective development observed with higher concentrations of hPLCζ–AID–EGFP mRNA was rescued following auxin treatment. Full-term offspring were obtained by round spermatid injection with optimized hPLCζ–AID activation. Our results indicate that this AID technology can be applied to regulate the protein levels in mouse oocytes and that our optimized PLCζ system could be used for assisted fertilization in mammals.
- 著者
- Arata HONDA Atsuo OGURA
- 出版者
- 日本繁殖生物学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.5, pp.435-438, 2017 (Released:2017-10-18)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 8
Although the laboratory rabbit has long contributed to many paradigmatic studies in biology and medicine, it is often considered to be a “classical animal model” because in the last 30 years, the laboratory mouse has been more often used, thanks to the availability of embryonic stem cells that have allowed the generation of gene knockout (KO) animals. However, recent genome-editing strategies have changed this unrivaled condition; so far, more than 10 mammalian species have been added to the list of KO animals. Among them, the rabbit has distinct advantages for application of genome-editing systems, such as easy application of superovulation, consistency with fertile natural mating, well-optimized embryo manipulation techniques, and the short gestation period. The rabbit has now returned to the stage of advanced biomedical research.
1 0 0 0 OA Maintenance of mouse trophoblast stem cells in KSR-based medium allows conventional 3D culture
- 著者
- Shuai SUN Shota YANO Momo O NAKANISHI Michiko HIROSE Kazuhiko NAKABAYASHI Kenichiro HATA Atsuo OGURA Satoshi TANAKA
- 出版者
- The Society for Reproduction and Development
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2020-119, (Released:2021-03-20)
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Mouse trophoblast stem cells (TSCs) can differentiate into trophoblast cells, which constitute the placenta. Under conventional culture conditions, in a medium supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS), fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF4), and heparin and in the presence of mouse embryonic fibroblast cells (MEFs) as feeder cells, TSCs maintain their undifferentiated, proliferative status. MEFs can be replaced by a 70% MEF-conditioned medium (MEF-CM) or by TGF-ß/activin A. To find out if KnockOutTM Serum Replacement (KSR) can replace FBS for TSC maintenance, we cultured mouse TSCs in KSR-based, FBS-free medium and investigated their proliferation capacity, stemness, and differentiation potential. The results indicated that fibronectin, vitronectin, or laminin coating was necessary for adhesion of TSCs under KSR-based conditions but not for their survival or proliferation. While the presence of FGF4, heparin, and activin A was not sufficient to support the proliferation of TSCs, the addition of a pan-retinoic acid receptor inverse agonist and a ROCK-inhibitor yielded a proliferation rate comparable to that obtained under the conventional FBS-based conditions. TSCs cultured under the KSR-based conditions had a gene expression and DNA methylation profile characteristic of TSCs and exhibited a differentiation potential. Moreover, under KSR-based conditions, we could obtain a suspension culture of TSCs using extracellular matrix (ECM) coating-free dishes. Thus, we have established here, KSR-based culture conditions for the maintenance of TSCs, which should be useful for future studies.
- 著者
- Jinsha LIU Keiji MOCHIDA Ayumi HASEGAWA Kimiko INOUE Atsuo OGURA
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.2, pp.117-127, 2018 (Released:2018-04-13)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 5
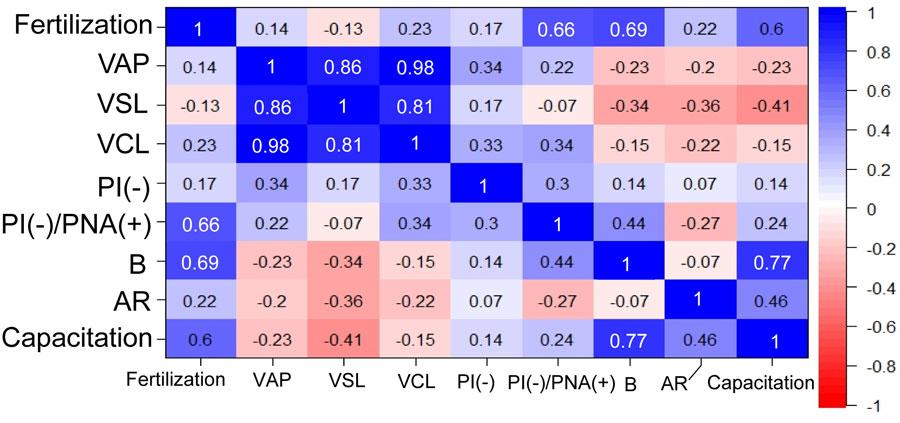
Although it is known that the susceptibility of mouse spermatozoa to freezing-thawing varies greatly with genetic background, the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. In this study, to map genetic regions responsible for the susceptibility of spermatozoa to freezing-thawing, we performed in vitro fertilization using spermatozoa from recombinant inbred mice derived from the C57BL/6J and DBA/2J strains, whose spermatozoa showed distinct fertilization abilities after freezing. Genome-wide interval mapping identified two suggestive quantitative trait loci (QTL) associated with fertilization on chromosomes 1 and 11. The strongest QTL on chromosome 11 included 70 genes at 59.237260–61.324742 Mb and another QTL on chromosome 1 included 43 genes at 153.969506–158.217850 Mb. These regions included at least 15 genes involved with testicular expression and possibly with capacitation or sperm motility. Specifically, the Abl2 gene on chromosome 1, which may affect subcellular actin distribution, had polymorphisms between C57BL/6J and DBA/2J that caused at least three amino acid substitutions. A correlation analysis using recombinant inbred strains revealed that the fertilization rate was strongly correlated with the capacitation rate of frozen-thawed spermatozoa after preincubation. This result is consistent with the fact that C57BL/6J frozen-thawed spermatozoa recover their fertilization capacity following treatment with methyl-β-cyclodextrin to enhance sperm capacitation. Thus, our data provide important clues to the molecular mechanisms underlying cryodamage to mouse spermatozoa.
- 著者
- Jinsha LIU Keiji MOCHIDA Ayumi HASEGAWA Kimiko INOUE Atsuo OGURA
- 出版者
- THE SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2017-148, (Released:2017-12-21)
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Although it is known that the susceptibility of mouse spermatozoa to freezing–thawing varies greatly with genetic background, the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. In this study, to map genetic regions responsible for the susceptibility of spermatozoa to freezing–thawing, we performed in vitro fertilization using spermatozoa from recombinant inbred mice derived from the C57BL/6J and DBA/2J strains, whose spermatozoa showed distinct fertilization abilities after freezing. Genome-wide interval mapping identified two suggestive quantitative trait loci (QTL) associated with fertilization on chromosomes 1 and 11. The strongest QTL on chromosome 11 included 70 genes at 59.237260–61.324742 Mb and another QTL on chromosome 1 included 43 genes at 153.969506–158.217850 Mb. These regions included at least 15 genes involved with testicular expression and possibly with capacitation or sperm motility. Specifically, the Abl2 gene on chromosome 1, which may affect subcellular actin distribution, had polymorphisms between C57BL/6J and DBA/2J that caused at least three amino acid substitutions. A correlation analysis using recombinant inbred strains revealed that the fertilization rate was strongly correlated with the capacitation rate of frozen-thawed spermatozoa after preincubation. This result is consistent with the fact that C57BL/6J frozen–thawed spermatozoa recover their fertilization capacity following treatment with methyl-β-cyclodextrin to enhance sperm capacitation. Thus, our data provide important clues to the molecular mechanisms underlying cryodamage to mouse spermatozoa.
- 著者
- Ayumi HASEGAWA Kazuya YONEZAWA Akihiko OHTA Keiji MOCHIDA Atsuo OGURA
- 出版者
- 日本繁殖生物学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Reproduction and Development (ISSN:09168818)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.58, no.1, pp.156-161, 2012 (Released:2012-03-22)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 1 18 4
The rapid increase in the number of genetically modified mouse strains has produced a high demand for their frozen spermatozoa from laboratories and mouse banking facilities. Historically, plastic straws have been used preferentially as containers for frozen mammalian spermatozoa because spermatozoa frozen in plastic straws have a high survival rate after thawing. However, plastic straws are more fragile and are used less often than the cryotubes used for conventional cell freezing. In this study, we sought to develop a new protocol for sperm freezing using cryotubes as the container to increase the accessibility of mouse sperm cryopreservation. Epididymal spermatozoa were collected from mature ICR or C57BL/6J (B6) males and were suspended in 18% raffinose and 3% skim milk solution. We then optimized the following conditions using the sperm survival rate as an index: 1) distance of cryotubes from the surface of the liquid nitrogen at freezing, 2) volume of the sperm suspension in the cryotube and 3) temperature of warming sperm during thawing. The best result was obtained when cryotubes containing 10 μl of sperm suspension were immersed 1 cm below the surface of the liquid nitrogen and then thawed at 50 C. The fertilization rates using spermatozoa frozen and thawed using this method were 63.1% in ICR mice and 28.2% in B6 mice. The latter rate was increased to 62.3% by adding reduced glutathione to the fertilization medium. After embryo transfer, 68% and 62% of the fertilized oocytes developed into normal offspring in the ICR and B6 strains, respectively. These results show that cryotubes can be used for cryopreservation of mouse spermatozoa under optimized conditions. This protocol is easy and reproducible, and it may be used in laboratories that do not specialize in sperm cryopreservation.