- 著者
- Daisaku Masuda Shizuya Yamashita
- 出版者
- Japan Atherosclerosis Society
- 雑誌
- Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis (ISSN:13403478)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.24, no.2, pp.95-109, 2017-02-01 (Released:2017-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 133
- 被引用文献数
- 32 108
Fasting hypertriglyceridemia is positively associated with the morbidity of coronary heart disease (CHD), and postprandial (non-fasting) hypertriglyceridemia is also correlated with the risk status for CHD, which is related to the increase in chylomicron (CM) remnant lipoproteins produced from the intestine. CM remnant particles, as well as oxidized low density lipoprotein (LDL) or very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) remnants, are highly atherogenic and act by enhancing systemic inflammation, platelet activation, coagulation, thrombus formation, and macrophage foam cell formation. The cholesterol levels of remnant lipoproteins significantly correlate with small, dense LDL; impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and CHD prevalence. We have developed an assay of apolipoprotein (apo)B-48 levels to evaluate the accumulation of CM remnants. Fasting apoB-48 levels correlate with the morbidity of postprandial hypertriglyceridemia, obesity, type III hyperlipoproteinemia, the metabolic syndrome, hypothyroidism, chronic kidney disease, and IGT. Fasting apoB-48 levels also correlate with carotid intima-media thickening and CHD prevalence, and a high apoB-48 level is a significant predictor of CHD risk, independent of the fasting TG level. Diet interventions, such as dietary fibers, polyphenols, medium-chain fatty acids, diacylglycerol, and long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), ameliorate postprandial hypertriglyceridemia, moreover, drugs for dyslipidemia (n-3 PUFA, statins, fibrates or ezetimibe) and diabetes concerning incretins (dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitor or glucagon like peptide-1 analogue) may improve postprandial hypertriglyceridemia. Since the accumulation of CM remnants correlates to impaired lipid and glucose metabolism and atherosclerotic cardiovascular events, further studies are required to investigate the characteristics, physiological activities, and functions of CM remnants for the development of new interventions to reduce atherogenicity.
4 0 0 0 OA Patients with CD36 Deficiency Are Associated with Enhanced Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases
- 著者
- Miyako Yuasa-Kawase Daisaku Masuda Taiji Yamashita Ryota Kawase Hajime Nakaoka Miwako Inagaki Kazuhiro Nakatani Kazumi Tsubakio-Yamamoto Tohru Ohama Akifumi Matsuyama Makoto Nishida Masato Ishigami Toshiharu Kawamoto Issei Komuro Shizuya Yamashita
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本動脈硬化学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis (ISSN:13403478)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, no.3, pp.263-275, 2012 (Released:2012-03-26)
- 参考文献数
- 48
- 被引用文献数
- 9 32
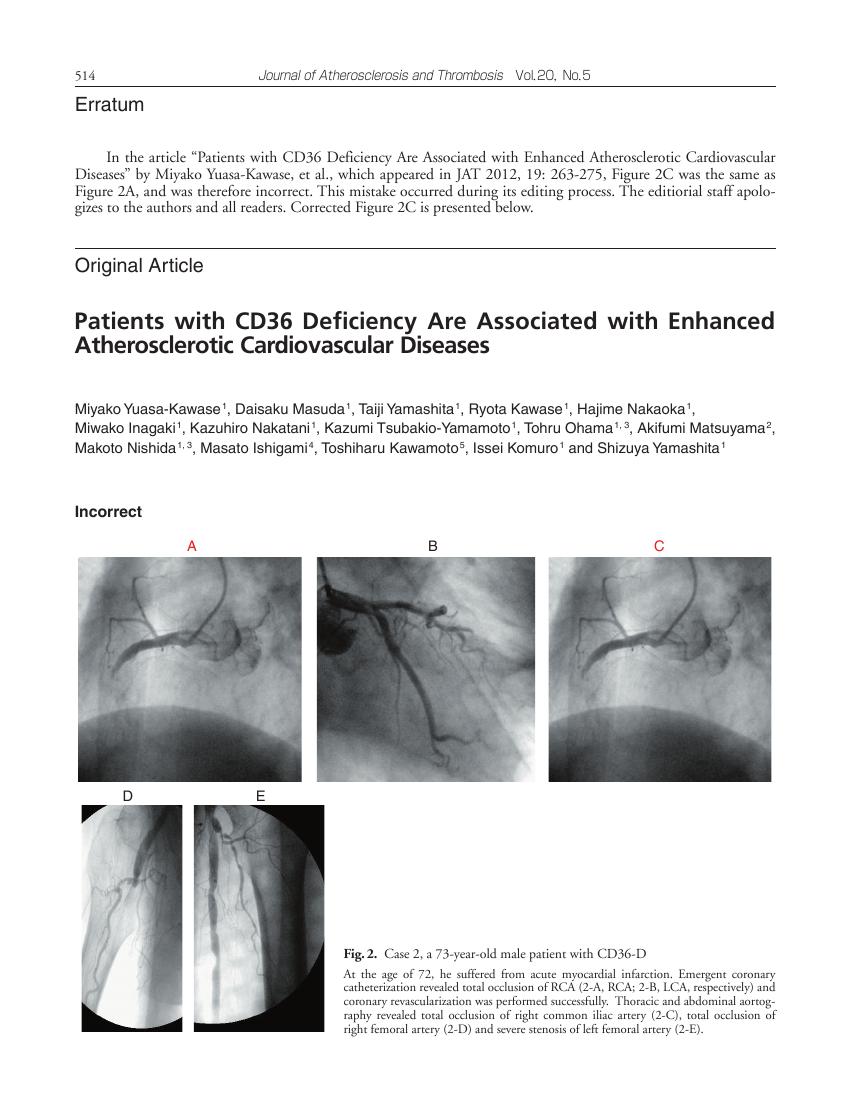
Aim: The clustering of dyslipidemia, impaired glucose tolerance and hypertension increases the morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular events. A class B scavenger receptor, CD36, is a receptor for oxidized LDL and a transporter of long-chain fatty acids. Because of the impaired uptake of oxidized LDL in CD36-deficient macrophages and from the results of CD36 knockout mice, CD36 deficiency (CD36-D) was supposed to be associated with reduced risks for coronary artery disease (CAD); however, CD36-D patients are often accompanied by a clustering of coronary risk factors. The current study aimed to investigate the morbidity and severity of cardiovascular diseases in CD36-D patients.Methods: By screening for CD36 antigen on platelets and monocytes using FACS or the absent myocardial accumulation of 123I-BMIPP by scintigraphy, 40 patients with type I CD36-D were collected, the morbidity of CAD and their features of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases were observed. Screening for CD36-D in both CAD patients (n =319) and healthy subjects (n =1,239) were underwent.Results: The morbidity of CAD was significantly higher in CD36-D patients than in the general population; 50% of patients (20 out of 40) had CAD identified by BMIPP scintigraphy and 37.5% (3 out of 8) by FACS screening, respectively. Three representative CD36-D cases demonstrated severe CAD and atherosclerosis. The frequency of CD36-D was three times higher in CAD patients than in healthy subjects (0.9% vs 0.3%, p <0.0001).Conclusion: The morbidity of CAD is significantly higher in CD36-D patients suffering from severe atherosclerosis, implying that the status of CD36-D might be atherogenic.
2 0 0 0 OA Patients with CD36 Deficiency Are Associated with Enhanced Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases
- 著者
- Miyako Yuasa-Kawase Daisaku Masuda Taiji Yamashita Ryota Kawase Hajime Nakaoka Miwako Inagaki Kazuhiro Nakatani Kazumi Tsubakio-Yamamoto Tohru Ohama Akifumi Matsuyama Makoto Nishida Masato Ishigami Toshiharu Kawamoto Issei Komuro Shizuya Yamashita
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本動脈硬化学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis (ISSN:13403478)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.5, pp.514-515, 2013 (Released:2013-05-29)
- 参考文献数
- 48
- 著者
- Hidenori Arai Hideaki Bujo Daisaku Masuda Toshiyuki Ishibashi Satoshi Nakagawa Kenichiro Tanabe Tatsuo Kagimura Hyun-Jae Kang Moo Hyun Kim Jidong Sung Sang-Hyun Kim Cheol-Ho Kim Jeong Euy Park Junbo Ge Byung-Hee Oh Toru Kita Yasushi Saito Masanori Fukushima Yuji Matsuzawa Shizuya Yamashita
- 出版者
- Japan Atherosclerosis Society
- 雑誌
- Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis (ISSN:13403478)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.62821, (Released:2021-04-18)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Aims: In this study, we integrated two randomized control trials, PROSPECTIVE and IMPACT, to address the effect of probucol on cerebrocardiovascular events and carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) in Japanese, Korean, and Chinese patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). Methods: A total of 1,025 patients from the PROSPECTIVE and IMPACT studies were enrolled. The time to the first major adverse cerebrocardiovascular event, in addition to carotid IMT and lipid levels, was compared between the control and probucol groups. Results: In the integrated analysis, the adjusted hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were 0.67 and 0.44–1.03, respectively, indicating a tendency to show the effect of probucol on cerebrocardiovascular events in secondary prevention. We also found no significant differences between the control and probucol groups in the mean IMT of the carotid arteries and its changes. However, we found a significant decrease in cerebrocardiovascular events in patients with reduced levels of HDL cholesterol (HDL-C) (≥ 6.25 mg/dL) compared with those with levels <6.25 mg/dL (p=0.024), without any increase in adverse events such as severe ventricular arrhythmias. Conclusion: We demonstrated a marginal effect of probucol on cerebrocardiovascular events in Asian patients with CAD, with reasonable safety profiles. A larger study may be needed to support the effect of probucol for cardiovascular prevention.
- 著者
- Shizuya Yamashita Hidenori Arai Hideaki Bujo Daisaku Masuda Tohru Ohama Toshiyuki Ishibashi Koji Yanagi Yasuji Doi Satoshi Nakagawa Koichi Yamashiro Kenichiro Tanabe Toru Kita Masunori Matsuzaki Yasushi Saito Masanori Fukushima Yuji Matsuzawa on Behalf of the PROSPECTIVE Study Group
- 出版者
- Japan Atherosclerosis Society
- 雑誌
- Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis (ISSN:13403478)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.55327, (Released:2020-04-24)
- 参考文献数
- 50
- 被引用文献数
- 26
Aims: Although intensive statin therapy reduced cardiovascular risks, cardiovascular events have not been completely prevented. Probucol is a potent antioxidant and reduces tendon xanthomas in familial hypercholesterolemia patients despite reduction of high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol (HDL-C). We investigated whether probucol can reduce cardiovascular events on top of conventional lipid-lowering therapy in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD). Methods: PROSPECTIVE is a multicenter, randomized, prospective study that recruited 876 Japanese patients with CHD and dyslipidemia with an low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol (HDL-C) level of ≥ 140 mg/dL without medication or those treated with lipid-lowering drugs. Lipid-lowering agents were administered during the study period in the control group (n=438), and probucol 500 mg/day was added to lipid-lowering therapy in the probucol group (n=438). Patients were randomly assigned to two treatment groups by adjusting the LDL-C level and presence of diabetes and hypertension and followed up for more than 3 years. The primary end point was a composite of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular events (cardiovascular disease death including sudden death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, hospitalization for heart failure, or coronary revascularization). The secondary end point was carotid intima–media thickness in a subset of patients. Results: The incidence of the primary end point showed a trend to be lower in the probucol group compared with that in the control group despite reduced HDL-C without serious adverse events. Anti-atherogenic effects of probucol may be attributed to its potent antioxidative function and enhancement of reverse cholesterol transport. Conclusion: Since there was no statistical significance between the probucol and control groups despite a marked reduction of HDL-C, further studies on the clinical outcomes of probucol on top of conventional therapy may be necessary in the future (UMIN000003307).