- 著者
- Kazuhide Inage Takeshi Sainoh Takayuki Fujiyoshi Otagiri Takuma Yasuchika Aoki Masahiro Inoue Yawara Eguchi Sumihisa Orita Yasuhiro Shiga Masao Koda Tsutomu Akazawa Takeo Furuya Junichi Nakamura Hiroshi Takahashi Miyako Suzuki Satoshi Maki Hideyuki Kinoshita Masaki Norimoto Tomotaka Umimura Takashi Sato Masashi Sato Masahiro Suzuki Keigo Enomoto Hiromitsu Takaoka Norichika Mizuki Takashi Hozumi Ryuto Tsuchiya Geundong Kim Tomohito Mukaihata Takahisa Hishiya Seiji Ohtori
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2020-0042, (Released:2020-07-10)
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Introduction: Mirogabalin should be equivalent to pregabalin, but with fewer incidences of adverse drug reactions (ADRs). To verify these benefits in actual clinical trials, our study investigated the frequency of ADRs and mirogabalin' s analgesic effects during treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain.Methods: This study included 74 patients with lower limb pain. We surveyed patient reports of ADRs during the follow-up period as the primary endpoint and examined the visual analog scale (VAS) reported for lower limb pain as the secondary endpoint (before administration, and two and four weeks after administration).Results: The occurrence of ADR was 27.0%, like the frequency of ADRs in the clinical trials for other disorders. However, the discontinuation rate of administration was 10.8%, which was significantly lower than the frequency of ADR occurrences. When the analgesic effect was assessed, a significant decrease in the temporal change of VAS for lower limb pain was observed before administration, and two and four weeks after administration.Conclusions: In this study, the occurrence of ADRs reported by the patients was like the frequency of ADRs reported in the clinical trials for other disorders. When assessing the analgesic effect, the temporal change of VAS for lower limb pain was found to decrease significantly before administration, and two and four weeks after administration.
- 著者
- Ryo Fukata Takeo Furuya Yuki Shiko Yohei Kawasaki Mayuko Kuwata Keita Takase Ryosuke Tadaki Tomoyo Akasaka Geundong Kim Yahiko Takeuchi Mitsuo Morita Atsushi Murata Seiji Ohtori
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.7, no.5, pp.414-420, 2023-09-27 (Released:2023-09-27)
- 参考文献数
- 31
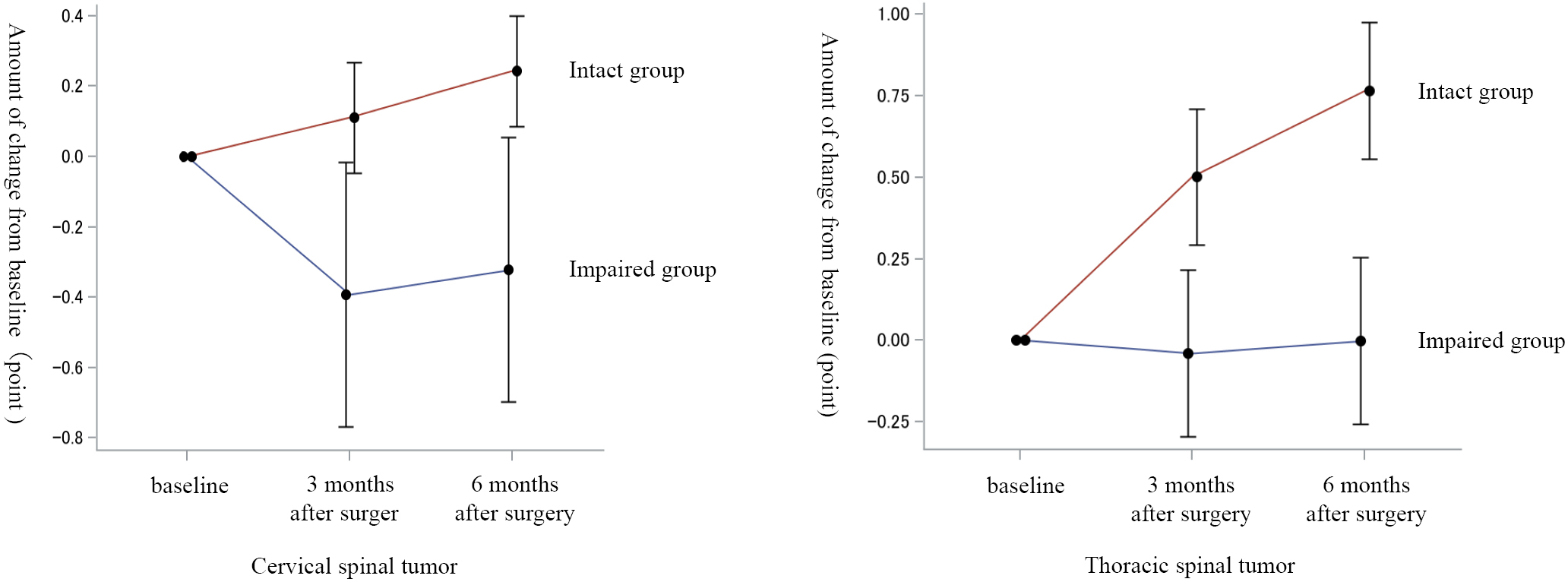
Introduction: We investigated the effect of preoperative joint position sense in the big toe on the postoperative recovery of gait function after spinal tumor surgery.Methods: Seventy-three patients with spinal tumors who underwent surgery at our hospital between 2014 and 2019 and could be followed for at least 6 months after surgery were included. The patients were divided into the cervical spinal (41 cases) and thoracic spinal (32 cases) groups according to the localization of the tumor. These groups were further classified into an Impaired group (cervical spinal, 34 cases; thoracic spinal, 19 cases) and an Intact group (cervical spinal, 7 cases; thoracic spinal, 13 cases) according to the presence or absence of preoperative joint position sense in the big toe. The amount of change in ambulatory function from the preoperative period to 3 and 6 months postoperatively was compared between the Impaired and Intact groups within each tumor localization category.Results: Impaired preoperative joint position sense in the big toe in patients undergoing thoracic spinal tumor surgery delayed the recovery of gait function in the early postoperative period.Conclusions: In patients with thoracic spinal tumor surgery, the absence of preoperative joint position sense in the big toe delayed the recovery of postoperative gait function.