- 著者
- Keisuke Inoue Shoji Takada Tsuyoshi Terakawa
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, pp.e190015, 2022 (Released:2022-05-11)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 2
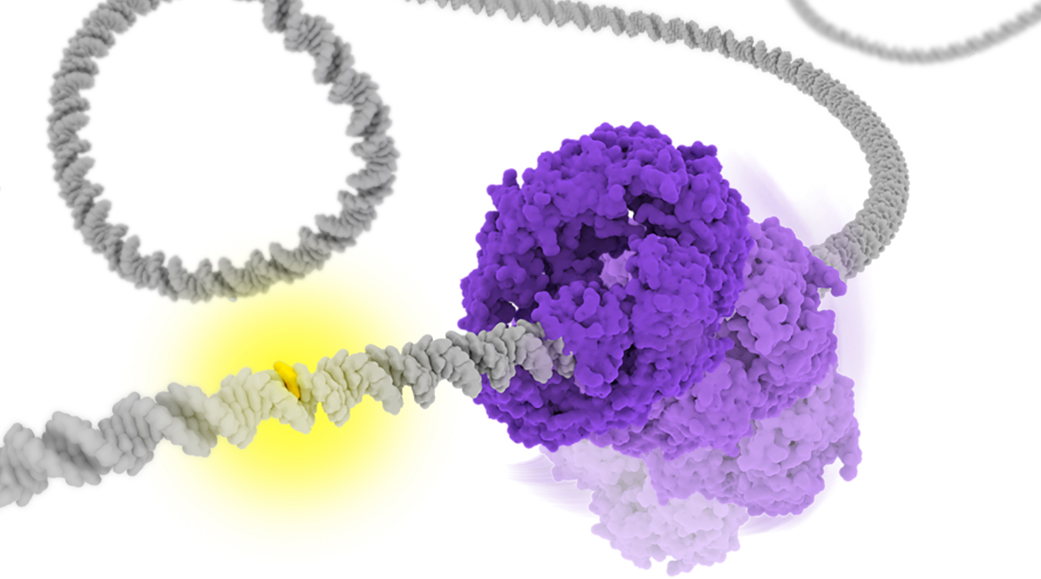
DNA mismatches are frequently generated by various intrinsic and extrinsic factors including DNA replication errors, oxygen species, ultraviolet, and ionizing radiation. These mismatches should be corrected by the mismatches repair (MMR) pathway to maintain genome integrity. In the Escherichia coli (E. coli) MMR pathway, MutS searches and recognizes a base-pair mismatch from millions of base-pairs. Once recognized, ADP bound to MutS is exchanged with ATP, which induces a conformational change in MutS. Previous single-molecule fluorescence microscopy studies have suggested that ADP-bound MutS temporarily slides along double-stranded DNA in a rotation-coupled manner to search a base-pair mismatch and so does ATP-bound MutS in a rotation-uncoupled manner. However, the detailed structural dynamics of the sliding remains unclear. In this study, we performed coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations of the E. coli MutS bound on DNA in three different conformations: ADP-bound (), ATP-bound open clamp (), and ATP-bound closed clamp () conformations. In the simulations, we observed conformation-dependent diffusion of MutS along DNA. and diffused along DNA in a rotation-coupled manner with rare and frequent groove-crossing events, respectively. In the groove-crossing events, MutS overcame an edge of a groove and temporarily diffused in a rotation-uncoupled manner. It was also indicated that mismatch searches by is inefficient in terms of mismatch checking even though it diffuses along DNA and reaches unchecked regions more rapidly than .
- 著者
- Miho YOSHIOKA Zen KOBAYASHI Keisuke INOUE Mayumi WATANABE Kaori KATO Kazunori TOYODA Yoshiyuki NUMASAWA Shoichiro ISHIHARA Hiroyuki TOMIMITSU Shuzo SHINTANI
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Brain Function and Rehabilitation
- 雑誌
- Journal of Rehabilitation Neurosciences (ISSN:24342629)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, no.1, pp.33-36, 2019 (Released:2019-10-25)
The Trail Making Test (TMT) is widely used as a measure of attention impairment. The time needed to complete TMT (TMT score) is prolonged in association with attention impairment in patients with brain diseases. Thus far, however, there have been no reports of serial changes in the TMT score after minor ischemic stroke. We retrospectively investigated serial changes in the TMT score of 19 patients with minor ischemic stroke. We included patients in whom TMT could be performed both 4-11 days after onset (initial evaluation) and 14-47 days after onset (second evaluation). The mean value of the initial TMT-A scores was 58 seconds, and that of the initial TMT-B scores was 144 seconds. The mean value of the second TMT-A scores was 43 seconds, and that of the second TMT-B scores was 119 seconds. The TMT-A and TMT-B scores improved in 89 % and 74 % of patients, respectively. This study demonstrated that most minor ischemic stroke patients showed improvement in the TMT score 14 days or later after onset.