- 著者
- Kohei Tsuji Takuya Kobayakawa Takahiro Ishii Nobuyo Higashi-Kuwata Chika Azuma Kouki Shinohara Yutaro Miura Kenichi Yamamoto Soshi Nishimura Shin-ichiro Hattori Haydar Bulut Hiroaki Mitsuya Hirokazu Tamamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.12, pp.879-886, 2023-12-01 (Released:2023-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 53
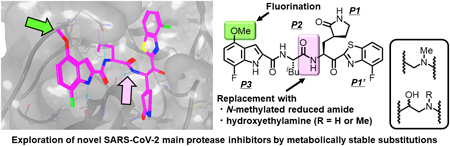
In the development of anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) drugs, its main protease (Mpro), which is an essential enzyme for viral replication, is a promising target. To date, the Mpro inhibitors, nirmatrelvir and ensitrelvir, have been clinically developed by Pfizer Inc. and Shionogi & Co., Ltd., respectively, as orally administrable drugs to treat coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19). We have also developed several potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro that include compounds 4, 5, TKB245 (6), and TKB248 (7), which possesses a 4-fluorobenzothiazole ketone moiety as a reactive warhead. In compounds 5 and TKB248 (7) we have also found that replacement of the P1-P2 amide of compounds 4 and TKB245 (6) with the corresponding thioamide improved their pharmacokinetics (PK) profile in mice. Here, we report the design, synthesis and evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors with replacement of a digestible amide bond by surrogates (9–11, 33, and 34) and introduction of fluorine atoms in a metabolically reactive methyl group on the indole moiety (8). As the results, these compounds showed comparable or less potency compared to the corresponding parent compounds, YH-53/5h (2) and 4. These results should provide useful information for further development of Mpro inhibitors.
- 著者
- Sungjin CHOI I-Li LIU Kenichi YAMAMOTO Muneki HONNAMI Takamasa SAKAI Shinsuke OHBA Ryosuke ECHIGO Shigeki SUZUKI Ryouhei NISHIMURA Ung-Il CHUNG Nobuo SASAKI Manabu MOCHIZUKI
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本獣医学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Veterinary Medical Science (ISSN:09167250)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.13-0054, (Released:2013-10-25)
- 被引用文献数
- 3 8
We investigated biodegradability and new bone formation after implantation of tetrapod-shaped granular artificial bone (Tetrabone®) or β-tricalcium phosphate granules (β-TCP) in experimental critical-size defects in dogs, which were created through medial and lateral femoral condyles. The defect was packed with Tetrabone® (Tetrabone group) or β-TCP (β-TCP group) or received no implant (control group). Computed tomography (CT) was performed at 0, 4 and 8 weeks after implantation. Micro-CT and histological analysis were conducted to measure the non-osseous tissue rate and the area and distribution of new bone tissue in the defect at 8 weeks after implantation. On CT, β-TCP was gradually resorbed, while Tetrabone® showed minimal resorption at 8 weeks after implantation. On micro-CT, non-osseous tissue rate of the control group was significantly higher compared with the β-TCP and Tetrabone groups (P<0.01), and that of the β-TCP group was significantly higher compared with the Tetrabone group (P<0.05). On histology, area of new bone tissue of the β-TCP group was significantly greater than those of the Tetrabone and control groups (P<0.05), and new bone distribution of the Tetrabone group was significantly greater than those of the β-TCP and control groups (P<0.05). These results indicate differences in biodegradability and connectivity of intergranule pore structure between study samples. In conclusion, Tetrabone® may be superior for the repair of large bone defects in dogs.