- 著者
- Yasuo Takatsu Masafumi Nakamura Satoshi Kobayashi Tosiaki Miyati
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- 雑誌
- Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences (ISSN:13473182)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.mp.2020-0050, (Released:2020-05-27)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Purpose: To investigate whether the contrast enhancement effect in hepatobiliary phase (HBP) images can be predicted using transitional phase (3-min delay) images on liver magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based on the quantitative liver–spleen contrast ratio (Q-LSC) and albumin–bilirubin (ALBI) grade.Methods: Overall, 212 patients (124 men and 88 women; mean age 66.7 ± 11.1 years) who underwent blood tests (assessed within 1 month of performing MRI) were included; patients with diffuse tumor, hepatectomy, splenectomy, Gamna–Gandy bodies in the spleen, and movement artifacts were excluded. Q-LSC was calculated using the signal intensity of the liver divided that of the spleen. Q-LSC > 1.5 (cut-off value) indicates a relatively higher sensitivity for detecting of hepatic lesions. To predict the contrast enhancement effect in HBP using Q-LSC of 3-min delay images, Q-LSC of 10- and 15-min delay images were compared for each ALBI grade based on Q-LSC of 3-min delay images. Furthermore, to verify the accuracy of this prediction, the proportion of cases with Q-LSC > 1.5 in 10- and 15 min delay images was calculated based on Q-LSC on 3-min delay images.Results: The higher the Q-LSC on the 3-min delay image, the higher was the Q-LSC on its 10- and 15-min delay images. The proportion of cases with Q-LSC > 1.5 in 10- and 15-min delay images was higher for ALBI grade 1 than for ALBI grades 2 and 3 even in the same Q-LSC on 3-min delay images. Q-LSC was <1 in a 3-min delay image and <1.5 in a 15-min delay image in 62.2% of patients with ALBI grade 1 and 82.1% of patients with ALBI grades 2 and 3.Conclusion: The liver contrast enhancement effect in HBP images could be predicted using a 3-min delay image based on Q-LSC and ALBI grade.
- 著者
- Takanori Mei Hiroshi Noguchi Kimitaka Suetsugu Yu Hisadome Keizo Kaku Yasuhiro Okabe Satohiro Masuda Masafumi Nakamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.10, pp.1600-1603, 2020-10-01 (Released:2020-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 3
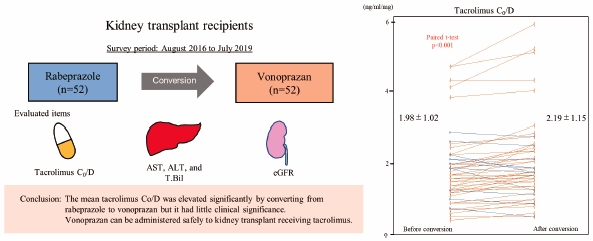
Vonoprazan fumarate (vonoprazan) is a new kind of acid suppressant with potent acid inhibitory effects. Therefore, it has been administered to kidney transplant recipients for treatment or prophylaxis of steroid ulcers, refractory peptic ulcers, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Because tacrolimus, which is a well-established immunosuppressant for kidney transplantation, and vonoprazan share the CYP3A4 system for metabolism, drug interactions are anticipated upon simultaneous administration. We retrospectively analyzed 52 kidney transplant recipients who were converted from rabeprazole, which has a small effect on the tacrolimus trough blood concentration (C0), to vonoprazan between August 2016 and July 2019. We compared the tacrolimus C0/tacrolimus dose (C0/D) before and after conversion and serum liver enzymes, serum total bilirubin, and the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). As a result, mean tacrolimus C0/D before and after conversion was 1.98 ± 1.02 and 2.19 ± 1.15 (ng/mL)/(mg/d), respectively, (p < 0.001). Additionally, mean aspartate transaminase (AST) before and after conversion was 18.6 ± 4.2 and 19.6 ± 5.2 IU/L, respectively, (p = 0.037). Mean alanine transaminase (ALT) before and after conversion was 15.8 ± 5.5 and 17.6 ± 7.1 IU/L, respectively, (p = 0.007). Mean eGFR before and after conversion was 50.6 ± 14.4 and 51.4 ± 14.7 mL/min/1.73 m2, respectively (p = 0.021). Mean AST, ALT, and eGFR were slightly but significantly elevated within normal ranges after conversion. In conclusion, our study suggests that the mean tacrolimus C0/D was elevated significantly by converting from rabeprazole to vonoprazan, but it had little clinical significance. Vonoprazan can be administered safely to kidney transplant recipients receiving tacrolimus.