- 著者
- Yurika Tahara Mikako Fujita Tianli Zhang Dongxing Wang Hiroshi Tateishi Akihiro Togami Perpetual Nyame Hiromi Terasawa Nami Monde Joyce Appiah-Kubi Wright Ofotsu Amesimeku Doaa Husham Majeed Alsaadi Mikiyo Wada Koji Sugimura Sevgi Gezici Halilibrahim Ciftci Faruk Karahan Nazim Sekeroglu Masami Otsuka Tomohiro Sawa Yosuke Maeda Takashi Watanabe Kazuaki Monde
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.11, pp.1535-1547, 2023-11-01 (Released:2023-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 67
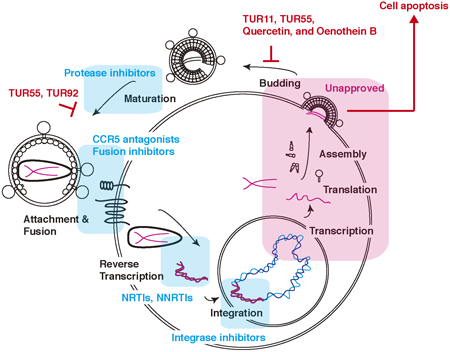
The introduction of combined anti-retroviral therapy (cART) in 1996, along with a continual breakthrough in anti-human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) drugs, has improved the life expectancies of HIV-1-infected individuals. However, the incidence of drug-resistant viruses between individuals undergoing cART and treatment-naïve individuals is a common challenge. Therefore, there is a requirement to explore potential drug targets by considering various stages of the viral life cycle. For instance, the late stage, or viral release stage, remains uninvestigated extensively in antiviral drug discovery. In this study, we prepared a natural plant library and selected candidate plant extracts that inhibited HIV-1 release based on our laboratory-established screening system. The plant extracts from Epilobium hirsutum L. and Chamerion angustifolium (L.) Holub, belonging to the family Onagraceae, decreased HIV-1 release and accelerated the apoptosis in HIV-1-infected T cells but not uninfected T cells. A flavonol glycoside quercetin with oenothein B in Onagraceae reduced HIV-1 release in HIV-1-infected T cells. Moreover, extracts from Chamerion angustifolium (L.) Holub and Senna alexandrina Mill. inhibited the infectivity of progeny viruses. Together, these results suggest that C. angustifolium (L.) Holub contains quercetin with oenothein B that synergistically blocks viral replication and kills infected cells via an apoptotic pathway. Consequently, the plant extracts from the plant library of Turkey might be suitable candidates for developing novel anti-retroviral drugs that target the late phase of the HIV-1 life cycle.
- 著者
- Hiroshi Tateishi Mika Tateishi Mohamed O Radwan Takuya Masunaga Kosuke Kawatashiro Yasunori Oba Misato Oyama Natsuki Inoue-Kitahashi Mikako Fujita Yoshinari Okamoto Masami Otsuka
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.69, no.11, pp.1123-1130, 2021-11-01 (Released:2021-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 12
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 (ADAM17) is a zinc-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of the extracellular domains of various transmembrane proteins. ADAM17 is regarded as a promising drug target for the suppression of various diseases, including cancer metastasis. We synthesized a new ADAM17 inhibitor, SN-4, composed of a zinc-binding dithiol moiety and an appendage that specifically binds to a pocket of ADAM17. We show that SN-4 inhibits the ability of ADAM17 to cleave tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in vitro. This activity was reduced by the addition of zinc, indicating the importance of the zinc chelating dithiol moiety. Inhibition of TNF-α cleavage by SN-4 in cells was also observed, and with an IC50 of 3.22 µM, SN-4 showed slightly higher activity than the well-studied ADAM17 inhibitor marimastat. Furthermore, SN-4 was shown to inhibit cleavage of CD44 by ADAM17, but not by ADAM10, and to suppress cell invasion. Molecular docking showed good fitting of the specificity pocket-binding group and one SH of SN-4 and hinted at possible means of structural optimization. This study provides clues for the development of potent and selective ADAM17 inhibitors.