- 著者
- Yurika Tahara Mikako Fujita Tianli Zhang Dongxing Wang Hiroshi Tateishi Akihiro Togami Perpetual Nyame Hiromi Terasawa Nami Monde Joyce Appiah-Kubi Wright Ofotsu Amesimeku Doaa Husham Majeed Alsaadi Mikiyo Wada Koji Sugimura Sevgi Gezici Halilibrahim Ciftci Faruk Karahan Nazim Sekeroglu Masami Otsuka Tomohiro Sawa Yosuke Maeda Takashi Watanabe Kazuaki Monde
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.11, pp.1535-1547, 2023-11-01 (Released:2023-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 67
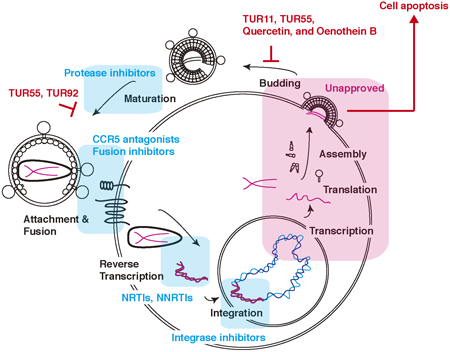
The introduction of combined anti-retroviral therapy (cART) in 1996, along with a continual breakthrough in anti-human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) drugs, has improved the life expectancies of HIV-1-infected individuals. However, the incidence of drug-resistant viruses between individuals undergoing cART and treatment-naïve individuals is a common challenge. Therefore, there is a requirement to explore potential drug targets by considering various stages of the viral life cycle. For instance, the late stage, or viral release stage, remains uninvestigated extensively in antiviral drug discovery. In this study, we prepared a natural plant library and selected candidate plant extracts that inhibited HIV-1 release based on our laboratory-established screening system. The plant extracts from Epilobium hirsutum L. and Chamerion angustifolium (L.) Holub, belonging to the family Onagraceae, decreased HIV-1 release and accelerated the apoptosis in HIV-1-infected T cells but not uninfected T cells. A flavonol glycoside quercetin with oenothein B in Onagraceae reduced HIV-1 release in HIV-1-infected T cells. Moreover, extracts from Chamerion angustifolium (L.) Holub and Senna alexandrina Mill. inhibited the infectivity of progeny viruses. Together, these results suggest that C. angustifolium (L.) Holub contains quercetin with oenothein B that synergistically blocks viral replication and kills infected cells via an apoptotic pathway. Consequently, the plant extracts from the plant library of Turkey might be suitable candidates for developing novel anti-retroviral drugs that target the late phase of the HIV-1 life cycle.
- 著者
- Miho Sakakibara Yosuke Maeda Kazuichi Nakamura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Toxicology
- 雑誌
- The Journal of Toxicological Sciences (ISSN:03881350)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.47, no.8, pp.327-336, 2022 (Released:2022-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 29
We used an abortion-prone mouse model, generated by mating female CBA/J mice with male DBA/2JJcl mice, to examine the effects of changes in the Th1/Th2 cell ratio and the percentage of regulatory T (Treg) cells on the maintenance of pregnancy. We subcutaneously injected female CBA/J mice once each with 50 μg/mouse of Dermatophagoides farinae (Df) extract and the squalene-based adjuvant (SquA); 10 days later, these mice were mated with male DBA/2JJcl mice. Compared with injection of vehicle or adjuvant, the Df treatment decreased the Th1/Th2 cell ratio and concomitantly increased the percentage of Treg cells in the spleen. In addition, fetal death rates were decreased. We then explored a substance which shifted the Th1/Th2 balance toward Th1 side. We found that 50 μg/mouse of keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) increased the splenic Th1/Th2 cell ratio of nonpregnant female CBA/J mice. We subcutaneously injected female CBA/J mice with KLH and SquA; 10 days later, these mice were mated with male DBA/2JJcl mice. Compared with injection of vehicle or adjuvant, treatment with KLH enhanced the Th1 bias during pregnancy and increased the fetal death rate. The percentage of Treg cells, however, was increased in these KLH-injected pregnant mice contrary to our presumption. All collected data showed strong positive correlation between the Th1/Th2 cell ratio and fetal death rate. The increase in Treg cells independent of effects on the fetal death rate suggests that Treg cells do not necessarily induce maternal tolerance to the fetus but may prevent excessive Th1/Th2 imbalance during pregnancy.