- 著者
- Tomoya SUZUKI Takeshi OGATA Mikiya TANAKA Tohru KOBAYASHI Hideaki SHIWAKU Tsuyoshi YAITA Hirokazu NARITA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.12, pp.1353-1360, 2019-12-10 (Released:2019-12-10)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 4
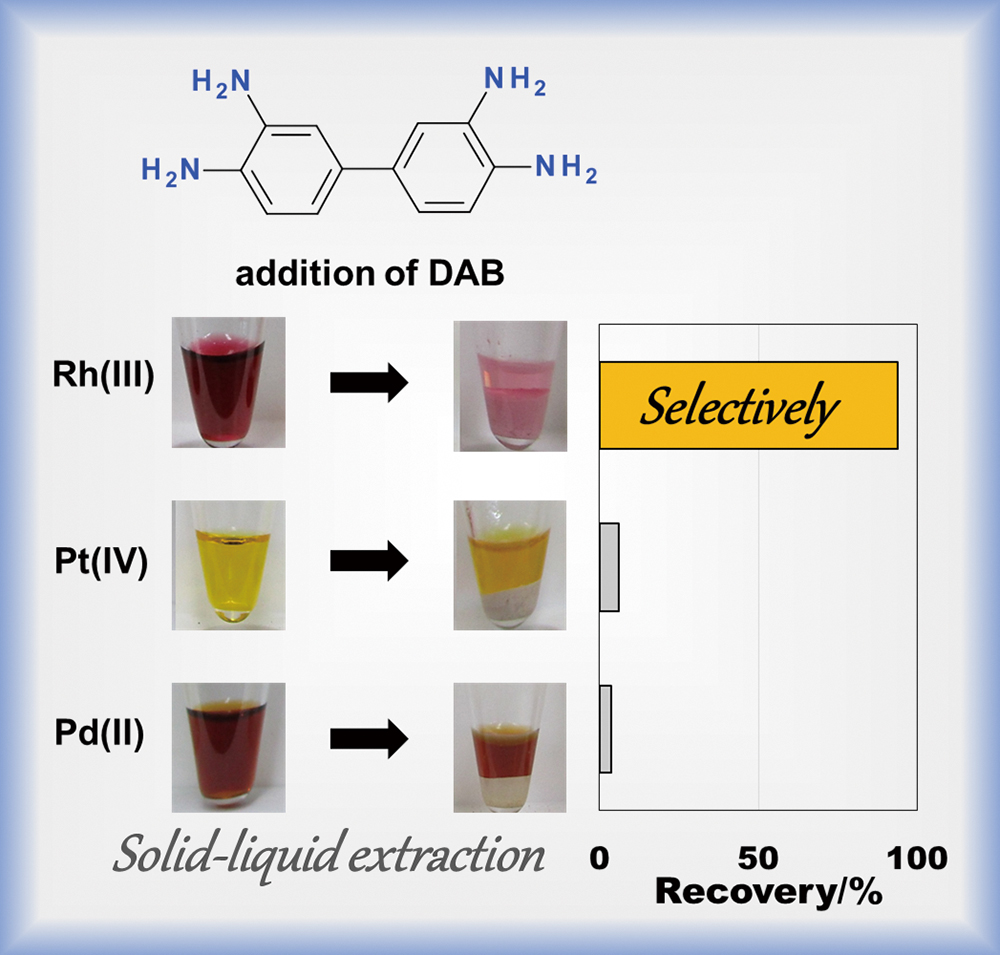
The effective recovery of Rh(III) from mixtures also containing Pd(II) and Pt(IV) is one of the most difficult tasks in platinum group metal refining. Adding 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) to 7 and 10 M HCl aqueous solutions containing Rh(III), Pd(II), and Pt(IV) chlorido species affords the effective separation of Rh(III) from Pd(II) and Pt(IV) through a process where Rh(III) becomes sequestered into solid phases composed of DAB. The stoichiometry and inner coordination sphere of the metal in Rh–DAB complexes were determined by estimating the Rh(III), H+, and Cl− concentrations in the solid phase and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements to clarify the mechanism of DAB selectivity for Rh(III). These results indicate that the Rh–DAB reaction in a concentrated HCl solution occurs in two steps: (1) the precipitation of DAB trihydrochloride salts, where DAB’s amino groups are protonated and (2) anion exchange of the trihydrochloride salts for chloride ions with [RhCl6]3−, which is the predominant species in a concentrated HCl solution. By contrast, ion-pair complexes with [PdCl4]2− and [PtCl6]2− were not observed in DAB phases. The significantly lower affinity of the DAB trihydro cation for [PtCl6]2− and [PdCl4]2− than for [RhCl6]3− in 7 and 10 M HCl solutions accounts for the effective separation of Rh(III) from Pd(II) and Pt(IV).