- 著者
- Tomoya Suzuki Akira S. Hirao Masaki Takenaka Koki Yano Koji Tojo
- 出版者
- The Genetics Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Genes & Genetic Systems (ISSN:13417568)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.20-00033, (Released:2021-01-24)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 3
We developed microsatellite markers for Appasus japonicus (Heteroptera: Belostomatidae). This belostomatid bug is distributed in East Asia (Japanese Archipelago, Korean Peninsula and mainland China) and often listed as an endangered species in the Red List or the Red Data Book at the national and local level in Japan. Here, we describe twenty novel polymorphic microsatellite loci developed for A. japonicus, and marker suitability was evaluated using 56 individuals from four A. japonicus populations (Nagano, Hiroshima and Yamaguchi prefectures, Japan, and Chungcheongnam-do, Korea). The number of alleles per locus ranged from 1 to 12 (mean = 2.5), and the average observed and expected heterozygosity and fixation index per locus were 0.270, 0.323 and 0.153, respectively. In addition, a population structure analysis was conducted using the software STRUCTURE, and its result suggested that the 20 markers described here will be useful for investigating the genetic structure of A. japonicus populations, which should contribute to population genetics studies of this species.
- 著者
- Tomoya Suzuki Kanto Nishikawa Yukuto Sato Mamoru Toda
- 出版者
- The Genetics Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Genes & Genetic Systems (ISSN:13417568)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.21-00046, (Released:2021-11-07)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Species identification using molecular techniques has recently become common for various taxa. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) is one of the easiest and least expensive molecular identification methods. Although few studies have developed LAMP assays for amphibians, we believe that LAMP is also useful for identifying endangered amphibians. Hynobius tokyoensis and H. lichenatus occur in Honshu, Japan, and have parapatric distributions. They are similar morphologically, especially at early developmental stages, including eggs and larvae. Hynobius tokyoensis has been listed as a national endangered species in Japan since 2020, and unambiguous identification of these species is therefore important for their conservation and management. In this study, we developed a LAMP primer set for the mitochondrial cytochrome b region to detect H. tokyoensis, and we evaluated the LAMP assay using total genomic DNA from four H. tokyoensis and three H. lichenatus individuals from across most of their ranges. Our LAMP primer set could distinguish these two species. This study should help to establish LAMP assays for other endangered species and morphologically similar species.
- 著者
- Tomoya Suzuki Akira S. Hirao Masaki Takenaka Koki Yano Koji Tojo
- 出版者
- The Genetics Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Genes & Genetic Systems (ISSN:13417568)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.95, no.6, pp.323-329, 2020-12-01 (Released:2021-03-23)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 3
We developed microsatellite markers for Appasus japonicus (Heteroptera: Belostomatidae). This belostomatid bug is distributed in East Asia (Japanese Archipelago, Korean Peninsula and mainland China) and often listed as an endangered species in the Red List or the Red Data Book at the national and local level in Japan. Here, we describe twenty novel polymorphic microsatellite loci developed for A. japonicus, and marker suitability was evaluated using 56 individuals from four A. japonicus populations (Nagano, Hiroshima and Yamaguchi prefectures, Japan, and Chungcheongnam-do, Korea). The number of alleles per locus ranged from 1 to 12 (mean = 2.5), and the average observed and expected heterozygosity and fixation index per locus were 0.270, 0.323 and 0.153, respectively. In addition, a population structure analysis was conducted using the software STRUCTURE, and its result suggested that the 20 markers described here will be useful for investigating the genetic structure of A. japonicus populations, which should contribute to population genetics studies of this species.
- 著者
- Tomoya SUZUKI Takeshi OGATA Mikiya TANAKA Tohru KOBAYASHI Hideaki SHIWAKU Tsuyoshi YAITA Hirokazu NARITA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.12, pp.1353-1360, 2019-12-10 (Released:2019-12-10)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 4
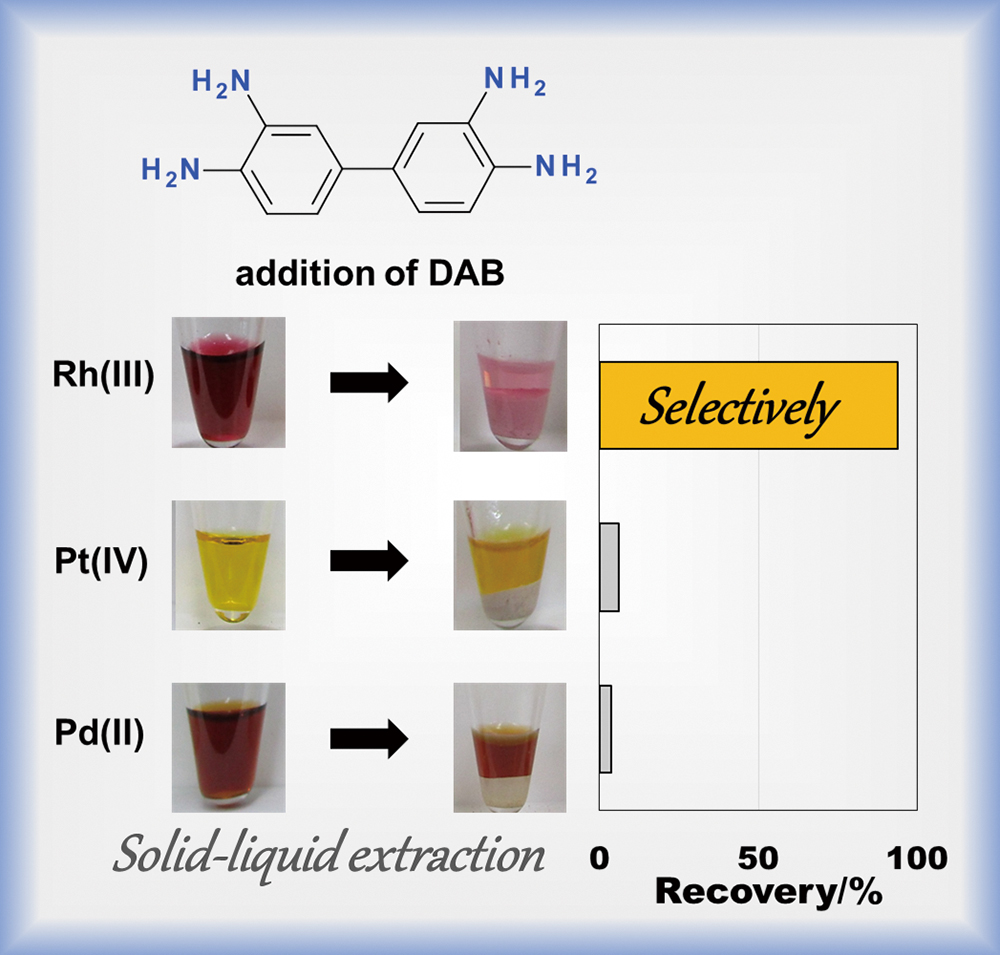
The effective recovery of Rh(III) from mixtures also containing Pd(II) and Pt(IV) is one of the most difficult tasks in platinum group metal refining. Adding 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) to 7 and 10 M HCl aqueous solutions containing Rh(III), Pd(II), and Pt(IV) chlorido species affords the effective separation of Rh(III) from Pd(II) and Pt(IV) through a process where Rh(III) becomes sequestered into solid phases composed of DAB. The stoichiometry and inner coordination sphere of the metal in Rh–DAB complexes were determined by estimating the Rh(III), H+, and Cl− concentrations in the solid phase and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements to clarify the mechanism of DAB selectivity for Rh(III). These results indicate that the Rh–DAB reaction in a concentrated HCl solution occurs in two steps: (1) the precipitation of DAB trihydrochloride salts, where DAB’s amino groups are protonated and (2) anion exchange of the trihydrochloride salts for chloride ions with [RhCl6]3−, which is the predominant species in a concentrated HCl solution. By contrast, ion-pair complexes with [PdCl4]2− and [PtCl6]2− were not observed in DAB phases. The significantly lower affinity of the DAB trihydro cation for [PtCl6]2− and [PdCl4]2− than for [RhCl6]3− in 7 and 10 M HCl solutions accounts for the effective separation of Rh(III) from Pd(II) and Pt(IV).