- 著者
- Satoko MOTAI Hiroki MUKAI Tetsu WATANUKI Kenji OHWADA Tatsuo FUKUDA Akihiko MACHIDA Chisaki KURAMATA Ryosuke KIKUCHI Tsuyoshi YAITA Toshihiro KOGURE
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人日本鉱物科学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (ISSN:13456296)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.150722, (Released:2016-06-08)
- 被引用文献数
- 15
Radioactive particles of around 50 µm size were collected from highly contaminated soil in the Fukushima Prefecture, Japan, and characterized using micro X–ray diffraction with synchrotron radiation (SR–µ–XRD). Two–dimensional diffraction patterns from individual particles rotated during X–ray irradiation were recorded on a flat imaging plate and a one–dimensional diffraction profile, as a function of 2θ, was derived from the pattern. Weathered biotite (WB) particles with plate–like morphology showed a broad peak corresponding to a basal reflection with d = 10–14 Å, indicating various degrees of vermiculitization. Another peak of ∼ 7 Å was also detected in these WB particles, suggesting the parallel growth of kaolinite in the biotite particles. These characteristics were also found in the WB collected from an Abukuma granitic body, which is widespread in the eastern part of Fukushima. SR–µ–XRD of radioactive soil particles consisting of fine minerals or of those rich in organic matter indicated that these particles contain very fine 2:1 type clay minerals alongside detrital rock–forming minerals such as quartz and feldspar.
- 著者
- Tomoya SUZUKI Takeshi OGATA Mikiya TANAKA Tohru KOBAYASHI Hideaki SHIWAKU Tsuyoshi YAITA Hirokazu NARITA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.12, pp.1353-1360, 2019-12-10 (Released:2019-12-10)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 4
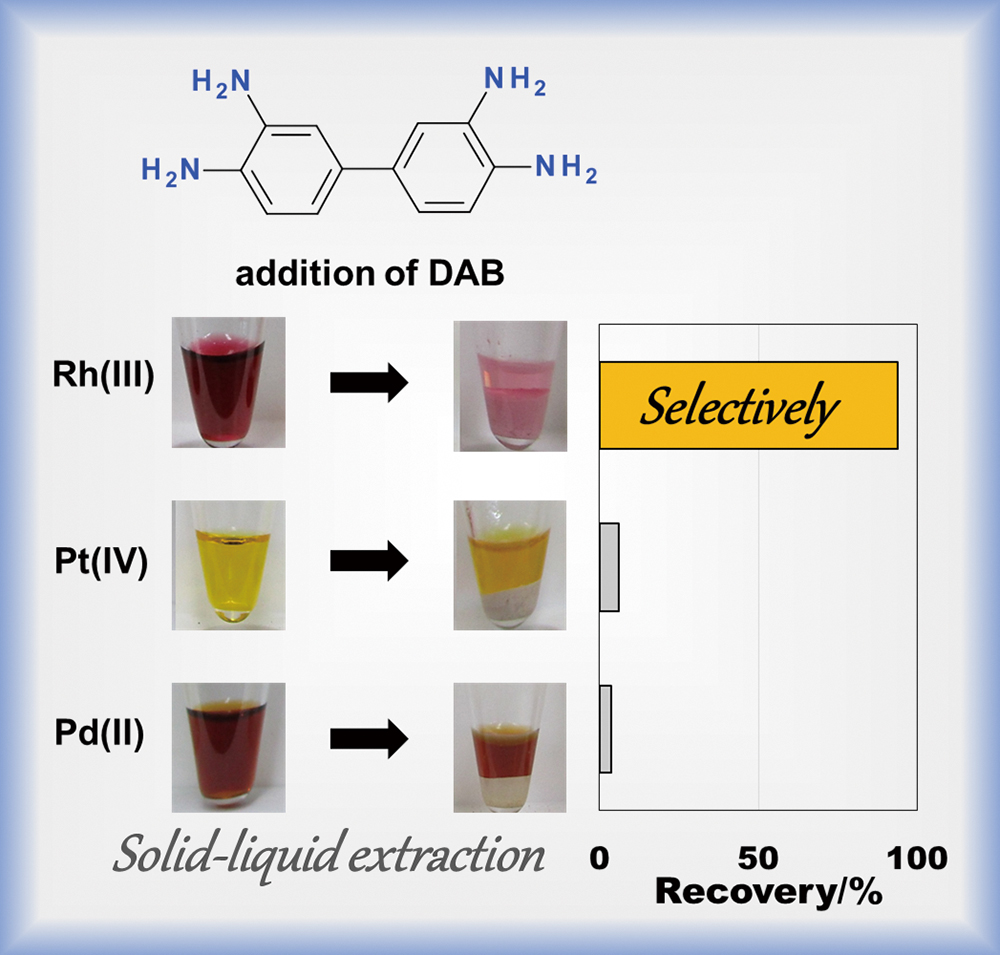
The effective recovery of Rh(III) from mixtures also containing Pd(II) and Pt(IV) is one of the most difficult tasks in platinum group metal refining. Adding 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) to 7 and 10 M HCl aqueous solutions containing Rh(III), Pd(II), and Pt(IV) chlorido species affords the effective separation of Rh(III) from Pd(II) and Pt(IV) through a process where Rh(III) becomes sequestered into solid phases composed of DAB. The stoichiometry and inner coordination sphere of the metal in Rh–DAB complexes were determined by estimating the Rh(III), H+, and Cl− concentrations in the solid phase and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements to clarify the mechanism of DAB selectivity for Rh(III). These results indicate that the Rh–DAB reaction in a concentrated HCl solution occurs in two steps: (1) the precipitation of DAB trihydrochloride salts, where DAB’s amino groups are protonated and (2) anion exchange of the trihydrochloride salts for chloride ions with [RhCl6]3−, which is the predominant species in a concentrated HCl solution. By contrast, ion-pair complexes with [PdCl4]2− and [PtCl6]2− were not observed in DAB phases. The significantly lower affinity of the DAB trihydro cation for [PtCl6]2− and [PdCl4]2− than for [RhCl6]3− in 7 and 10 M HCl solutions accounts for the effective separation of Rh(III) from Pd(II) and Pt(IV).