- 著者
- Akihiko Nakamura Kei-ichi Okazaki Tadaomi Furuta Minoru Sakurai Jun Ando Ryota Iino
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, pp.51-58, 2020 (Released:2020-07-10)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 4 5
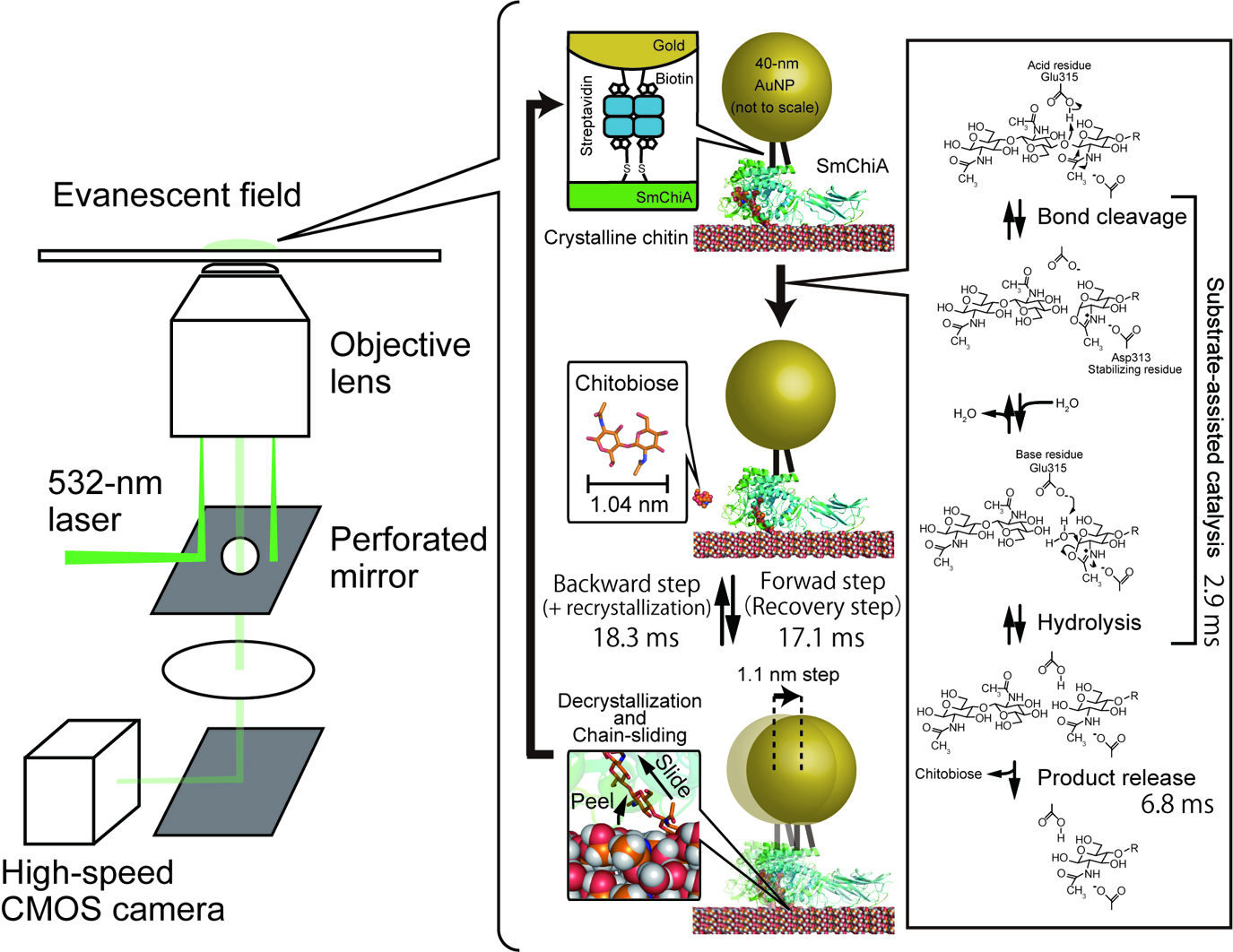
Motor proteins are essential units of life and are well-designed nanomachines working under thermal fluctuations. These proteins control moving direction by consuming chemical energy or by dissipating electrochemical potentials. Chitinase A from bacterium Serratia marcescens (SmChiA) processively moves along crystalline chitin by hydrolysis of a single polymer chain to soluble chitobiose. Recently, we directly observed the stepping motions of SmChiA labeled with a gold nanoparticle by dark-field scattering imaging to investigate the moving mechanism. Time constants analysis revealed that SmChiA moves back and forth along the chain freely, because forward and backward states have a similar free energy level. The similar probabilities of forward-step events (83.5%=69.3%+14.2%) from distributions of step sizes and chain-hydrolysis (86.3%=(1/2.9)/(1/2.9+1/18.3)×100) calculated from the ratios of time constants of hydrolysis and the backward step indicated that SmChiA moves forward as a result of shortening of the chain by a chitobiose unit, which stabilizes the backward state. Furthermore, X-ray crystal structures of sliding intermediate and molecular dynamics simulations showed that SmChiA slides forward and backward under thermal fluctuation without large conformational changes of the protein. Our results demonstrate that SmChiA is a burnt-bridge Brownian ratchet motor.
- 著者
- Akihiko Nakamura Kei-ichi Okazaki Tadaomi Furuta Minoru Sakurai Jun Ando Ryota Iino
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.BSJ-2020004, (Released:2020-06-09)
- 被引用文献数
- 5
- 著者
- Tatsushi Nishimoto Yuta Takahashi Shohei Miyama Tadaomi Furuta Minoru Sakurai
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.16, pp.196-204, 2019 (Released:2019-11-29)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 3 2
Group 3 late embryogenesis abundant (G3LEA) proteins, which act as a well-characterized desiccation protectant in anhydrobiotic organisms, are structurally disordered in solution, but they acquire a predominantly α-helical structure during drying. Thus, G3LEA proteins are now accepted as intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Their functional regions involve characteristic 11-mer repeating motifs. In the present study, to elucidate the origin of the IDP property of G3LEA proteins, we applied replica exchange molecular dynamics (REMD) simulation to a model peptide composed of two tandem repeats of an 11-mer motif and its counterpart peptide whose amino acid sequence was randomized with the same amino acid composition as that of the 11-mer motif. REMD simulations were performed for a single α-helical chain of each peptide and its double-bundled strand in a wide water content ranging from 5 to 78.3 wt%. In the latter case, we tested different types of arrangement: 1) the dipole moments of the two helices were parallel or anti-parallel and 2) due to the amphiphilic nature of the α-helix of the 11-mer motif, two types of the side-to-side contact were tested: hydrophilic-hydrophilic facing or hydrophobic-hydrophobic facing. Here, we revealed that the single chain alone exhibits no IDP-like properties, even if it involves the 11-mer motif, and the hydrophilic interaction of the two chains leads to the formation of a left-handed α-helical coiled coil in the dry state. These results support the cytoskeleton hypothesis that has been proposed as a mechanism by which G3LEA proteins work as a desiccation protectant.