- 著者
- Kei Kawada Tomoaki Ishida Kohei Jobu Tsuyoshi Ohta Hitoshi Fukuda Shumpei Morisawa Tetsushi Kawazoe Naohisa Tamura Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.6, pp.720-723, 2022-06-01 (Released:2022-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Aggression is the most common adverse effect of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). This study aimed to investigate the association of aggression with AED use. The reporting odds ratio (ROR) from adverse event reports, submitted to the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report database between 2004 and 2020, was used to calculate and investigate the association between AEDs and aggression. We also analyzed the association of aggression with the combined use of AEDs and the relationship between AED-associated aggression and patient characteristics. A total of 433 patients developed aggression. Significant aggression signals were detected for perampanel (crude ROR: 325.04, 95% confidence interval (CI): 118.48–752.58, p < 0.01), levetiracetam (crude ROR: 17.14, 95% CI: 10.33–26.90, p < 0.01), lacosamide (crude ROR: 16.90, 95% CI: 2.02–62.51, p < 0.01), lamotrigine (crude ROR: 15.98, 95% CI: 9.99–24.39, p < 0.01), valproate (crude ROR: 6.68, 95% CI: 4.27–10.02, p < 0.01), and carbamazepine (crude ROR: 2.47, 95% CI: 1.17–4.59, p < 0.01). The combined therapy with perampanel and levetiracetam had a significant aggression signal (adjusted ROR: 25.90, 95% CI: 1.14–59.10, p < 0.01). In addition, we found that aggression frequently occurred in patients <60 year (adjusted ROR: 2.88, 95% CI: 1.49–5.56, p < 0.01) treated with levetiracetam. These results may be useful for minimizing the risk of aggression during the treatment of AEDs.
- 著者
- Tomoaki Ishida Kei Kawada Shumpei Morisawa Kohei Jobu Yasuyo Morita Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.10, pp.1570-1576, 2020-10-01 (Released:2020-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 1 18
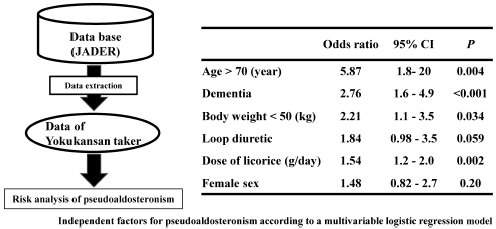
Yokukansan is a Kampo formula that is commonly used by the elderly because it is expected to improve peripheral symptoms of dementia and delirium. However, side effects from its use are frequently reported in the elderly. In particular, pseudoaldosteronism caused by the licorice contained in yokukansan leads to hypertension, hypokalemia, and muscle weakness, which may result in death. This study aimed to identify the risk factors of pseudoaldosteronism with yokukansan use. Using cases reported in the Japanese Adverse Drug Report (JADER) database, the reporting odds ratio (ROR) was calculated and compared to assess the risk of pseudoaldosteronism for each licorice-containing Kampo formula. We also analyzed the risk factors for pseudoaldosteronism in patients taking yokukansan. Yokukansan (ROR 2.4, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.9–2.8; p < 0.001) had a higher risk of pseudoaldosteronism than that of other licorice-containing Kampo formulas. Furthermore, the results of a logistic regression analysis in patients taking yokukansan showed that the licorice dose (OR 1.5, 95% CI 1.2–2.0; p < 0.01), older age (<70 years, OR 5.9, 95% CI 1.8–20; p < 0.01), dementia (OR 2.8, 95% CI 1.6–4.9; p < 0.001), low body weight (<50 kg, OR 2.2, 95% CI 1.1–3.5; p = 0.034) were risk factors for pseudoaldosteronism, Although not significant, treatment with loop diuretics (OR 1.8, 95% CI 0.98–3.5; p = 0.059) tended to increase the risk of pseudoaldosteronism. In summary, patients must understand the risk factors when considering taking yokukansan and reduce the licorice dose they consume.
- 著者
- Ayumu Hirata Hiroki Funato Megumi Nakai Michiro Iizuka Noriaki Abe Yusuke Yagi Hisashi Shiraishi Kohei Jobu Junko Yokota Kahori Hirose Masamitsu Hyodo Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.7, pp.1107-1111, 2016-07-01 (Released:2016-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 9
We previously prepared and pharmaceutically evaluated ginger orally disintegrating (OD) tablets, optimized the base formulation, and carried out a clinical trial in healthy adults in their 20 s and 50s to measure their effect on salivary substance P (SP) level and improved swallowing function. In this study, we conducted clinical trials using the ginger OD tablets in older people to clinically evaluate the improvements in swallowing function resulting from the functional components of the tablet. The ginger OD tablets were prepared by mixing the excipients with the same amount of mannitol and sucrose to a concentration of 1% ginger. Eighteen healthy older adult volunteers aged 63 to 90 were included in the swallowing function test. Saliva was collected before and 15 min after administration of the placebo and ginger OD tablets. Swallowing endoscopy was performed by an otolaryngologist before administration and 15 min after administration of the ginger OD tablets. A scoring method was used to evaluate the endoscopic swallowing. Fifteen minutes after taking the ginger OD tablets, the salivary SP amount was significantly higher than prior to ingestion or after taking the placebo (p<0.05). Among 10 subjects, one scored 1–3 using the four evaluation criteria. Overall, no aspiration occurred and a significant improvement in the swallowing function score was observed (p<0.05) after taking the ginger OD tablets. Our findings showed that the ginger OD tablets increased the salivary SP amount and improved swallowing function in older people with appreciably reduced swallowing function.
- 著者
- Tomoaki Ishida Kei Kawada Kohei Jobu Tetsushi Kawazoe Naohisa Tamura Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.4, pp.460-466, 2022-04-01 (Released:2022-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Bofutsushosan is a traditional Japanese Kampo medicine. In recent years, it has been reported to be effective in the treatment of lifestyle-related diseases, and its use is increasing. However, side effects from bofutsushosan administration are common, with drug-induced liver injury being the most frequently reported complication. In this study, we analyzed the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) database regarding the occurrence of liver injury after bofutsushosan administration. The results showed that bofutsushosan presented a significant reporting odds ratio (ROR) signal [crude ROR 14, 95% confidence interval (CI) 12–17; p < 0.001], indicating liver injury. Furthermore, the incidents of adverse events following bofutsushosan administration, as recorded in the JADER database, were higher in women aged between 30 and 59 years. The results of logistic regression analysis in patients taking this agent showed that females in the aforementioned age range had higher odds of developing drug-induced liver injury (adjusted ROR 5.5, 95% CI 2.8–11; p < 0.001). Therefore, although bofutsushosan is a useful drug for lifestyle-related diseases, it may be necessary to refrain from its overuse, and caution should be taken during its occasional use to avoid severe adverse events.
- 著者
- Hisashi Shiraishi Maho Fujino Naoki Shirakawa Nanao Ishida Hiroki Funato Ayumu Hirata Noriaki Abe Michiro Iizuka Kohei Jobu Junko Yokota Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.10, pp.1700-1705, 2017-10-01 (Released:2017-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 2 2
Minerals are essential for life, as they are a vital part of protein constituents, enzyme cofactors, and other components in living organisms. Deep sea water is characterized by its cleanliness and stable low temperature, and its possible health- and medical benefits are being studied. However, no study has yet evaluated the physical properties of the numerous commercially available deep sea water products, which have varying water sources and production methods. We analyzed these products’ mineral content and investigated their effect on living organism, focusing on immune functions, and investigated the relation between physiological immunoactivities and mineral intake. We qualitatively analyzed the mineral compositions of the deep sea water drinks and evaluated the drinks’ physical properties using principal component analysis, a type of multivariate analysis, of their mineral content. We create an iron and copper-deficient rat model and administered deep sea water drinks for 8 weeks. We then measured their fecal immunoglobulin A (IgA) to evaluate immune function. Principal component analysis suggested that physical properties of deep sea water drinks could be determined by their sources. Administration of deep sea water drinks increased fecal IgA, thus tending to stimulate immune function, but the extent of this effect varied by drink. Of the minerals contained in deep sea water, iron showed positive correlations with the fecal IgA. The principal component analysis used in this study is suitable for evaluating deep sea water containing many minerals, and our results form a useful basis for comparative evaluations of deep sea water’s bioactivity.
- 著者
- Yasuyo Morita Tomoaki Ishida Shumpei Morisawa Kohei Jobu Yangran Ou Hiroko Fujita Kazuhiro Hanazaki Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.1, pp.32-38, 2021-01-01 (Released:2021-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Sarcopenia is a disease whose symptoms include decreased muscle mass and weakened muscle strength with age. In sarcopenia, decreased production of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) increases ubiquitin ligases, such as Atrogin1 and Muscle RING-Finger Protein-1 (MuRF1), by activating forkhead box O (FOXO), and inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress increase the expression of ubiquitin ligases by activating the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB). In addition, increased levels of ubiquitin ligases cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Conversely, sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) is known to regulate the expression of ubiquitin ligases by suppressing the activities of NF-κB and FOXO. In this study, we evaluated the effect that juzentaihoto hot water extract (JTT) has on skeletal muscle atrophy and motor function by administering it to senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 (SAMP8). The group treated with JTT displayed larger gastrocnemius muscle (GA) and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) weights, larger GA muscle fiber cross-sectional areas, and motor function decline during rota-rod tests. JTT also increased IGF-1 serum levels, as well as mRNA Sirt1 levels in GA. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and mRNA levels of Atrogin1 and MuRF1 in GA were reduced by JTT. The muscle fiber cross-sectional area of GA was correlated with the mRNA levels of Sirt1 in GA. The results of this study suggested that JTT administration suppresses skeletal muscle atrophy and motor function decline in SAMP8 mice. This effect may be associated with the increased expression levels of Sirt1 and IGF-1 by JTT.
- 著者
- Tomoaki Ishida Michiro Iizuka Yanglan Ou Shunpei Morisawa Ayumu Hirata Yusuke Yagi Kohei Jobu Yasuyo Morita Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.7, pp.1128-1133, 2019-07-01 (Released:2019-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 7
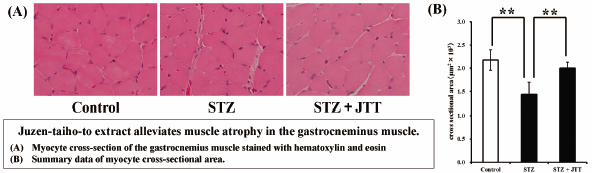
In diabetic patients, skeletal muscle atrophy occurs due to increased oxidative stress and inflammation. Skeletal muscle atrophy reduces the QOL of patients and worsens life prognosis. Therefore, development of preventive therapy for muscle atrophy in hyperglycemic state is eagerly awaited. Juzentaihoto is a medicinal herb that has a function to supplement physical strength, and it is expected to prevent muscle atrophy. To determine the preventive effect of juzentaihoto on muscle atrophy in hyperglycemic state, streptozotocin (STZ) was administered to induce diabetes in mice and the preventive effect of juzentaihoto was evaluated. Mice that received juzentaihoto extract (JTT) showed that the decrease in muscle fiber cross-sectional area in the gastrocnemius muscle was reversed. Additionally, the expression level of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), an inflammatory cytokine, in serum decreased, and that of ubiquitin ligase (atrogin-1, muscle RING-finger protein-1) mRNA in skeletal muscle decreased. An anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 showed increased levels in the serum and increased levels in spleen cell culture supernatant collected from mice that received JTT. JTT had no effect on the blood glucose level. These results suggest that prophylactic administration of JTT to STZ-induced diabetic mice affects immune cells such as in spleen, causing an anti-inflammatory effect and inhibiting excessive activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, to reverse muscle atrophy.