- 著者
- Kazuo Yamada Atsushi Watanabe Haruo Takeshita Atsushi Fujita Noriko Miyake Naomichi Matsumoto Ken-ichi Matsumoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.9, pp.1596-1599, 2019-09-01 (Released:2019-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 5 5
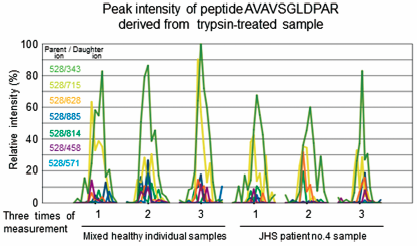
Joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) (also termed hypermobility type Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, hEDS) is a heritable connective tissue disorder that is characterized by generalized joint hypermobility, chronic pain, fatigue, and minor skin changes. Initially, it was reported that there is a small subset of patients with JHS/hEDS who have haploinsufficiency of tenascin-X (TNX). However, the relationship between TNXB and JHS/hEDS has not been reported at all afterwards. EDS was reclassified into thirteen types in 2017, and the causative gene of JHS/hEDS remained to be identified. Therefore, in this study in order to determine whether JHS/hEDS can be diagnosed by the concentrations of serum form of TNX (sTNX), we measured the concentrations of sTNX in 17 JHS/hEDS patients. The sTNX concentrations in half of the JHS/hEDS patients were significantly lower than those in healthy individuals. No mutations, insertions or deletions were detected in the TNX exon sequence of the JHS/hEDS patients except for one in patient. That patient has a heterozygous mutation. A correlation between sTNX concentration and mutation of the TNXB genomic sequence was not found in the JHS/hEDS patients. These results indicate that the decrease in sTNX concentration could be used as a risk factor for JHS/hEDS.
- 著者
- Makiko Takenaka Noriko Miyake Toshiyuki Kimura Setsuko Todoriki Tetsuo Urushiyama
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Food Science and Technology
- 雑誌
- Food Science and Technology Research (ISSN:13446606)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.3, pp.245-255, 2022 (Released:2022-05-20)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 2
This study aimed to find an effective protocol as a cooking pre-treatment for the petioles and young spikes of Petasites japonicus to reduce their contents of pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs), a type of natural toxin in plants such as the Asteraceae and Boraginaceae families. After determining the most common cooking pre-treatment methods for petioles and young spikes of Petasites japonicus from a survey of recipes, various treatments were examined for their effectiveness at reducing PAs. It was concluded that both boiling and soaking processes were important for the reduction of PAs in pre-treatment of cooking the petioles and the young spikes of Petasites japonicus, and that a longer soaking time had a greater effect in reducing PAs. PAs in the petioles and young spikes decreased to less than 50% of the original amount in 1 h and 6 h, respectively during soaking after boiling (and peeling).