- 著者
- Toshihiro Nishizawa Osamu Toyoshima Ryo Kondo Kazuma Sekiba Yosuke Tsuji Hirotoshi Ebinuma Hidekazu Suzuki Chizu Tanikawa Koichi Matsuda Kazuhiko Koike
- 出版者
- SOCIETY FOR FREE RADICAL RESEARCH JAPAN
- 雑誌
- Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition (ISSN:09120009)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.20-41, (Released:2020-07-16)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 10
The ABC method combined with Helicobacter pylori antibody and serum pepsinogen is a useful predictive method for stomach cancer. Kyoto classification is a new grading system for endoscopic gastritis. However, the consistency of the Kyoto score with the ABC method remains unclear. The Kyoto classification score, which ranges from 0 to 8, is based on the following findings: atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, diffuse redness, nodularity, and enlarged folds. Furthermore, we defined a simplified Kyoto classification score as the sum of scores of just atrophy and intestinal metaplasia. The association between the Kyoto classification score and the ABC method was analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis and Steel-Dwass tests. A total of 307 subjects were enrolled. Kyoto classification scores were similar in groups B, C, and D, while scores in group A were significantly lower than those of the other groups. The simplified Kyoto classification score showed the same stepwise increase as the classification of the ABC method. In conclusion, unlike the Kyoto classification score, the simplified Kyoto score showed the same significant stepwise increase as the classification of the ABC method.
- 著者
- Ryo Kondo Ayuki Nakano Daiki Asano Akane Morita Shiho Arima Asami Mori Kenji Sakamoto Tohru Nagamitsu Tsutomu Nakahara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.5, pp.859-863, 2020-05-01 (Released:2020-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 26
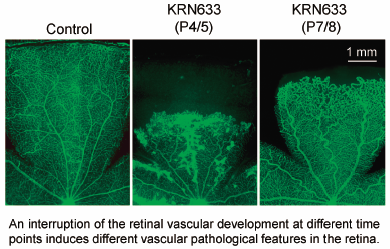
Pathological angiogenesis is a leading cause of blindness in several retinal diseases. The key driving factor inducing pathological angiogenesis is the pronounced hypoxia leading to a marked, increased production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The aim of this study was to determine whether the abnormal vascular growth occurs in a manner dependent on the degree of the vascular defects. Vascular defects of two different degrees were created in the retina by subcutaneously treating neonatal rats with the VEGF receptor (VEGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor KRN633 on postnatal day (P) 4 and P5 (P4/5) or P7 and P8 (P7/8). The structure of the retinal vasculature changes was examined immunohistochemically. Prevention of vascular growth and regression of some preformed capillaries were observed on the next day, after completion of each treatment (i.e., P6 and P9). The vascular regrowth occurred as a result of eliminating the inhibitory effect on the VEGFR signaling pathway. KRN633 (P4/5)-treated rats exhibited a retinal vasculature with aggressive intravitreal neovascularization on P21. On the other hand, the appearance of tortuous arteries is a representative vascular pathological feature in retinas of KRN633 (P7/8)-treated groups. These results suggest that an interruption of the retinal vascular development at different time points induces different vascular pathological features in the retina. Pharmacological agents targeting the VEGF signaling pathway are useful for creating an abnormal retinal vasculature with various pathological features in order to evaluate the efficacy of anti-angiogenic compounds.