- 著者
- Nobutaka Nagano Atsuko Muranaka Ryo Nishikawa Wataru Ohwada Hidemichi Kouzu Naoyuki Kamiyama Takefumi Fujito Atsushi Mochizuki Daigo Nagahara Mitsuhiro Nakanishi Yukiko Ohkubo Shin Hisahara Satoshi Nakao Nagaaki Katoh Aki Ishikawa Akihiro Sakurai Toshiyuki Yano
- 出版者
- International Heart Journal Association
- 雑誌
- International Heart Journal (ISSN:13492365)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.1, pp.168-175, 2022-01-29 (Released:2022-01-29)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Diagnostic strategies for symptomatic transthyretin (ATTR) cardiac amyloidosis showing typical morphological features such as increased ventricular wall thickness and myocardial injury such as an elevation in serum troponin T level have been established, but those for subclinical cardiac amyloidosis are limited. In the era when effective therapies to suppress/delay progression of ATTR cardiac amyloidosis are available, early detection of cardiac involvement plays a crucial role in appropriate decision-making for treatment in TTR mutation carriers who have a family history of heart failure and death due to ATTR amyloidosis. Findings of three cases with known pathogenic transthyretin (TTR) mutations (p.Ser70Arg, p.Phe53Val, and p.Val50Met) and family histories of death for amyloidosis were presented. Two cases were asymptomatic, and a case carrying p.Phe53Val had gastrointestinal symptoms and autonomic neuropathy. Levels of plasma N-terminal fragment of pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and troponin T were within normal ranges in all cases, but results of cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) and bone scintigraphy clearly revealed the presence of cardiac involvement in all cases, even in a case without echocardiographic abnormalities including left ventricular hypertrophy and relative apical sparing of longitudinal strain shown by two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography. Electrocardiography revealed modest abnormalities including reduced R wave amplitude in V2 and a trend toward left axis deviation in all cases. In conclusion, CMR, bone scintigraphy, and electrocardiography are useful for early detection of ATTR cardiac amyloidosis in TTR mutation carriers. The role of comprehensive cardiac assessment in the early detection of cardiac amyloidosis in TTR mutation carriers is discussed.
- 著者
- Satoshi Nakao Haruna Hatahira Sayaka Sasaoka Shiori Hasegawa Yumi Motooka Natsumi Ueda Junko Abe Akiho Fukuda Misa Naganuma Hiroyuki Kanoh Mariko Seishima Motoyuki Ishiguro Yasutomi Kinosada Mitsuhiro Nakamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.12, pp.2158-2165, 2017-12-01 (Released:2017-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 50
- 被引用文献数
- 10 27
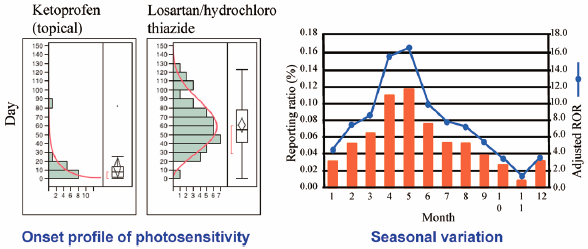
Drug-induced photosensitivity (DIP) refers to the development of cutaneous disorders caused by the combined effects of different medications and light. The aim of this study was to obtain new information on drug risk comparisons and on DIP onset profiles, including seasonal variations, for clinically used prescription drugs. We analyzed reports of DIP recorded in the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) database using a reporting odds ratio (ROR). We also used Weibull proportional-hazards models for each drug to examine the patterns of DIP. The JADER database contains 430587 reports recorded from April 2004 to November 2016. The ROR values (95% confidence interval [CI]) of losartan/hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), valsartan/HCTZ, and ketoprofen were 214.5 (162.1–283.9), 104.7 (66.3–165.5), and 117.9 (76.6–181.5), respectively. For time-to-onset analysis, the median durations (interquartile range) for DIP caused by losartan/HCTZ, valsartan/HCTZ, and ketoprofen were 56 (41–78), 49 (38–88), and 8 (2–14) days, respectively. The lower limit of the 95% CI for the Weibull shape parameter β value for losartan/HCTZ was greater than 1. More than half of the reports of DIP onset following the administration of ketoprofen were recorded within 10 d of treatment initiation. The seasonal variation of photosensitivity reactions was shown to follow an annual sinusoidal pattern with a peak in April and May. Based on the results, losartan/HCTZ, valsartan/HCTZ, and ketoprofen should be used carefully in clinical practice to avoid DIP.