- 著者
- Ikuya Yamada Yuta Kato Hiroshi Nakajima Hidekazu Ikeno Shigeo Mori Shogo Kawaguchi
- 出版者
- The Japan Institute of Metals and Materials
- 雑誌
- MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS (ISSN:13459678)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.MT-MG2022005, (Released:2023-01-10)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 1
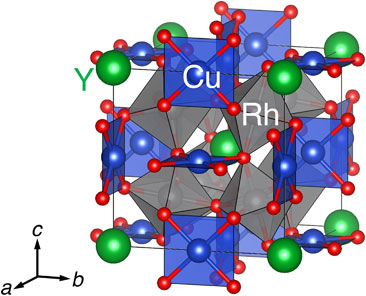
A novel oxide YCu3Rh4O12 has been obtained using high-pressure and high-temperature conditions of 12 GPa and 1573 K. Electron diffraction and synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction data demonstrates that YCu3Rh4O12 crystallizes in a cubic AA′3B4O12-type quadruple perovskite structure. The valence state is estimated to be Y3+Cu3+3Rh3+4O12 by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The electric resistivity and magnetization data prove that YCu3Rh4O12 is a diamagnetic insulator, which is expected from the electron configurations of Cu3+ (3d8, low spin, S = 0) and Rh3+ (4d6, low spin, S = 0) ions. The first-principle calculation displays the insulating band structure for YCu3Rh4O12. The valence state transition from Ca2+Cu2.8+3Rh3.4+4O12 to Y3+Cu3+3Rh3+4O12 indicates that the doped electrons by the substitution of Y3+ for Ca2+ are not simply injected to Cu and/or Rh ions, realizing unusual charge redistributions consisting of the simultaneous Cu oxidation (Cu2.8+ → Cu3+) and Rh reduction (Rh3.4+ → Rh3+).
- 著者
- Syota SEINO Takeru KIMOTO Hidemi YOSHIDA Kunikazu TANJI Tomoh MATSUMIYA Ryo HAYAKARI Kazuhiko SEYA Shogo KAWAGUCHI Kazushi TSURUGA Hiroshi TANAKA Tadaatsu IMAIZUMI
- 出版者
- Biomedical Research Press
- 雑誌
- Biomedical Research (ISSN:03886107)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.105-115, 2018-06-01 (Released:2018-06-12)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 10 15
Accumulation and oligomerization of amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptides have been known to be a potent cause of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). To expand the possibilities of preventing AD, we investigated the effects of resveratrol dimers, gnetin C and ε-viniferin, on Aβ 1–42 (Aβ42) production and the reduced cell viability observed after Aβ42 treatment (monomers, 10 μM) in cultured SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Among them, addition of gnetin C (20 μM) into the media reduced Aβ42 production most efficiently. Gnetin C suppressed the expression of β-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme-1 (BACE1, β-secretase). Furthermore, gnetin C ameliorated the Aβ42-reduced cell viability most significantly. Concomitantly, gnetin C reduced intracellular Aβ oligomers (ca. 15 and 130 kDa) and elevated both levels of intracellular and extracellular Aβ monomers. Under the treatment with or without Aβ42, gnetin C upregulated the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14) which is assumed to be an Aβ-decomposing enzyme. Gnetin C may thereby prevent Aβ toxicity by suppressing BACE1 and enhancing MMP-14, together with reducing both internalization and oligomerization of exogenous Aβ monomers. The use of gnetin C may lead to the prevention of Aβ-mediated diseases, particularly AD.