7 0 0 0 OA Pathology of Sapien 3 After Impella-CP Insertion for Acute Coronary Syndrome With Cardiogenic Shock
- 著者
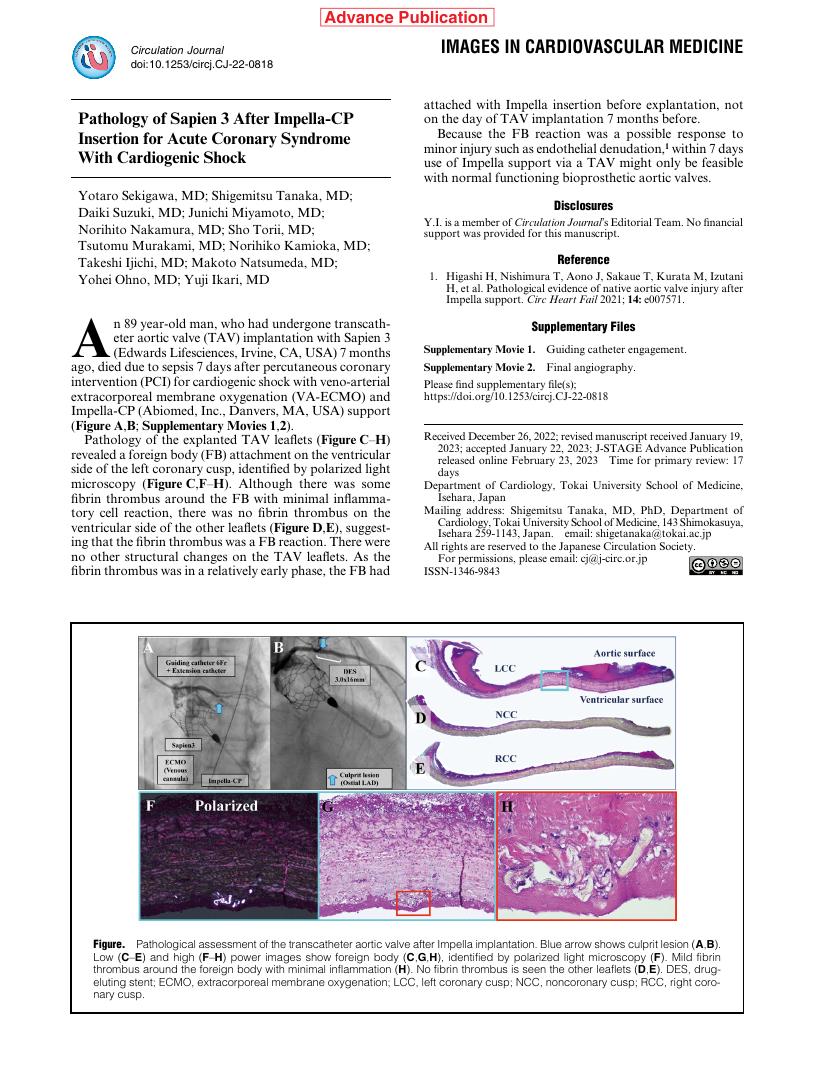
- Yotaro Sekigawa Shigemitsu Tanaka Daiki Suzuki Junichi Miyamoto Norihito Nakamura Sho Torii Tsutomu Murakami Norihiko Kamioka Takeshi Ijichi Makoto Natsumeda Yohei Ohno Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.87, no.5, pp.672, 2023-04-25 (Released:2023-04-25)
- 参考文献数
- 1
2 0 0 0 OA Pathology of Sapien 3 After Impella-CP Insertion for Acute Coronary Syndrome With Cardiogenic Shock
- 著者
- Yotaro Sekigawa Shigemitsu Tanaka Daiki Suzuki Junichi Miyamoto Norihito Nakamura Sho Torii Tsutomu Murakami Norihiko Kamioka Takeshi Ijichi Makoto Natsumeda Yohei Ohno Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0818, (Released:2023-02-23)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Tsuyoshi Shiga Tsuyoshi Suzuki Keisuke Kida Atsushi Suzuki Takashi Kohno Akiko Ushijima Shunsuke Kiuchi Shunsuke Ishii Makoto Murata Takeshi Ijichi Makoto Suzuki Masako Nishikawa on behalf of the EXCILE-HF Trial Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CR-22-0134, (Released:2023-03-24)
- 参考文献数
- 15
Background: A high resting heart rate is an independent risk factor for mortality and morbidity in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Ivabradine selectively inhibits the funny current (If) and decreases heart rate without affecting cardiac conduction, contractility, or blood pressure. The effect of ivabradine on exercise tolerance in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) on standard drug therapies remains unclear.Methods and Results: This multicenter interventional trial of patients with HFrEF and a resting heart rate ≥75 beats/min in sinus rhythm treated with standard drug therapies will consist of 2 periods: a 12-week open-label, randomized, parallel-group intervention period (standard drug treatment+ivabradine group and standard drug treatment group) to compare changes in exercise tolerance between the 2 groups; and a 12-week open-label ivabradine treatment period for all patients to evaluate the effect of adding ivabradine on exercise tolerance. The primary endpoint will be the change in peak oxygen uptake (V̇O2) during the cardiopulmonary exercise test from Week 0 (baseline) to Week 12. Secondary endpoints will be time-dependent changes in peak V̇O2from Week 0 to Weeks 12 and 24. Adverse events will also be evaluated.Conclusions: The EXCILE-HF trial will provide meaningful information regarding the effects of ivabradine on exercise tolerance in patients with HFrEF receiving standard drug therapies and suggestions for the initiation of ivabradine treatment.
- 著者
- Makoto Natsumeda Gaku Nakazawa Tsutomu Murakami Sho Torii Takeshi Ijichi Yohei Ohno Naoki Masuda Norihiko Shinozaki Nobuhiko Ogata Fuminobu Yoshimachi Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.79, no.4, pp.802-807, 2015-03-25 (Released:2015-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 18 20
Background:Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) guided with fractional flow reserve (FFR) has been shown to improve clinical outcome. Although coronary angiography is the standard method for PCI guidance, the visual severity of stenosis is not always correlated with functional severity, suggesting that there are additional angiographic factors that affect functional ischemia.Methods and Results:To evaluate angiographic predictors of positive FFR in stenotic lesions, angiographic characteristics of 260 consecutive patients (362 lesions) who underwent FFR testing from April 2009 to September 2012 were analyzed. A scoring system (STABLED score) using these predictors was developed and compared with quantitative coronary angiography (QCA). %Diameter stenosis >50% (OR, 8.43; P<0.0001), tandem lesion (OR, 4.00; P<0.0001), true bifurcation (OR, 2.42; P=0.028), lesion length >20 mm (OR, 5.40; P=0.0002), and distance from ostium <20 mm (OR, 1.94; P=0.028) were determined as independent predictors of positive FFR. Area under the ROC curve for probability of positive FFR using the STABLED score (Stenosis 2 points, TAndem lesion 1 point, Bifurcation 1 point, LEsion length 1 point, Distance from ostium 1 point) was 0.85, higher than that for QCA stenosis alone (0.76). STABLED score ≥3 had 72.3% sensitivity and 83.6% specificity for predicting positive FFR, and PPV was 76.7%.Conclusions:Specific angiographic features are applicable for predicting functional ischemia. STABLED score correlates well with FFR. (Circ J 2015; 79: 802–807)