- 著者
- Mitsuaki Sawano Shun Kohsaka Hideki Ishii Yohei Numasawa Kyohei Yamaji Taku Inohara Tetsuya Amano Yuji Ikari Masato Nakamura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0098, (Released:2021-06-24)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 24
Background:Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) hospital survivors experience a wide array of late adverse cardiac events, despite considerable advances in the quality of care. We investigated 30-day and 1-year outcomes of ACS hospital survivors using a Japanese nationwide cohort.Methods and Results:We studied 20,042 ACS patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in 2017: 10,242 (51%) with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), 3,027 (15%) with non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and 6,773 (34%) with unstable angina (UA). The mean (±SD) age was 69.6±12.4 years, 77% of the patients were men, and 20% had a previous history of PCI. The overall 30-day all-cause, cardiac, and non-cardiac mortality rates were 3.0%, 2.4%, and 0.6%, respectively. The overall 1-year incidence of all-cause, cardiac, and non-cardiac death was 7.1%, 4.2%, and 2.8%, respectively. Compared with UA patients, STEMI patients had a higher risk of all fatal events, non-fatal ischemic stroke, and acute heart failure, and NSTEMI patients had a higher risk of heart failure.Conclusions:The results from our ACS hospital survivor PCI database suggest the need to improve care for the acute myocardial infarction population to lessen the burden of 30-day mortality due to ACS, heart failure, and sudden cardiac death, as well as 1-year ischemic stroke and heart failure events.
11 0 0 0 OA JCS 2022 Guideline Focused Update on Diagnosis and Treatment in Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease
- 著者
- Shintaro Nakano Shun Kohsaka Taishiro Chikamori Kenji Fukushima Yoshio Kobayashi Ken Kozuma Susumu Manabe Hitoshi Matsuo Masato Nakamura Takayuki Ohno Mitsuaki Sawano Koichi Toda Yasunori Ueda Hiroyoshi Yokoi Yodo Gatate Tokuo Kasai Yoshiaki Kawase Naoya Matsumoto Hitoshi Mori Ryo Nakazato Nozomi Niimi Yuichi Saito Ayumi Shintani Ippei Watanabe Yusuke Watanabe Yuji Ikari Masahiro Jinzaki Masami Kosuge Kenichi Nakajima Takeshi Kimura on behalf of the JCS Joint Working Group
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-1041, (Released:2022-03-11)
- 参考文献数
- 245
- 被引用文献数
- 40
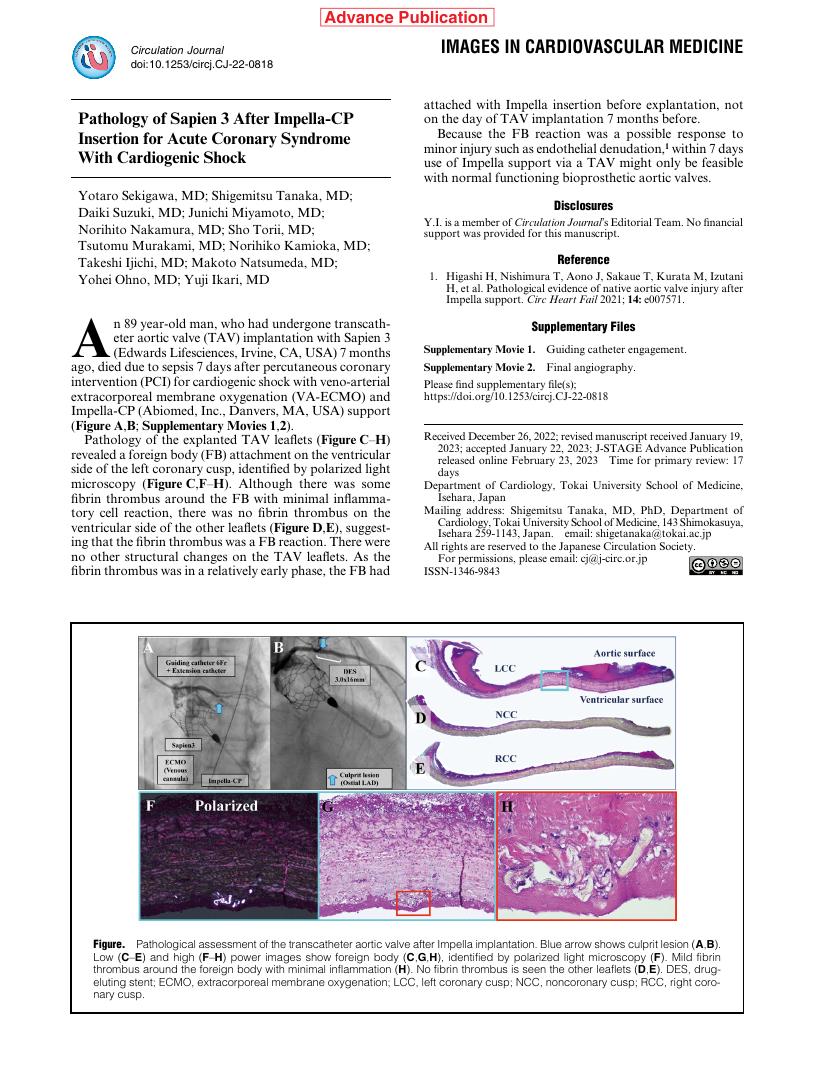
7 0 0 0 OA Pathology of Sapien 3 After Impella-CP Insertion for Acute Coronary Syndrome With Cardiogenic Shock
- 著者
- Yotaro Sekigawa Shigemitsu Tanaka Daiki Suzuki Junichi Miyamoto Norihito Nakamura Sho Torii Tsutomu Murakami Norihiko Kamioka Takeshi Ijichi Makoto Natsumeda Yohei Ohno Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.87, no.5, pp.672, 2023-04-25 (Released:2023-04-25)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Yuji Ikari Yuya Matsue Sho Torii Misaki Hasegawa Kazuki Aihara Shunsuke Kuroda Takahide Sano Takeshi Kitai Taishi Yonetsu Shun Kohsaka Takuya Kishi Issei Komuro Ken-ichi Hirata Koichi Node Shingo Matsumoto
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0087, (Released:2021-04-29)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 13
Background:Cardiovascular diseases and/or risk factors (CVDRF) have been reported as risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Methods and Results:In total, we selected 693 patients with CVDRF from the CLAVIS-COVID database of 1,518 cases in Japan. The mean age was 68 years (35% females). Statin use was reported by 31% patients at admission. Statin users exhibited lower incidence of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) insertion (1.4% vs. 4.6%, odds ratio [OR]: 0.295, P=0.037) and septic shock (1.4% vs. 6.5%, OR: 0.205, P=0.004) despite having more comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus.Conclusions:This study suggests the potential benefits of statins use against COVID-19.
2 0 0 0 OA Pathology of Sapien 3 After Impella-CP Insertion for Acute Coronary Syndrome With Cardiogenic Shock
- 著者
- Yotaro Sekigawa Shigemitsu Tanaka Daiki Suzuki Junichi Miyamoto Norihito Nakamura Sho Torii Tsutomu Murakami Norihiko Kamioka Takeshi Ijichi Makoto Natsumeda Yohei Ohno Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0818, (Released:2023-02-23)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Hitomi Horinouchi Tomoo Nagai Yohei Ohno Junichi Miyamoto Tsutomu Murakami Norihiko Kamioka Koichiro Yoshioka Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine
- 雑誌
- Internal Medicine (ISSN:09182918)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.0638-22, (Released:2023-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Objective This study retrospectively compared the outcomes of emergently admitted patients with aortic stenosis (AS) with or without urgent transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). Methods Patients hospitalized between February 2015 and December 2019 for symptomatic AS were retrospectively analyzed by comparing the received conservative management (continued medical therapy with or without elective surgical transcatheter replacement [SAVR] or TAVR scheduled after the index hospitalization) and urgent TAVR (TAVR during the index hospitalization). Results The cohort comprised 114 patients with symptomatic AS who required emergency admission. Urgent TAVR was performed for 37 patients, while conservative management was provided for 77 patients, including 1 who received urgent SAVR. Urgent TAVR was more likely to be performed in patients with a history of hospitalization for heart failure, high New York Heart Association class scores, a lower clinical frailty scale at admission, and a high aortic valve peak velocity (P = 0.01, P <0.001, P <0.01, and P = 0.02, respectively). Kaplan-Meier analyses with log-rank test revealed favorable outcomes of urgent TAVR in all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events within 60 days of admission (p <0.01, p <0.01, respectively). Conclusions Urgent TAVR had better short-term outcomes in patients with symptomatic AS who required emergency hospital admission than conservative management. When considering urgent TAVR, patients with typical heart failure symptoms due to AS with a history of heart failure hospitalization and relatively little frailty can be selected.
- 著者
- Shintaro Nakano Shun Kohsaka Taishiro Chikamori Kenji Fukushima Yoshio Kobayashi Ken Kozuma Susumu Manabe Hitoshi Matsuo Masato Nakamura Takayuki Ohno Mitsuaki Sawano Koichi Toda Yasunori Ueda Hiroyoshi Yokoi Yodo Gatate Tokuo Kasai Yoshiaki Kawase Naoya Matsumoto Hitoshi Mori Ryo Nakazato Nozomi Niimi Yuichi Saito Ayumi Shintani Ippei Watanabe Yusuke Watanabe Yuji Ikari Masahiro Jinzaki Masami Kosuge Kenichi Nakajima Takeshi Kimura on behalf of the JCS Joint Working Group
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.5, pp.882-915, 2022-04-25 (Released:2022-04-25)
- 参考文献数
- 245
- 被引用文献数
- 40
- 著者
- Makoto Natsumeda Gaku Nakazawa Tsutomu Murakami Sho Torii Takeshi Ijichi Yohei Ohno Naoki Masuda Norihiko Shinozaki Nobuhiko Ogata Fuminobu Yoshimachi Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.79, no.4, pp.802-807, 2015-03-25 (Released:2015-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 18 20
Background:Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) guided with fractional flow reserve (FFR) has been shown to improve clinical outcome. Although coronary angiography is the standard method for PCI guidance, the visual severity of stenosis is not always correlated with functional severity, suggesting that there are additional angiographic factors that affect functional ischemia.Methods and Results:To evaluate angiographic predictors of positive FFR in stenotic lesions, angiographic characteristics of 260 consecutive patients (362 lesions) who underwent FFR testing from April 2009 to September 2012 were analyzed. A scoring system (STABLED score) using these predictors was developed and compared with quantitative coronary angiography (QCA). %Diameter stenosis >50% (OR, 8.43; P<0.0001), tandem lesion (OR, 4.00; P<0.0001), true bifurcation (OR, 2.42; P=0.028), lesion length >20 mm (OR, 5.40; P=0.0002), and distance from ostium <20 mm (OR, 1.94; P=0.028) were determined as independent predictors of positive FFR. Area under the ROC curve for probability of positive FFR using the STABLED score (Stenosis 2 points, TAndem lesion 1 point, Bifurcation 1 point, LEsion length 1 point, Distance from ostium 1 point) was 0.85, higher than that for QCA stenosis alone (0.76). STABLED score ≥3 had 72.3% sensitivity and 83.6% specificity for predicting positive FFR, and PPV was 76.7%.Conclusions:Specific angiographic features are applicable for predicting functional ischemia. STABLED score correlates well with FFR. (Circ J 2015; 79: 802–807)
- 著者
- Yoichi Takaya Teiji Akagi Hidehiko Hara Hideaki Kanazawa Yuji Ikari Akihiro Isotani Shinichi Shirai Shunsuke Kubo Takao Morikawa Toru Naganuma Mike Saji Shingo Kuwata Go Hiasa Yusuke Watanabe Masahiro Yamawaki Masao Imai Takashi Matsumoto Masanori Yamamoto Tsutomu Murakami Masahiko Asami Isamu Mizote Tsukasa Okai Hiroki Bota Hiroshi Ito
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0048, (Released:2022-04-05)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Background: Transcatheter mitral valve repair with the MitraClip system has been established in selected high-risk patients. The MitraClip procedure results in a relatively large iatrogenic atrial septal defect (iASD). This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and clinical course of iASD requiring transcatheter closure following the MitraClip procedure.Methods and Results: This study was conducted at all 59 institutions that perform transcatheter mitral valve repair with the MitraClip system in Japan. The data of patients on whom transcatheter iASD closure was performed were collected. Of the 2,722 patients who underwent the MitraClip procedure, 30 (1%) required transcatheter iASD closure. The maximum iASD size was 9±4 mm (range, 3–18 mm). The common clinical course of transcatheter iASD closure was hypoxemia with right-to-left shunt or right-sided heart failure with left-to-right shunt. Of the 30 patients, 22 (73%) required transcatheter closure within 24 h following the MitraClip procedure, including 12 with hypoxemia and 5 with right-sided heart failure complicated with cardiogenic shock. Of the 5 patients, 2 required mechanical circulatory support devices. Twenty-one patients immediately underwent transcatheter iASD closure, and hemodynamic deteriorations were resolved; however, 1 patient died without having undergone transcatheter closure.Conclusions: Transcatheter iASD closure was required in 1% of patients who underwent the MitraClip procedure. Many of these patients immediately underwent transcatheter iASD closure because of hypoxemia with right-to-left shunt or right-sided heart failure with left-to-right shunt.
- 著者
- Shingo Matsumoto Satoshi Noda Sho Torii Yuji Ikari Shunsuke Kuroda Takeshi Kitai Taishi Yonetsu Shun Kohsaka Koichi Node Takanori Ikeda Yuya Matsue
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.7, pp.315-321, 2022-07-08 (Released:2022-07-08)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: Male sex is associated with a worse clinical course and outcomes of COVID-19, particularly in older patients. However, studies on COVID-19 patients with cardiovascular disease and/or risk factors (CVDRF), which are representative risk factors of COVID-19, are limited. In this study, we investigated the effect of sex on the outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with CVDRF.Methods and Results: We analyzed 693 COVID-19 patients with CVDRF. Patients were divided into 2 groups based on sex, and baseline characteristics and in-hospital outcomes were compared between the 2 groups. The mean age of the 693 patients was 68 years; 64.8% were men and 96.1% were Japanese. In a univariate analysis model, sex was not significantly associated with in-hospital mortality (odds ratio [OR] 1.22; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.74–2.02; P=0.43). However, men had higher in-hospital mortality than women, especially among older (age ≥80 years) patients (OR 2.21; 95% CI 1.11–4.41; P=0.024). After adjusting for age and pivotal risk factors (hypertension, diabetes, heart failure, coronary artery disease, chronic lung disease, and chronic kidney disease), multivariate analysis suggested that male sex was an independent predictor of in-hospital mortality (OR 2.20; 95% CI 1.23–3.92; P=0.008).Conclusions: In this post hoc analysis of a nationwide registry focusing on patients with COVID-19 and CVDRF, men had higher in-hospital mortality than women, especially among older patients.
- 著者
- Yoshihiro Morino Seiji Tamiya Naoki Masuda Yota Kawamura Masakazu Nagaoka Takashi Matsukage Nobuhiko Ogata Gaku Nakazawa Teruhisa Tanabe Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.1006040751, (Released:2010-06-09)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 26 47
Background: Several studies have indicated that the clinical outcomes of sirolimus-eluting stents (SES) are significantly associated with longitudinal positioning of the stent relative to the underlying plaque distribution. Methods and Results: Optimal SES landing was determined using unique stepwise intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) criteria, mainly targeting the sites with plaque burden <50% (plaque area/external elastic membrane area ×100). To verify the criteria, (1) achievability and (2) actual impact on clinical and angiographic outcomes were assessed. A total of 162 consecutive patients with 180 lesions were enrolled and treated according to the IVUS criteria. Plaque burden at the proximal and distal margins was 41.4±13.6% (n=144) and 34.9±15.6% (n=170), respectively (within 3 mm of stent ends). The target was achieved in 72.3% of the proximal and 84.1% of the distal margin for the criteria. A strikingly low angiographic margin re-stenosis rate (2.7% of proximal and 1.4% of distal margin) and low target lesion revascularization rate (2.2%) were achieved. Receiver operator characteristic curve indicated that plaque burden was the strongest predictor of margin re-stenosis and its threshold (51.6%) was almost identical to that of the criteria. Conclusions: The proposed stepwise IVUS criteria mainly targeting plaque burden <50% are feasible and useful in the real-world practice of SES implantation.
- 著者
- Shiro Uemura Hiroshi Okamoto Michikazu Nakai Kunihiro Nishimura Yoshihiro Miyamoto Satoshi Yasuda Nobuhiro Tanaka Shun Kohsaka Kazushige Kadota Yoshihiko Saito Hiroyuki Tsutsui Issei Komuro Yuji Ikari Hisao Ogawa Masato Nakamura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-19-0004, (Released:2019-04-24)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 17
Background:Primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI) is strongly recommended by guidelines for patients presenting with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), but its applications in elderly patients are less clear.Methods and Results:The JROAD-DPC is a Japanese nationwide registry for patients with cardiovascular diseases combined with an administrative claim-based database. Among 2,369,165 records from 2012 to 2015, data for 115,407 AMI patients were extracted for this study. Elderly patients (≥75 years) comprised 45,645 subjects (39.6%), and received pPCI less frequently (62.2%) than younger patients (79.2%, P<0.001). Clinical variables such as higher age, female sex, higher Killip class, and renal dysfunction, but not functional status on admission, were predictors of non-application of pPCI. Endpoint 30-day mortality increased with aging, and was significantly higher in elderly patients (10.7%) than in younger patients (3.8%, P<0.001). Indeed, pPCI was independently associated with lower 30-day mortality only in subgroups of patients aged ≥60 years. Propensity score-matching analysis confirmed a similar reduction in endpoint 30-day mortality with pPCI in elderly patients. Duration of hospitalization was significantly shorter and functional ability on discharge was significantly better in elderly patients who underwent pPCI.Conclusions:Elderly patients with AMI underwent pPCI less frequently, but it was consistently associated with better clinical outcome in these patients. Our findings support the proactive application of pPCI for elderly AMI patients when they are eligible for an invasive strategy.
- 著者
- Atsushi Shioi Yuji Ikari
- 出版者
- Japan Atherosclerosis Society
- 雑誌
- Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis (ISSN:13403478)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.RV17020, (Released:2017-12-12)
- 参考文献数
- 69
- 被引用文献数
- 170
Plaque calcification develops by the inflammation-dependent mechanisms involved in progression and regression of atherosclerosis. Macrophages can undergo two distinct polarization states, that is, pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype in progression and anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype in regression. In plaque progression, predominant M1 macrophages promote the initial calcium deposition within the necrotic core of the lesions, called as microcalcification, through not only vesicle-mediated mineralization as the result of apoptosis of macrophages and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), but also VSMC differentiation into early phase osteoblasts. On the other hand, in plaque regression M2 macrophages are engaged in the healing response to plaque inflammation. In association with the resolution of chronic inflammation, M2 macrophages may facilitate macroscopic calcium deposition, called as macrocalcification, through induction of osteoblastic differentiation and maturation of VSMCs. Oncostatin M, which has been shown to promote osteoblast differentiation in bone, may play a pivotal role in the development of plaque calcification. Clinically, two types of plaque calcification have distinct implications. Macrocalcification leads to plaque stability, while microcalcification is more likely to be associated with plaque rupture. Statin therapy, which reduces cardiovascular mortality, has been shown to exert its dual actions on plaque morphology, that is, regression of atheroma and increment of macroscopic calcium deposits. Statins may facilitate the healing process against plaque inflammation by enhancing M2 polarization of macrophages. Vascular calcification has pleiotropic properties as pro-inflammatory “microcalcification” and anti-inflammatory “macrocalcification”. The molecular mechanisms of this process in relation with plaque progression as well as plaque regression should be intensively elucidated.