- 著者
- Itsuki Iwamoto Ade Kurniawan Hiroki Hasegawa Yoshiaki Kashiwaya Takahiro Nomura Tomohiro Akiyama
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.12, pp.2483-2490, 2022-12-15 (Released:2022-12-15)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 2
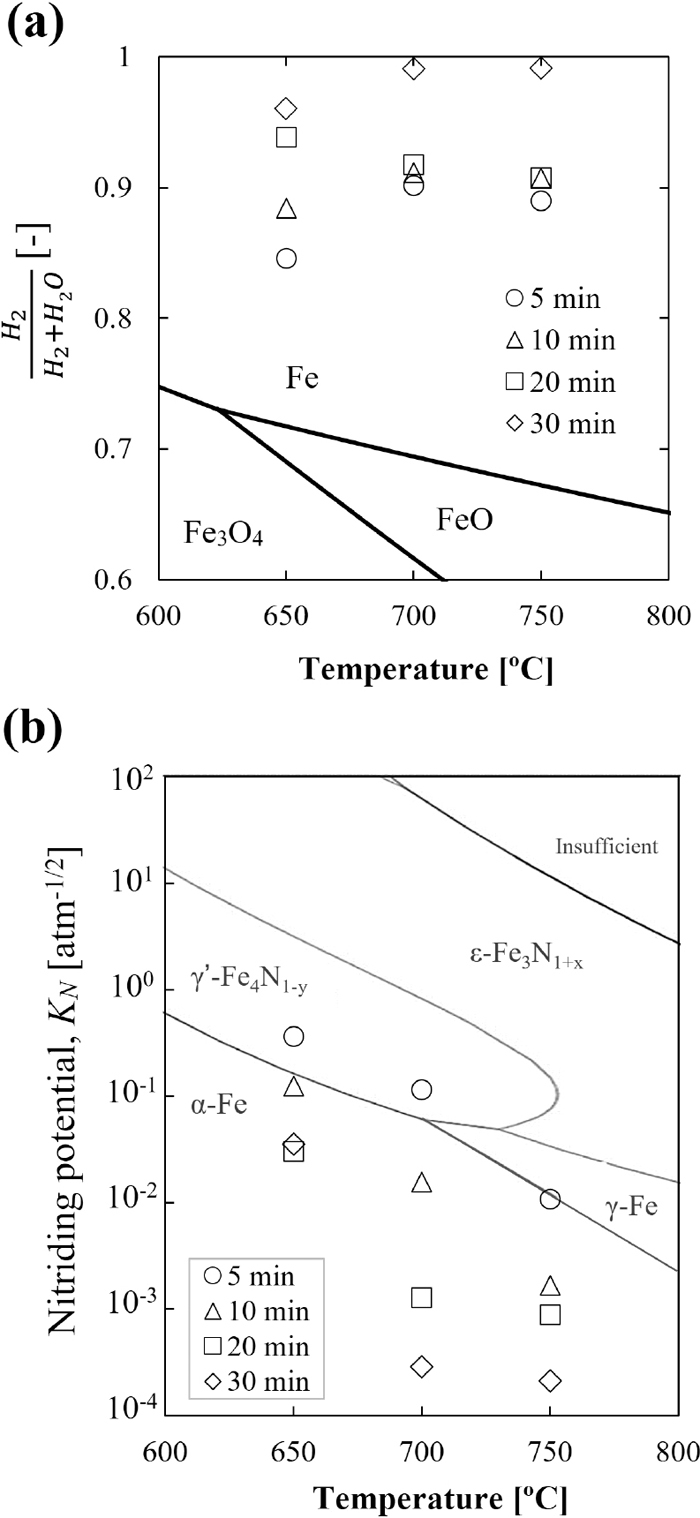
As one of the hydrogen carriers, ammonia has become one promising candidate as a reducing agent for implementing hydrogen-based ironmaking to reduce CO2 emissions. On the other hand, the abundant high combined water (CW) iron ore has recently been investigated as a raw material for ironmaking. Goethite (FeOOH), the main component of high-CW iron ore, can change to porous hematite (Fe2O3) by dehydration, enhancing its reactivity. This paper describes the fundamental study of the ore reduction behavior using ammonia as reducing agent. The effects of different ore types (i.e., high- and low-CW ores), reduction temperatures (i.e., 650, 700, and 750°C), and conditions of post-reduction treatments (i.e., quenching by NH3, fast- and slow- quenching by inert gas) on ore reduction behavior. The results reveal that the dehydrated high-CW one exhibits a higher ammonia utilization rate and is reduced faster due to the high specific surface area of the pores generated from the ore dehydration. The reduction degree of the sample increased at a higher temperature. However, in contrast, the nitriding degree decreases since the decomposition of nitrides occur highly at elevated temperatures. During quenching at temperatures lower than 700°C, the metallic Fe in the sample was nitrided in the presence of NH3. In contrast, the nitrides were easily decomposed into metallic Fe in the absence of NH3 at 700°C. This finding suggests that the quenching conditions significantly affect the generated phases. Thus, the generated phases of the reduced ore could be easily controlled in the post-reduction process.
- 著者
- Alya Naili Rozhan Mohd Hanafi Ani Hamzah Mohd Salleh Tomohiro Akiyama Hadi Purwanto
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.2, pp.436-440, 2015-02-15 (Released:2015-02-20)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 1 6
This paper presents a technology to utilize bio-char and bio-tar from the pyrolysis of oil palm empty fruit bunch, EFB. In this study, tar vapor from pyrolysis of EFB was infiltrated within porous bio-char and carbon deposition occurred on the pore surface by chemical vapor infiltration process. For preparation, EFB particles were made into pellets. In the first part of experiments, porous bio-char pellets were produced by slowly heating the EFB pellets in a tube furnace in argon atmosphere to terminal temperatures of 500–800°C. In the second part, the porous bio-char pellets were used as precursor for tar decomposition process to deposit carbon within the bio-char pores. Tar vapor was obtained from the pyrolysis of EFB at 400–500°C at a fast heating rate for tar decomposition to occur. The purpose of this research is to investigate the amount of carbon deposited within bio-char by this tar carbonization process as compared to carbon contents of metallurgical coke. We showed how EFB bio-char was used as the tar filter and in the process to produce carbon-infiltrated bio-char, a useful renewable energy source for ironmaking process.
- 著者
- Takeshi Ebara Ryohei Azuma Naoto Shoji Tsuyoshi Matsukawa Yasuyuki Yamada Tomohiro Akiyama Takahiro Kurihara Shota Yamada
- 出版者
- (公社)日本産業衛生学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Occupational Health (ISSN:13419145)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.17-0101-OA, (Released:2017-08-24)
- 被引用文献数
- 12
Objectives: Objective measurements using built-in smartphone sensors that can measure physical activity/inactivity in daily working life have the potential to provide a new approach to assessing workers' health effects. The aim of this study was to elucidate the characteristics and reliability of built-in step counting sensors on smartphones for development of an easy-to-use objective measurement tool that can be applied in ergonomics or epidemiological research.Methods: To evaluate the reliability of step counting sensors embedded in seven major smartphone models, the 6-minute walk test was conducted and the following analyses of sensor precision and accuracy were performed: 1) relationship between actual step count and step count detected by sensors, 2) reliability between smartphones of the same model, and 3) false detection rates when sitting during office work, while riding the subway, and driving.Results: On five of the seven models, the inter-class correlations coefficient (ICC (3,1)) showed high reliability with a range of 0.956–0.993. The other two models, however, had ranges of 0.443–0.504 and the relative error ratios of the sensor-detected step count to the actual step count were ±48.7%–49.4%. The level of agreement between the same models was ICC (3,1): 0.992–0.998. The false detection rates differed between the sitting conditions.Conclusions: These results suggest the need for appropriate regulation of step counts measured by sensors, through means such as correction or calibration with a predictive model formula, in order to obtain the highly reliable measurement results that are sought in scientific investigation.