- 著者
- Yuta Fujii Yutaka Kodama
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.1, pp.81-87, 2015-03-25 (Released:2015-04-04)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 3 22
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) was discovered from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria, and several improvements have been carried out to change its physicochemical properties. The resulting improved GFP variants have been used as reporter proteins for bioimaging techniques in various research fields including plant science. Almost all GFP variants were developed using Escherichia coli to improve fluorescence properties in mammalian cells, but the impact in other organisms such as plant cells remains to be determined. In this study, we performed comparative analysis of four improved GFP variants, GFP-S65T, eGFP, frGFP and sfGFP, with reference to the fluorescence intensity in Arabidopsis protoplasts, and found that sfGFP is the brightest. Using non-fluorescent fragments from the GFP variants, we also conducted bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays to find appropriate fragment pairs of GFP-based BiFC for visualization of protein–protein interactions in living plant cells. Our observations revealed that the brightest is the sfGFP-based BiFC. Further, as an evaluation method for the sfGFP-based BiFC, a BiFC competition assay was successfully completed for the first time in planta. The present study provides useful information for selection and improvement of the GFP molecule and its application to BiFC technology in plants.
- 著者
- Tatsushi Fukushima Yutaka Kodama
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.4, pp.345-354, 2022-12-25 (Released:2022-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 36
- 被引用文献数
- 1
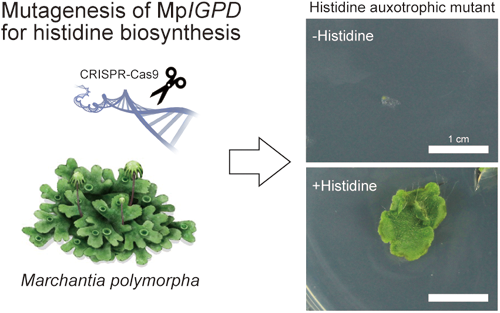
Marchantia polymorpha has emerged as a model liverwort species, with molecular tools increasingly available. In the present study, we developed an auxotrophic strain of M. polymorpha and an auxotrophic selective marker gene as new experimental tools for this valuable model system. Using CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats)/Cas9-mediated genome editing, we mutated the genomic region for IMIDAZOLEGLYCEROL-PHOSPHATE DEHYDRATASE (IGPD) in M. polymorpha to disrupt the biosynthesis of histidine (igpd). We modified an IGPD gene (IGPDm) with silent mutations, generating a histidine auxotrophic selective marker gene that was not a target of our CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing. The M. polymorpha igpd mutant was a histidine auxotrophic strain, growing only on medium containing histidine. The igpd mutant could be complemented by transformation with the IGPDm gene, indicating that this gene could be used as an auxotrophic selective marker. Using the IGPDm marker in the igpd mutant background, we produced transgenic lines without the need for antibiotic selection. The histidine auxotrophic strain igpd and auxotrophic selective marker IGPDm represent new molecular tools for M. polymorpha research.
- 著者
- Hitomi Takahashi Yutaka Kodama
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.4, pp.449-452, 2021-12-25 (Released:2021-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 7
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Ongoing research has generated many important lines of the model liverwort Marchantia polymorpha, including mutants and transgenic lines. To maintain these lines, researchers typically spend a lot of time and effort periodically replanting thalli (e.g., every month). To avoid this routine maintenance, researchers have developed methods for cryopreservation of dried and frozen gemmae. In this study, we developed a culture-based method for preserving gemmalings and thalli without encapsulation, drying, or freezing. The method requires only tissue culture on agar medium supplemented with sucrose in the dark at regular temperature (22°C). These culture conditions severely inhibit growth of gemmalings and thalli; however, these tissues remained alive after more than 1 year of storage. Survival rate of tissues using this method was 100% in all tests. This method thus enables preservation of gemmaling and thallus cultures on medium under regular temperature conditions, thereby relieving researchers of labor-intensive routine maintenance.
- 著者
- Hitomi Takahashi Yutaka Kodama
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.21.0902a, (Released:2021-12-14)
- 参考文献数
- 7
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Ongoing research has generated many important lines of the model liverwort Marchantia polymorpha, including mutants and transgenic lines. To maintain these lines, researchers typically spend a lot of time and effort periodically replanting thalli (e.g., every month). To avoid this routine maintenance, researchers have developed methods for cryopreservation of dried and frozen gemmae. In this study, we developed a culture-based method for preserving gemmalings and thalli without encapsulation, drying, or freezing. The method requires only tissue culture on agar medium supplemented with sucrose in the dark at regular temperature (22°C). These culture conditions severely inhibit growth of gemmalings and thalli; however, these tissues remained alive after more than 1 year of storage. Survival rate of tissues using this method was 100% in all tests. This method thus enables preservation of gemmaling and thallus cultures on medium under regular temperature conditions, thereby relieving researchers of labor-intensive routine maintenance.
- 著者
- Kazusato Oikawa Takuto Imai Yutaka Kodama Keiji Numata
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.2, pp.257-262, 2021-06-25 (Released:2021-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Mitochondria-selective fluorescent probes such as MitoTracker are often used for mitochondria imaging in various plants. Although some of the probes are reported to induce mitochondria dysfunction in animal cells, the effect on plant cells remains to be determined. In the present study, we applied quantitative methods to analyze mitochondrial movement, speed frequency, and speed-angle changes, based on trajectory analysis of mitochondria in mesophyll protoplast cells of Arabidopsis thaliana expressing the mitochondria-localized fluorescent protein. Using the quantitative method, we assessed whether MitoTracker Red (FM and CMXRos) induce mitochondria dysfunction in A. thaliana. Although both the fluorescent probes well-stained mitochondria, the CMXRos probe, not the FM probe, gave a severe effect on mitochondrial movement at the low concentration (10 nM), indicating a MitoTracker-induced mitochondria dysfunction in A. thaliana. These results revealed that our quantitative method based on mitochondrial movement can be used to determine the appropriate concentrations of mitochondria-selective fluorescent probes in plants.